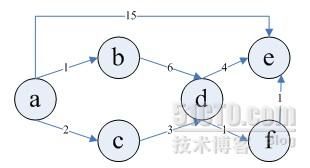
Dijkstra迪杰斯特拉 算法详细步骤及实现
(2)算法详细步骤如下表:
|
步骤
|
S集合中
|
U集合中
|
|
初始化
|
选入a,此时s={a}
此时最短路径有a->a=0
以a为中间点,从a开始找
|
U={b,c,d,e,f}
a->b=1
a->c=2
a->e=15
a->其他U中顶点为无穷
|
|
1
|
从U={b,c,d,e,f}中发现路径a->b=1最短
选入b,S={a,b}
此时最短路径有a->a=0,a->b=1
以b为中间点,从a->b=1这条最短路径开始找
|
U={c,d,e,f}
(a->b->d=7)<初始的无穷
改写a->b->d=无穷为当前的a->b->d=7
a-> b->其他U中顶点为无穷
|
|
2
|
从U={c,d,e,f}中发现路径a->c=2最短
选入c,S={a,b,c}
此时最短路径有
a->a=0,a->b=1,a->c=2
以b为中间点,从a->c=2这条最短路径开始找
|
U={d,e,f}
(a->c->d=5)<已有的7
改写为a->c->d=5
|
|
3
|
从U={d,e,f}中发现路径a->c->d=5最短
选入d,S={a,b,c,d}
此时最短路径有
a->a=0,a->b=1,a->c=2,a->c->d=5
以d为中间点,从a->c->d=5这条最短路径开始找
|
U={e,f}
(a->c->d->e=9)<步骤1中的15
改写为a->c->d->e=9
(a->c->d->f=6)<初始的无穷
改写为a->c->d->f=6
|
|
4
|
从U={e,f}中发现路径a->c->d->f=6最短
选入f,S={a,b,c,d,f}
此时最短路径有
a->a=0,a->b=1,a->c=2,a->c->d=5
a->c->d->f=6
以f为中间点,从a->c->d->f=6这条最短路径开始找
|
U={e}
(a->c->d->f->e=7)<步骤3中改写成的9
改写为a->c->d->f->e=7
|
|
5
|
从U={f}中发现路径a->c->d->f->e=7最短
选入f,S={a,b,c,d,f,e}
此时最短路径有
a->a=0,a->b=1,a->c=2,a->c->d=5
a->c->d->f=6,a->c->d->f->e=7
|
U集合已空,查找完毕。
|
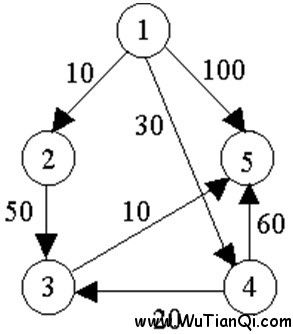
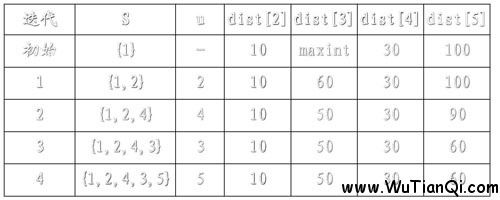
例如,对下图中的有向图,应用Dijkstra算法计算从源顶点1到其它顶点间最短路径的过程列在下表中。
主题好好理解上图!
以下是具体的实现(C/C++):
#include < iostream >
using namespace std;
const int maxnum = 100 ;
const int maxint = 999999 ;
void Dijkstra( int n, int v, int * dist, int * prev, int c[maxnum][maxnum])
{
bool s[maxnum]; // 判断是否已存入该点到S集合中
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++ i)
{
dist[i] = c[v][i]; //初始化其他点到源点的最短距离
s[i] = 0 ; // 初始都未用过该点
if (dist[i] == maxint) //初始化其他点距离源点最短路径的 前一个点
prev[i] = 0 ; //其他点到源点 不存在路径时,
else
prev[i] = v;
}
dist[v] = 0 ;
s[v] = 1 ;
// 依次将未放入S集合的结点中,取dist[]最小值的结点,放入结合S中
// 一旦S包含了所有V中顶点,dist就记录了从源点到所有其他顶点之间的最短路径长度
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= n; ++ i)
{
int tmp = maxint;
int u = v;
// 找出当前未使用的点j的dist[j]最小值
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n; ++ j)
if (( ! s[j]) && dist[j] < tmp)
{
u = j; // u保存当前邻接点中距离最小的点的号码
tmp = dist[j];
}
s[u] = 1 ; // 表示u点已存入S集合中
// 更新其他点距离源点 最短距离点的 dist
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n; ++ j)
if (( ! s[j]) && c[u][j] < maxint)
{
int newdist = dist[u] + c[u][j];
if (newdist < dist[j])
{
dist[j] = newdist;
prev[j] = u;
}
}
}
}
void searchPath( int * prev, int v, int u)
{
int que[maxnum];
int tot = 1 ;
que[tot] = u;
tot ++ ;
int tmp = prev[u];
while (tmp != v)
{
que[tot] = tmp;
tot ++ ;
tmp = prev[tmp];
}
que[tot] = v;
for ( int i = tot; i >= 1 ; -- i)
if (i != 1 )
cout << que[i] << " -> " ;
else
cout << que[i] << endl;
}
int main()
{
freopen( " input.txt " , " r " , stdin);
// 各数组都从下标1开始
int dist[maxnum]; // 表示当前点到源点的最短路径长度
int prev[maxnum]; // 记录当前点的前一个结点
int c[maxnum][maxnum]; // 记录图的两点间路径长度
int n, line; // 图的结点数和路径数
// 输入结点数
cin >> n;
// 输入路径数
cin >> line;
int p, q, len; // 输入p, q两点及其路径长度
// 初始化c[][]为maxint
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++ i)
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n; ++ j)
c[i][j] = maxint;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= line; ++ i)
{
cin >> p >> q >> len;
if (len < c[p][q]) // 有重边
{
c[p][q] = len; // p指向q
c[q][p] = len; // q指向p,这样表示无向图
}
}
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++ i)
dist[i] = maxint;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++ i)
{
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n; ++ j)
printf( " %8d " , c[i][j]);
printf( " \n " );
}
Dijkstra(n, 1 , dist, prev, c);
// 最短路径长度
cout << " 源点到最后一个顶点的最短路径长度: " << dist[n] << endl;
// 路径
cout << " 源点到最后一个顶点的路径为: " ;
searchPath(prev, 1 , n);
}
输入数据:
5
7
1 2 10
1 4 30
1 5 100
2 3 50
3 5 10
4 3 20
4 5 60
输出数据:
999999 10 999999 30 100
10 999999 50 999999 999999
999999 50 999999 20 10
30 999999 20 999999 60
100 999999 10 60 999999
源点到最后一个顶点的最短路径长度: 60
源点到最后一个顶点的路径为: 1 -> 4 -> 3 -> 5
以下是java实现
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
public class DijkstraPath {
/**
* @param args
*/
static int[][] cost;
static ArrayList<String> visited = new ArrayList<String>();
static ArrayList<String> unVisited = new ArrayList<String>();
static ArrayList<String> vertexs = new ArrayList<String>();
static LinkedHashMap<String ,Integer> shortPath = new LinkedHashMap<String ,Integer>();
static ArrayList<arc> arcs = new ArrayList<arc>();
static LinkedHashMap<String ,String> shortPathWay = new LinkedHashMap<String ,String>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//init the verges set
arcs.add(new arc("A","B",2));
arcs.add(new arc("A","C",4));
arcs.add(new arc("A","D",15));
arcs.add(new arc("B","D",5));
arcs.add(new arc("B","C",1));
arcs.add(new arc("C","D",7));
arcs.add(new arc("D","E",4));
//init the nodes set
vertexs.add("A");
vertexs.add("B");
vertexs.add("C");
vertexs.add("D");
vertexs.add("E");
// init the novisited set
visited.add("A");
//init the visited set
unVisited.add("B");
unVisited.add("C");
unVisited.add("D");
unVisited.add("E");
//init the shortPath map
for(String unvisitNode:unVisited)
{
boolean access = false;
for(arc a:arcs)
{
if(a.startNode.equals("A") && a.endNode.equals(unvisitNode))
{
shortPath.put(unvisitNode,a.weight);
access = true;
break;
}
}
if(access == false)
{
shortPath.put(unvisitNode, -1);
}
}
//把第一个临近节点的前驱找到
initFirstShortPathWay();
while(unVisited.size()>0){
String lastVisitedNode = getLastVisitedNode();
for(String unvisitNode:unVisited)
{
//获得最后一访问节点到未访问节点到距离
int newPath = getWeight(lastVisitedNode,unvisitNode);
if(newPath > 0)
{
//获得源点到未访问节点的距离
int oldPath = getOldPath(unvisitNode);
//如果二者都存在话,改变shortPath 的相应值为最小值
if(oldPath > 0)
{
if(oldPath > getOldPath(lastVisitedNode)+newPath){
resetShortPath(unvisitNode,getOldPath(lastVisitedNode)+newPath);
shortPathWay.put(unvisitNode,lastVisitedNode);//后继——前驱
}
}
//如果原来不可达的话,但是通过中间节点可以到达,那么同样要改变shortPath
else
{
resetShortPath(unvisitNode,getOldPath(lastVisitedNode)+newPath);
shortPathWay.put(unvisitNode,lastVisitedNode);
}
}
}
String minNode = getTheMinPathNode();
removeNode(minNode,unVisited);
addNode(minNode,visited);
}
//输出最终结果
printResult();
}
//初始化第一个 路径的前驱
public static void initFirstShortPathWay()
{
int min = 500;
String firstNode ="";
for(String vertex:shortPath.keySet())
{
int tem = shortPath.get(vertex);
if(tem > 0){
min = min > tem?tem:min;
}
}
for(String vertex:shortPath.keySet())
{
if(min == shortPath.get(vertex))firstNode = vertex;
}
shortPathWay.put(firstNode,"A");
}
//add a node to the set
public static void addNode(String node,ArrayList<String> set)
{
set.add(node);
}
// remove a node of the set
public static void removeNode(String delNode,ArrayList<String> set){
int index = 0;
for(int i=0;i<set.size();i++)
{
if(delNode.equals(set.get(i)))
{
index = i;
}
}
set.remove(index);
}
//得到未访问结点中shutPath的最小值的点
public static String getTheMinPathNode()
{
int min = 500; //距离超过500为不可达
String node = "";
for(String unode:unVisited)
{
int tem = shortPath.get(unode);
if(tem>0){
min = min>tem?tem:min;
}
}
for(String unode:unVisited)
{
if(min == shortPath.get(unode))node=unode;
}
return node;
}
//得到源点到未访问结点的最短距离
public static int getOldPath(String node)
{
if(node.equals("A"))return 0;
return shortPath.get(node);
}
//重新设定 shortPath
public static void resetShortPath(String node,int path)
{
for(String snode:shortPath.keySet())
{
if(snode.equals(node))shortPath.put(snode, path);
}
}
//get the last node of the visited set
public static String getLastVisitedNode()
{
return visited.get(visited.size()-1);
}
// get the weight
public static int getWeight(String startNode, String endNode)
{
int weight=-1;
for(arc a:arcs)
{
if(a.startNode.equals(startNode) && a.endNode.equals(endNode))
{
weight = a.weight;
System.out.println(a.startNode+"-->"+a.endNode+"="+weight);
}
}
return weight;
}
// get the min num
public static void printResult()
{
for(String vertex:shortPath.keySet())
{
System.out.print("从源点A到"+vertex+"的最短路径为");
printPath(vertex);
System.out.print(vertex);
System.out.print("长度为:"+shortPath.get(vertex));
System.out.println(" ");
}
}
public static void printPath(String vertex)
{
String node = shortPathWay.get(vertex);
if(!node.equals("A"))printPath(node);
System.out.print(node+" ");
}
}
class arc{
String startNode = "";
String endNode = "";
int weight =0;
public arc(String startNode,String endNode,int weight){
this.startNode = startNode;
this.endNode = endNode;
this.weight = weight;
}
}