zoj zju 2992 Monkey Vines 二叉树
Monkey Vines
Time Limit: 2 Seconds Memory Limit: 65536 KB
Deep in the Amazon jungle, exceptionally tall trees grow that support a rich biosphere of figs and juniper bugs, which happen to be the culinary delight of brown monkeys.
Reaching the canopy of these trees requires the monkeys to perform careful navigation through the tall tree��s fragile vine system. These vines operate like a see-saw: an unbalancing of weight at any vine junction would snap the vine from the tree, and the monkeys would plummet to the ground below. The monkeys have figured out that if they work together to keep the vines properly balanced, they can all feast on the figs and juniper bugs in the canopy of the trees.
A vine junction supports exactly two sub-vines, each of which must contain the same number of monkeys, or else the vine will break, leaving a pile of dead monkeys on the jungle ground. For purposes of this problem, a vine junction is denoted by a pair of matching square brackets [ ], which may contain nested information about junctions further down its sub-vines. The nesting of vines will go no further than 25 levels deep.
You will write a program that calculates the minimum number of monkeys required to balance a particular vine configuration. There is always at least one monkey needed, and, multiple monkeys may hang from the same vine.
Input
The first line of input contains a single integer N, (1 <= N <= 1000) which is the number of datasets that follow.
Each dataset consists of a single line of input containing a vine configuration consisting of a string of [ and ] characters as described above. The length of the string of [ and ] will be greater than or equal to zero, and less than or equal to 150.
Output
For each dataset, you should generate one line of output with the following values: The dataset number as a decimal integer (start counting at one), a space, and the minimum number of monkeys required to reach the canopy successfully. Assume that all the hanging vines are reachable from the jungle floor, and that all monkeys jump on the vines at the same time.
Sample Input
3
[]
[[][[]]]
Sample Output
1 2
2 1
3 8
Time Limit: 2 Seconds Memory Limit: 65536 KB
Deep in the Amazon jungle, exceptionally tall trees grow that support a rich biosphere of figs and juniper bugs, which happen to be the culinary delight of brown monkeys.
Reaching the canopy of these trees requires the monkeys to perform careful navigation through the tall tree��s fragile vine system. These vines operate like a see-saw: an unbalancing of weight at any vine junction would snap the vine from the tree, and the monkeys would plummet to the ground below. The monkeys have figured out that if they work together to keep the vines properly balanced, they can all feast on the figs and juniper bugs in the canopy of the trees.
A vine junction supports exactly two sub-vines, each of which must contain the same number of monkeys, or else the vine will break, leaving a pile of dead monkeys on the jungle ground. For purposes of this problem, a vine junction is denoted by a pair of matching square brackets [ ], which may contain nested information about junctions further down its sub-vines. The nesting of vines will go no further than 25 levels deep.
You will write a program that calculates the minimum number of monkeys required to balance a particular vine configuration. There is always at least one monkey needed, and, multiple monkeys may hang from the same vine.
Input
The first line of input contains a single integer N, (1 <= N <= 1000) which is the number of datasets that follow.
Each dataset consists of a single line of input containing a vine configuration consisting of a string of [ and ] characters as described above. The length of the string of [ and ] will be greater than or equal to zero, and less than or equal to 150.
Output
For each dataset, you should generate one line of output with the following values: The dataset number as a decimal integer (start counting at one), a space, and the minimum number of monkeys required to reach the canopy successfully. Assume that all the hanging vines are reachable from the jungle floor, and that all monkeys jump on the vines at the same time.
Sample Input
3
[]
[[][[]]]
Sample Output
1 2
2 1
3 8
Note: The second line of sample input is a blank line.
题意:有一棵完整的二叉树,下面有一群猴子。要求出最小的猴子数量,来使这棵二叉树是平衡的。平衡就是指同一个父节点下面两个儿子节点上面呆的猴子数量必须相同。还有这个树上至少要有一只猴子。
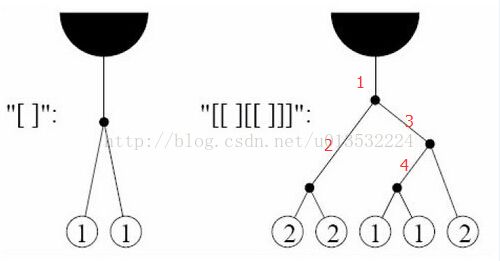
思路:画几个图就可以看出,二叉树上如果想平衡,要看最深的节点的深度。2^dep 就是最少需要多少只猴子来平衡这棵树。但是输入的时候,所给的是用括号来表示这棵树。左括号是表示向下延伸,右括号表示回到父亲节点。注意这棵二叉树的根的上面还有一个根。所以要从图片中的黑色实心半球开始。图中红色数字表示那串左右括号,在这棵树上走的先后顺序。所以求深度,只用一次线性扫描就行了,左括号+,右括号-。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t;
int cas=1;
int n;
char str[500];
int op;
int ans,dep;
scanf("%d",&t);
getchar();
while(t--)
{
gets(str);
ans=0;
dep=0;
for(int i=0;str[i];i++)
{
if(str[i]=='[')
dep++;
else
dep--;
if(dep>ans)
ans=dep;
}
int er=1;
for(int i=0;i<ans;i++)
{
er*=2;
}
printf("%d %d\n",cas++,er);
}
return 0;
}