Asp.net中的认证与授权(web.config + Global.ascx)
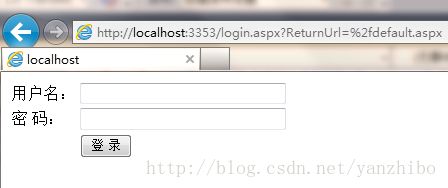
login.aspx : 登录页面
logout.aspx: 用来处理用户注销 (非必需,但建议把注销逻辑放在这里,以便任何需要注销的地方重复利用)
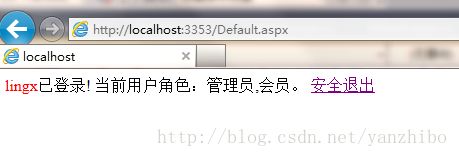
default.aspx: 登录完成后的显示页面
gotoUrl.aspx : 登录完成后,用来辅助做页面跳转的页面(非必需,但建议加上)
web.config:配置用户认证的方式(Forms),和浏览目录权限
Global.ascx:每个aspx页面在请求认证时,都会触发Application_AuthenticateRequest事件
login.aspx代码:
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeBehind="login.aspx.cs" Inherits="WebApplication2.login" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head id="Head1" runat="server">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<table>
<tr>
<td>
用户名:
</td>
<td>
<asp:TextBox ID="txtUserName" runat="server" Style="width: 200px"></asp:TextBox>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
密 码:
</td>
<td>
<asp:TextBox ID="txtPassword" runat="server" TextMode="Password" Style="width: 200px"></asp:TextBox>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
</td>
<td>
<asp:Button ID="Button1" runat="server" Text="登 录" OnClick="Button1_Click" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
后台代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using System.Web.Security;
namespace WebApplication2
{
public partial class login : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string user = this.txtUserName.Text; //读取用户名
string password = this.txtPassword.Text; //读取密码
if (ValidateUser(user, password) == true) //ValidateUser方法用来验证用户合法性的
{
//建立表单验证票据
FormsAuthenticationTicket Ticket = new FormsAuthenticationTicket(1, user, DateTime.Now, DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(30), true, "管理员,会员", "/");
//使用webcongfi中定义的方式,加密序列化票据为字符串
string HashTicket = FormsAuthentication.Encrypt(Ticket);
//将加密后的票据转化成cookie
HttpCookie UserCookie = new HttpCookie(FormsAuthentication.FormsCookieName, HashTicket);
//添加到客户端cookie
Context.Response.Cookies.Add(UserCookie);
//登录成功后重定向
Response.Redirect("GotoUrl.aspx?returnUrl=" + Server.UrlEncode("Default.aspx"));
}
else
{
//登录失败后的处理
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 验证用户名/密码是否正确
/// </summary>
/// <param name="userName"></param>
/// <param name="pwd"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private bool ValidateUser(string userName, string pwd)
{
return true; //当然实际开发中,您可以到数据库里查询校验,这里只是示例而已
}
}
GotoUrl.aspx:这个页面只是单纯的辅助跳转而已,所以aspx页面本身不用加什么代码,只需要在后置cs代码里简单处理一下
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
namespace WebApplication2
{
public partial class gotoUrl : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string _returnUrl = Request["returnUrl"];
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(_returnUrl))
{
_returnUrl = "~/default.aspx";
}
Response.Redirect(_returnUrl);
}
}
}
接下来应该是Default.aspx了,这里只是演示,所以没有后置代码,判断的逻辑全写在default.aspx本身:
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeBehind="default.aspx.cs" Inherits="WebApplication2._default" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
<% if (User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
{
Response.Write("<span style='color:red'>" + User.Identity.Name + "</span>已登录!");
if (User.IsInRole("管理员"))
{
Response.Write(" 当前用户角色:管理员");
}
if (User.IsInRole("会员"))
{
Response.Write(",会员。");
}
Response.Write(" <a href='logout.aspx'>安全退出</a>");
}
else
{
//Response.Write("请先<a href='login.aspx'>登录</a>");
}
%>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
注销页面logout.aspx,类似的,这个页面本身只负责注销cookie票据,所以界面上没东西,只有后置代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using System.Web.Security;
namespace WebApplication2
{
public partial class logout : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//注销cookie票据(从浏览器删除Forms身份验证)
FormsAuthentication.SignOut();
Response.Redirect("default.aspx");
}
}
}
web.config文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!--
有关如何配置 ASP.NET 应用程序的详细消息,请访问
http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=169433
-->
<configuration>
<!--,“?”的意思指匿名用户,而“*”则表示所有用户。
下面这个意思就是说根目录下的所有页面拒绝被匿名用户访问。
当然你也可以在users中填写指定的用户ID,不过那样并不常用。
还有deny,allow的顺序是先写allow完了再deny,不然就会出现问题。
这个大家要记住。-->
<location path="">
<system.web>
<authorization>
<allow users="*"/>
</authorization>
</system.web>
</location>
<location path="default.aspx">
<system.web>
<authorization>
<deny users="?"/>
</authorization>
</system.web>
</location>
<system.web>
<compilation debug="true" targetFramework="4.0" />
<authentication mode="Forms">
<forms
name=".ASPXAUTH"
loginUrl="login.aspx"
timeout="30"
path="/"
requireSSL="false"
domain="">
</forms>
</authentication>
</system.web>
</configuration>
其中<authentication mode= "forms"> 表示本应用程序采用Forms验证方式。
1. <forms>标签中的name表示指定要用于身份验证的 HTTP Cookie。默认情况下,name 的值是 .ASPXAUTH。采用此种方式验证用户后,以此用户的信息建立一个FormsAuthenticationTicket类型的身份验证票,再加密序列化为一个字符串,最后将这个字符串写到客户端的name指定名字的Cookie中.一旦这个Cookie写到客户端后,此用户再次访问这个web应用时会将连同Cookie一起发送到服务端,服务端将会知道此用户是已经验证过的.
再看一下身份验证票都包含哪些信息呢,我们看一下FormsAuthenticationTicket类:
CookiePath: 返回发出 Cookie 的路径。注意,窗体的路径设置为 /。由于窗体区分大小写,这是为了防止站点中的 URL 的大小写不一致而采取的一种保护措施。这在刷新 Cookie 时使用
Expiration: 获取 Cookie 过期的日期/时间。
IsPersistent: 如果已发出持久的 Cookie,则返回 true。否则,身份验证 Cookie 将限制在浏览器生命周期范围内。
IssueDate: 获取最初发出 Cookie 的日期/时间。
Name: 获取与身份验证 Cookie 关联的用户名。
UserData :获取存储在 Cookie 中的应用程序定义字符串。
Version: 返回字节版本号供将来使用。
2. <forms>标签中的loginUrl指定如果没有找到任何有效的身份验证 Cookie,为登录将请求重定向到的 URL。默认值为 default.aspx。loginUrl指定的页面就是用来验证用户身份的,一般此页面提供用户输入用户名和密码,用户提交后由程序来根据自己的需要来验证用户的合法性(大多情况是将用户输入信息同数据库中的用户表进行比较),如果验证用户有效,则生成同此用户对应的身份验证票,写到客户端的Cookie,最后将浏览器重定向到用户初试请求的页面.一般是用FormsAuthentication.RedirectFromLoginPage 方法来完成生成身份验证票,写回客户端,浏览器重定向等一系列的动作.
public static void RedirectFromLoginPage( string userName, bool createPersistentCookie, string strCookiePath );
userName: 就是此用户的标示,用来标志此用户的唯一标示,不一定要映射到用户账户名称.
createPersistentCookie: 标示是否发出持久的 Cookie。 若不是持久Cookie,Cookie的有效期Expiration属性有当前时间加上web.config中timeout的时间,每次请求页面时,在验证身份过程中,会判断是否过了有效期的一半,要是的话更新一次cookie的有效期;若是持久cookie,Expiration属性无意义,这时身份验证票的有效期有cookie的Expires决定,RedirectFromLoginPage方法给Expires属性设定的是50年有效期。
strCookiePath: 标示将生成的Cookie的写到客户端的路径,身份验证票中保存这个路径是在刷新身份验证票Cookie时使用(这也是生成Cookie的Path),若没有strCookiePath 参数,则使用web.config中 path属性的设置。这里可以看到,此方法参数只有三个,而身份验证票的属性有七个,不足的四个参数是这么来的:
IssueDate: Cookie发出时间由当前时间得出,
Expiration:过期时间由当前时间和下面要说的<forms>标签中timeout参数算出。此参数对非持久性cookie有意义。
UserData: 这个属性可以用应用程序写入一些用户定义的数据,此方法没有用到这个属性,只是简单的将此属性置为空字符串,请注意此属性,在后面我们将要使用到这个属性。
Version: 版本号由系统自动提供.
RedirectFromLoginPage方法生成生成身份验证票后,会调用FormsAuthentication.Encrypt 方法,将身份验证票加密为字符串,这个字符串将会是以.ASPXAUTH为名字的一个Cookie的值。这个Cookie的其它属性的生成:Domain,Path属性为确省值,Expires视createPersistentCookie参数而定,若是持久cookie,Expires设为50年以后过期;若是非持久cookie,Expires属性不设置。 生成身份验证Cookie后,将此Cookie加入到Response.Cookies中,等待发送到客户端。 最后RedirectFromLoginPage方法调用FormsAuthentication.GetRedirectUrl 方法获取到用户原先请求的页面,重定向到这个页面。
3. <forms>标签中的timeout和path,是提供了身份验证票写入到Cookie过期时间和默认路径。
以上就是基于Forms身份验证的过程,它完成了对用户身份的确认。下面介绍基于Forms身份验证的访问授权。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Security;
using System.Web.SessionState;
using System.Security.Principal;
namespace WebApplication2
{
public class Global : System.Web.HttpApplication
{
protected void Application_Start(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
protected void Session_Start(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
protected void Application_BeginRequest(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
/// <summary>
/// 每个aspx页面要求认证时被触发
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
protected void Application_AuthenticateRequest(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpContext _ctx = HttpContext.Current;
if (_ctx.User != null)
{
if (_ctx.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated == true) //认证成功的用户,才进行授权处理
{
FormsIdentity _Identity = (FormsIdentity)_ctx.User.Identity;
string[] Roles = _Identity.Ticket.UserData.Split(','); //将角色字符串,即login.aspx.cs中的“管理员,会员”,变成数组
_ctx.User = new GenericPrincipal(_Identity, Roles); //将带有角色的信息,重新生成一个GenericPrincipal赋值给User
}
}
}
protected void Application_Error(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
protected void Session_End(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
protected void Application_End(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
}
}
运行浏览default.aspx页面,因为在web.config中把设置default.aspx不可以匿名访问,就会自动跳转到login.aspx也是在web.config设置
登陆成功后,就可以登陆default.aspx页面
原文:http://www.itniwo.net/blog/v/225004.html