EventBus3.0源码解读
综述
EventBus是我们在项目当中最常用的开源框架之一。对于EventBus的使用方法也是非常的简单。然而EventBus内部的实现原理也不是很复杂。在这里便针对EventBus3.0的源码进行一下详细的分析。对于EventBus的详细使用可以参考EventBus3.0使用详解这篇文章。
EventBus3.0源码解析
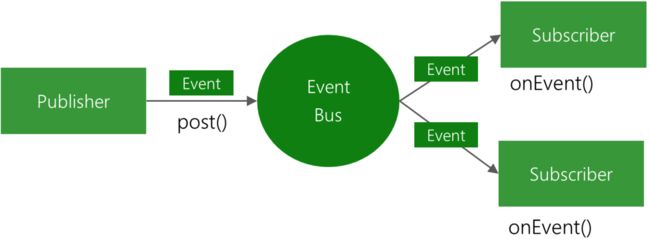
从下面这个图中可以看到,对于EventBus的工作过程很简单,用一句话概括为:事件被提交到EventBus后进行查找所有订阅该事件的方法并执行这些订阅方法。
获取EventBus对象
无论是订阅者的注册,还是事件的发布首先必须要获得EventBus对象。那么下面就来看一下如何获取EventBus对象。可以通过EventBus.getDefault()获得EventBus对象。然后就来看一下这个getDefault方法。
public static EventBus getDefault() {
if (defaultInstance == null) {
synchronized (EventBus.class) {
if (defaultInstance == null) {
defaultInstance = new EventBus();
}
}
}
return defaultInstance;
}在这通过单例模式获取EventBus对象。下面就来看一下EventBus的构造方法。
public EventBus() {
this(DEFAULT_BUILDER);
}EventBus(EventBusBuilder builder) {
//以事件类型作为Key,Subscription的List集合作为Value的Map集合
subscriptionsByEventType = new HashMap<>();
//订阅者作为Key,订阅事件作为Value的Map集合
typesBySubscriber = new HashMap<>();
stickyEvents = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//Handler对象,用于切换到主线程中执行订阅方法
mainThreadPoster = new HandlerPoster(this, Looper.getMainLooper(), 10);
//Runable对象
backgroundPoster = new BackgroundPoster(this);
//Runable对象
asyncPoster = new AsyncPoster(this);
indexCount = builder.subscriberInfoIndexes != null ? builder.subscriberInfoIndexes.size() : 0;
subscriberMethodFinder = new SubscriberMethodFinder(builder.subscriberInfoIndexes,
builder.strictMethodVerification, builder.ignoreGeneratedIndex);
logSubscriberExceptions = builder.logSubscriberExceptions;
logNoSubscriberMessages = builder.logNoSubscriberMessages;
sendSubscriberExceptionEvent = builder.sendSubscriberExceptionEvent;
sendNoSubscriberEvent = builder.sendNoSubscriberEvent;
throwSubscriberException = builder.throwSubscriberException;
eventInheritance = builder.eventInheritance;
executorService = builder.executorService;
}我们可以通过构造一个EventBusBuilder,来对EventBus进行配置。并且在这里注意到对于EventBus可以采用单实例模式获取,但是EventBus的构造方法为公共的。很显然也就是说明了在应用中可以存在多个EventBus,对于存在多个的EventBus情况下,它们之间相互独立,会发布和订阅各自的事件进行接收执行。
订阅者的注册
在获取到EventBus对象以后,便可以将订阅者注册到EventBus中。下面就再来看一下register方法。
public void register(Object subscriber) {
Class<?> subscriberClass = subscriber.getClass();
List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = subscriberMethodFinder.findSubscriberMethods(subscriberClass);
synchronized (this) {
for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : subscriberMethods) {
subscribe(subscriber, subscriberMethod);
}
}
}在这里可以看到register这个方法中的代码很简短,但是在它的内容却一点也不简单。对于register中的参数,就是我们的订阅者,也就是我们经常传入的this对象。在这个方法中主要完成了两件事情。首先通过findSubscriberMethods方法来查找订阅者中所有的订阅方法。然后遍历订阅者的订阅方法来完成订阅者的订阅操作。下面来详细的分析这两步的实现过程。
订阅方法的查找过程
首先在这里来看一下findSubscriberMethods这个方法是如何查找订阅者的订阅方法。在这先描述一下SubscriberMethod类。对于SubscriberMethod类中,主要就是用保存订阅方法的Method对象,线程模式,事件类型,优先级,是否粘性事件等属性。下面就来看一下findSubscriberMethods方法。
List<SubscriberMethod> findSubscriberMethods(Class<?> subscriberClass) {
//从缓存中获取SubscriberMethod集合
List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = METHOD_CACHE.get(subscriberClass);
if (subscriberMethods != null) {
return subscriberMethods;
}
//ignoreGeneratedIndex是否忽略注解器生成的MyEventBusIndex
if (ignoreGeneratedIndex) {
//通过反射获取subscriberMethods
subscriberMethods = findUsingReflection(subscriberClass);
} else {
//通过注解器生成的MyEventBusIndex信息获取subscriberMethods,
//如果没有配置MyEventBusIndex,依然通过通过反射获取subscriberMethods
subscriberMethods = findUsingInfo(subscriberClass);
}
if (subscriberMethods.isEmpty()) {
throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriberClass
+ " and its super classes have no public methods with the @Subscribe annotation");
} else {
METHOD_CACHE.put(subscriberClass, subscriberMethods);
return subscriberMethods;
}
} 在这个方法里面的逻辑依然也是十分的清晰。首先会从缓存中查找是否有订阅方法的集合,若是存在则直接返回缓存中的该订阅者的订阅方发集合。若是不存在,便从订阅者中找出全部的订阅方法。对于ignoreGeneratedIndex属性表示是否忽略注解器生成的MyEventBusIndex(在项目重新rebuild以后,会自动生成在build文件夹下,类名也可以自己定义)。如何生成MyEventBusIndex类以及他的使用,可以参考官方文档。ignoreGeneratedIndex的默认值为false,可以通过EventBusBuilder来设置它的值。在这里会根具ignoreGeneratedIndex的值来采用不同的方式获取订阅方法的集合subscriberMethods。在获得subscriberMethods以后,如果订阅者中不存在@Subscribe注解且为public的订阅方法,则会抛出异常。这也就是说对于订阅者若是要成功注册到EventBus中,在订阅者中必须存在通过@Subscribe注解且为public类型的订阅方法。在成功获取到订阅方法集合以后,便将订阅方法集合添加到缓存中。对于这个缓存它是以订阅者的类作为key,订阅方法集合作为value的Map类型。
由于在我们的项目中经常通过EventBus单例模式来获取默认的EventBus对象。所以就针对ignoreGeneratedIndex为false的情况下看一下EventBus是如何获得订阅方法集合的。在这里调用了findUsingInfo方法。下面就来看一下findUsingInfo这个方法。
private List<SubscriberMethod> findUsingInfo(Class<?> subscriberClass) {
//创建和初始化FindState对象
FindState findState = prepareFindState();
findState.initForSubscriber(subscriberClass);
while (findState.clazz != null) {
//获取订阅者信息,没有配置MyEventBusIndex返回null
findState.subscriberInfo = getSubscriberInfo(findState);
if (findState.subscriberInfo != null) {
SubscriberMethod[] array = findState.subscriberInfo.getSubscriberMethods();
for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : array) {
if (findState.checkAdd(subscriberMethod.method, subscriberMethod.eventType)) {
findState.subscriberMethods.add(subscriberMethod);
}
}
} else {
//通过反射来查找订阅方法
findUsingReflectionInSingleClass(findState);
}
//进入父类查找订阅方法
findState.moveToSuperclass();
}
//回收处理findState,并返回订阅方法的List集合
return getMethodsAndRelease(findState);
} 在FindState里面,它保存了一些订阅者的方法以及对订阅方法的校验。通过initForSubscriber初始化了FindState的clazz属性。于是下面便进入while循环当中。通过getSubscriberInfo方法来获取订阅者信息。在我们开始查找订阅方法的时候并没有忽略注解器为我们生成的索引MyEventBusIndex,如果我们通过EventBusBuilder配置了MyEventBusIndex,便会获取到subscriberInfo。而在MyEventBusIndex中会将订阅方法相关的信息存放在SubscriberMethodInfo类中,这个时候就不在需要通过注解进行获取订阅方法。如果没有配置MyEventBusIndex,便会执行findUsingReflectionInSingleClass方法,将订阅方法保存到findState中。最后再通过getMethodsAndRelease方法对findState做回收处理并反回订阅方法的List集合。
对于MyEventBusIndex的配置它是一个可选项。它的执行过程在这里就不在进行详细的介绍,下面就来看一下如何通过反射来查找订阅方法,也就是看一下findUsingReflectionInSingleClass的执行过程。
private void findUsingReflectionInSingleClass(FindState findState) {
Method[] methods;
try {
// This is faster than getMethods, especially when subscribers are fat classes like Activities
methods = findState.clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
} catch (Throwable th) {
// Workaround for java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError, see https://github.com/greenrobot/EventBus/issues/149
methods = findState.clazz.getMethods();
findState.skipSuperClasses = true;
}
for (Method method : methods) {
//对订阅方法的类型进行过滤
int modifiers = method.getModifiers();
if ((modifiers & Modifier.PUBLIC) != 0 && (modifiers & MODIFIERS_IGNORE) == 0) {
//定于方法中只能有一个参数
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (parameterTypes.length == 1) {
//查找包含Subscribe的注解
Subscribe subscribeAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(Subscribe.class);
if (subscribeAnnotation != null) {
//保存到findState对象当中
Class<?> eventType = parameterTypes[0];
if (findState.checkAdd(method, eventType)) {
ThreadMode threadMode = subscribeAnnotation.threadMode();
findState.subscriberMethods.add(new SubscriberMethod(method, eventType, threadMode,
subscribeAnnotation.priority(), subscribeAnnotation.sticky()));
}
}
} else if (strictMethodVerification && method.isAnnotationPresent(Subscribe.class)) {
String methodName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName();
throw new EventBusException("@Subscribe method " + methodName +
"must have exactly 1 parameter but has " + parameterTypes.length);
}
} else if (strictMethodVerification && method.isAnnotationPresent(Subscribe.class)) {
String methodName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName();
throw new EventBusException(methodName +
" is a illegal @Subscribe method: must be public, non-static, and non-abstract");
}
}
}这段代码的执行过程其实并不是很复杂。在这里主要是使用了Java的反射和对注解的解析。首先通过反射来获取订阅者中所有的方法。并根据方法的类型,参数和注解来找到订阅方法。找到订阅方法后将订阅方法相关信息保存到FindState当中。到这里便完成对订阅者中所有订阅方法的查找。
订阅者的注册过程
在查找完所有的订阅方法以后便开始对所有的订阅方法进行注册,下面就开看一下这个订阅方法。
private void subscribe(Object subscriber, SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod) {
//获取订阅方法中的订阅事件
Class<?> eventType = subscriberMethod.eventType;
//创建一个Subscription来保存订阅者和订阅方法
Subscription newSubscription = new Subscription(subscriber, subscriberMethod);
//获取当前订阅事件中Subscription的List集合
CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType);
if (subscriptions == null) {
//该事件对应的Subscription的List集合不存在,则重新创建并保存在subscriptionsByEventType中
subscriptions = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
subscriptionsByEventType.put(eventType, subscriptions);
} else {
//判断是订阅者是否已经被注册
if (subscriptions.contains(newSubscription)) {
throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriber.getClass() + " already registered to event "
+ eventType);
}
}
//将newSubscription按照订阅方法的优先级插入到subscriptions中
int size = subscriptions.size();
for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) {
if (i == size || subscriberMethod.priority > subscriptions.get(i).subscriberMethod.priority) {
subscriptions.add(i, newSubscription);
break;
}
}
//通过订阅者获取该订阅者所订阅事件的集合
List<Class<?>> subscribedEvents = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber);
if (subscribedEvents == null) {
subscribedEvents = new ArrayList<>();
typesBySubscriber.put(subscriber, subscribedEvents);
}
//将当前的订阅事件添加到subscribedEvents中
subscribedEvents.add(eventType);
//粘性事件的处理,在这里不做详细分析
if (subscriberMethod.sticky) {
if (eventInheritance) {
// Existing sticky events of all subclasses of eventType have to be considered.
// Note: Iterating over all events may be inefficient with lots of sticky events,
// thus data structure should be changed to allow a more efficient lookup
// (e.g. an additional map storing sub classes of super classes: Class -> List<Class>).
Set<Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object>> entries = stickyEvents.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> entry : entries) {
Class<?> candidateEventType = entry.getKey();
if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(candidateEventType)) {
Object stickyEvent = entry.getValue();
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);
}
}
} else {
Object stickyEvent = stickyEvents.get(eventType);
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);
}
}
}在这个方法中便是订阅者真正的注册过程。首先会根据subscriber和subscriberMethod来创建一个Subscription对象。之后根据事件类型获取或创建一个Subscription集合subscriptions并添加到typesBySubscriber对象中。最后将刚才创建的Subscription对象添加到subscriptions之中。于是这样就完成了一次订阅者的注册操作。
事件的发送
现在来看一下事件的整个发送过程。在获取到EventBus对象以后,通过post方法来进行对事件的提交,下面就来看一下整个post方法是如何对事件进行提交的。
public void post(Object event) {
//PostingThreadState保存着事件队列和线程状态信息
PostingThreadState postingState = currentPostingThreadState.get();
//获取事件队列,并将当前事插入到事件队列中
List<Object> eventQueue = postingState.eventQueue;
eventQueue.add(event);
if (!postingState.isPosting) {
//当前线程是否为主线程
postingState.isMainThread = Looper.getMainLooper() == Looper.myLooper();
postingState.isPosting = true;
if (postingState.canceled) {
throw new EventBusException("Internal error. Abort state was not reset");
}
try {
//处理队列中的所有事件
while (!eventQueue.isEmpty()) {
postSingleEvent(eventQueue.remove(0), postingState);
}
} finally {
postingState.isPosting = false;
postingState.isMainThread = false;
}
}
}在PostingThreadState中保存了事件队列,以及线程的一些状态信息。首先从PostingThreadState对象中取出事件队列,然后再将当前的事件插入到事件队列当中。最后将队列中的事件依次交由postSingleEvent方法进行处理,并移除该事件。下面就在进入postSingleEvent方法中看一下。
private void postSingleEvent(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState) throws Error {
Class<?> eventClass = event.getClass();
boolean subscriptionFound = false;
if (eventInheritance) {
//获取所有事件并存放在List中,这里表示事件存在继承关系,向上查找事件的父类
List<Class<?>> eventTypes = lookupAllEventTypes(eventClass);
//处理事件
int countTypes = eventTypes.size();
for (int h = 0; h < countTypes; h++) {
Class<?> clazz = eventTypes.get(h);
subscriptionFound |= postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, clazz);
}
} else {
subscriptionFound = postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, eventClass);
}
//找不到该事件时的异常处理
if (!subscriptionFound) {
if (logNoSubscriberMessages) {
Log.d(TAG, "No subscribers registered for event " + eventClass);
}
if (sendNoSubscriberEvent && eventClass != NoSubscriberEvent.class &&
eventClass != SubscriberExceptionEvent.class) {
post(new NoSubscriberEvent(this, event));
}
}
}对于eventInheritance表示是否向上查找事件的父类。它的默认值为true,可以通过在EventBusBuilder中来进行配置。当eventInheritance为true时,则通过lookupAllEventTypes找到所有的父类事件并存发在List中,然后通过postSingleEventForEventType方法对事件逐一处理。下面就跟进到postSingleEventForEventType方法中查看一下。
private boolean postSingleEventForEventType(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState, Class<?> eventClass) {
//同步取出该事件对应的Subscription集合
CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions;
synchronized (this) {
subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventClass);
}
if (subscriptions != null && !subscriptions.isEmpty()) {
for (Subscription subscription : subscriptions) {
postingState.event = event;
postingState.subscription = subscription;
boolean aborted = false;
try {
//对事件进行处理
postToSubscription(subscription, event, postingState.isMainThread);
aborted = postingState.canceled;
} finally {
postingState.event = null;
postingState.subscription = null;
postingState.canceled = false;
}
if (aborted) {
break;
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}还记得在订阅者进行注册时候,以订阅事件作为Key,将Subscription的List集合作为Value保存到了一个Map集合当中。而就在这个方法中通过事件类型取出Subscription的List集合,然后调用了postToSubscription方法来处理事件并执行订阅方法。下面再来看一下postToSubscription方法。
private void postToSubscription(Subscription subscription, Object event, boolean isMainThread) {
switch (subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode) {
case POSTING:
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
break;
case MAIN:
if (isMainThread) {
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
} else {
mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
}
break;
case BACKGROUND:
if (isMainThread) {
backgroundPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
} else {
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
}
break;
case ASYNC:
asyncPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown thread mode: " + subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode);
}
} 这一路对订阅事件的分发,总算差不多要到头了。在这里取出订阅方法的线程模式,之后根据订阅方法所设置的线程模式来选择线程来执行订阅方法的线程。
订阅方法的线程模式为MAIN的时候。提交事件的线程是主线程则直接执行invokeSubscriber方法。否则加入到mainThreadPoster对象的队列中,而mainThreadPoster对象他是HandlerPoster对象。HandlerPoster继承自Handler,也即是通过Handler将订阅方法切换到主线程执行。
当执行订阅方法需要在子线程中的时候。EventBus是通过Java中的newCachedThreadPool线程池来创建线程并执行的任务。对于Java中的线程池可以参考Java中的线程池这篇文章。而BackgroundPoster和AsyncPoster它们都是一个Runable对象。而执行它们们run方法也是在enqueue方法中。
总结
从整个EventBus的执行过程来它,他实际上就是一个典型的观察者模式。通过对事件的发布与订阅,实现了一种一对多的依赖关系,并有效的为我们事件的发送者与接收者之间进行了解耦。