传智播客c/c++公开课学习笔记--Linux网络流媒体服务器的核心代码揭秘
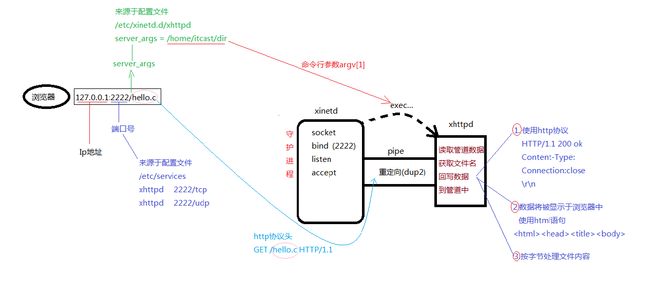
Xinetd
从守护进程的概念可以看出,对于系统所要通过的每一种服务,都必须运行一个监听某个端口连接所发生的守护进程,这通常意味着资源浪费。
为了解决这个问题,Linux引进了"网络守护进程服务程序"的概念。xinted(extended InterNET daemon)
xinetd同时监听多个指定的端口,接受用户请求时,根据请求端口,启动不同的网络服务进程来处理这些用户请求。
可以把xinetd看做一个管理启动服务的管理服务器,它决定把一个客户请求交给哪个程序处理,然后启动相应的守护进程。
xinetd无时不在运行并监听它所管理的所有端口上的服务。
当某个要连接它管理的某项服务的请求到达时,xinetd就会为该服务启动合适的服务器。
安装及配置xinetd
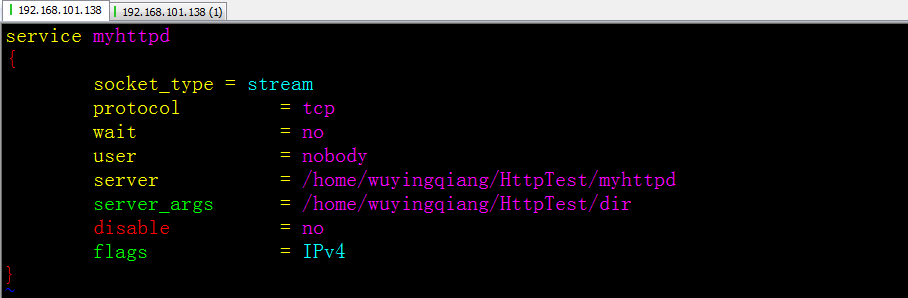
1. sudo apt-get install xinetd (sudo aptitude show/install xinetd)2. sudo vi /etc/xinetd.d/myhttpd (注意三个统一)
service myhttpd
{
socket_type = stream
protocol = tcp
wait = no
user = nobody
server = /home/wuyingqiang/HttpTest/myhttpd
server_args = /home/wuyingqiang/HttpTest/dir
disable = no
flags = IPv4
}
socket_type: 网络套接字类型,流或者数据包.
protocol: IP协议,通常时TCP或者UDP
wait: 取值yes/no
user: 运行进程的用户ID
server: 执行的完整路径
server_args: 传递给server的值
disable: 用于在默认的{}中禁止服务
flags: 所使用的互联网协议
3. sudo vi /etc/services 向其中加入端口号,如:2222
4. 重启xinetd服务器 sudo service xinetd restart
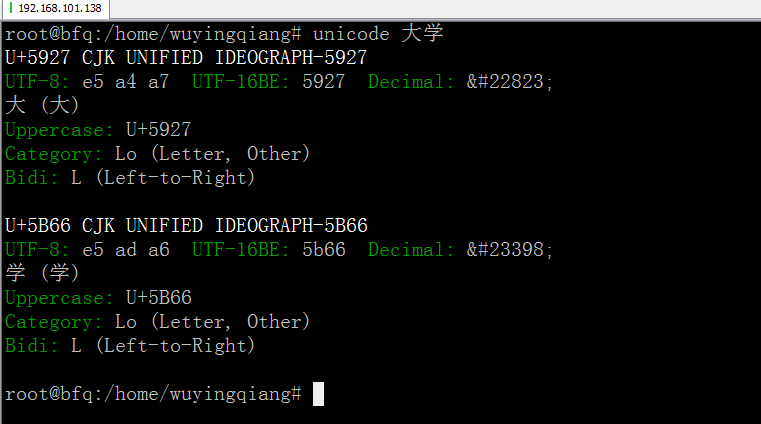
URL编码扩展问题:
可以查看中文的unicode编码。#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#define SERVER_NAME "xhttpd"
#define PROTOCOL "HTTP/1.1"
#define SERVER_URL "http://www.itcast.cn/"
#define FORMAT_DATE "%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S GMT"
#define N 4096
#ifdef DEBUG
#define log(info, str)\
do{
fprintf(fp_tmp, "%s%s", info, str);
fflush(fp_tmp);
}while(0)
/* put them in the right place.
//fp_tmp = fopen(/home/akaedu/dir/log.text, "a");
//log("argv[1]", argv[1]);
//log("line:", line);
*/
#endif
//设置http协议头部分
static void send_headers(int status, char *title, char *extra_header, char *mime_type, off_t length, time_t mod);
//返回出错页面
static void send_error(int status, char *title, char *extra_header, char *text);
//用于文件名编码,对应strdecode
static void strencode(char *to, size_t tosize, const char *from);
//输出文件相关属性详细信息
static void file_infos(char *dir, char *name);
//URL解码
static void strdecode(char *to, char *from);
//通过文件名推断文件的mime_type
static char *get_mime_type(char *name);
//十六进制转换为十进制数
static int hexit(char c);
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char line[N*2], method[N*2], path[N*2], protocol[N*2], idx[N*4], location[N*4];
char *file;
size_t len;
int ich, i, n;
struct stat sb;
FILE *fp;
struct dirent **dl;
if (argc != 2) //xinetd中的server_args
send_error(500, "Internal Error", NULL, "Config error - no dir specified.");
//xinetd启动时把根路径(xhttpd服务器文档的根目录)传给本程序,这步非常非常重要
if (chdir(argv[1]) < 0) //更改工作目录
send_error(500, "Internal Error", NULL, "Config error - couldn't chdir.");
//http协议第一行 如:GET /hello.c HTTP/1.1
if (fgets(line, sizeof(line), stdin) == NULL) //提取请求行,包含请求方法/路径/协议
send_error(400, "Bad Request", NULL, "No request found.");
/* "%[^ ] %[^ ] %[^ ]" 将一行字符串按空格切割为三个子串
应用举例:
GET方法:在浏览器的地址栏中输入网址访问网页时,浏览器采用GET方法向服务器获取资源,
eg:GET /form.html HTTP/1.1
method = GET
path = /form.html
protocol = HTTP/1.1
返回值:成功返回实际读到的字段个数,失败返回-1
*/
if (sscanf(line, "%[^ ] %[^ ] %[^ ]", method, path, protocol) != 3) //提取方法/路径/协议
send_error(400, "Bad Request", NULL, "Can't parse request.");
//读到请求头结束
while (fgets(line, sizeof(line), stdin) != NULL) { //注意stdin被dup2至xinetd管道的读端
if (strcmp(line, "\n") == 0 || strcmp(line, "\r\n") == 0)
break;
}
//只支持GET请求,strcasecmp,忽略大小写
if (strcasecmp(method, "GET") != 0)
send_error(501, "Not Implemented", NULL, "That method is not implemented.");
//path必须从‘/’开始。
if (path[0] != '/')
send_error(400, "Bad Request", NULL, "Bad filename.");
file = &(path[1]); //file = path+1
//解码路径名,搞掉%20之类的东西
strdecode(file, file);
if (file[0] == '\0')
file = "./";
//检测是否为合法的文件格式,防止越界访问到根目录上级目录
len = strlen(file);
if (file[0] == '/' || strcmp(file, "..") == 0
|| strncmp(file, "../", 3) == 0
|| strstr(file, "/../") != NULL
|| strcmp(&(file[len-3]), "/..") == 0)
{
send_error(400, "Bad Request", (char*)0, "Illegal filename.");
}
//测试有无请求之文件(或目录),stat为获取指定目录位置文件file函数,sb为传出参数。
if (stat(file, &sb) < 0)
send_error(404, "Not Found", (char*)0, "File not found.");
/*
*404页面 当用户输入了错误的链接时,返回的页面,用户无法解决该错误
*标准化可配置HTTP协议错误,定位在400到505之间
*
*1、无法在所请求的端口上访问Web站点
*2、Web服务扩展锁定策略阻止本请求
*3、MIME映射测略阻止本请求
*
*/
//请求路径是目录吗
if (S_ISDIR(sb.st_mode)) { //路径名对应目录
if (file[len-1] != '/') { //路径名要以"/"结尾
snprintf(location, sizeof(location), "Location: %s/", path);
send_error(302, "Found", location, "Directories must end with a slash.");
}
//有index.html则处理之
snprintf(idx, sizeof(idx), "%sindex.html", file);
if (stat(idx, &sb) >= 0) {
file = idx;
goto do_file; //如果有index.html则跳到do_file:
}
//显示请求目录下的文件列表
send_headers(200, "Ok", NULL, "text/html", -1, sb.st_mtime);
printf("<html><head><title>Index of %s</title></head>"
"\n<body bgcolor=\"#99cc99\"><h4>Index of %s</h4>\n<pre>\n"
, file, file);
/*
* int scandir(const char *dirp,
* struct dirent ***namelist,
* int (*filter)(const struct dirent *),
* int (*compar)(const struct dirent **, const struct dirent **)
* );
* 依据匹配项目,扫描一个目录
* 扫描dirp目录下(不包括子目录)满足filter过滤模式的文件,
* 返回的结果是compare函数经过排序的,并保存在namelist中。
*
* scandir() 函数扫描目录 dirp,对每一个目录项(文件名)调用filter()。
* 把每一个filter() 返回非零项目保存在一个通过malloc(3) 分配的缓存区里,
* 再通过比较函数是compar() 的qsort(3) 函数排序,最后收集在namelist 的数组里,
* 这个数组也是通过malloc(3) 分配的。如果filter 是 NULL,所有项目都被选择
*
* alphasort和versionsort是使用到的两种排序的函数
*
* scandir() 函数返回被选择的目录条数,或者如果出错返回 -1。
*/
n = scandir(file, &dl, NULL, alphasort); //读取目录下各个目录项,并返回每个文件信息.
if (n < 0)
perror("scandir");
else
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
file_infos(file, dl[i]->d_name);
printf("</pre>\n<hr>\n<address><a href=\"%s\">%s</a></address>\n</body></html>\n"
, SERVER_URL, SERVER_NAME);
} else { //所请求非目录而是一个文件
do_file: //获取文件内容并返回给客户端
fp = fopen(file, "r"); //只读方式将文件打开
if (fp == (FILE*)0)
send_error(403, "Forbidden", (char*)0, "File is protected.");
//发送http协议头,200表示成功, OK是随便写的
send_headers(200, "Ok", (char*)0, get_mime_type(file), sb.st_size, sb.st_mtime);
while ((ich = getc(fp)) != EOF)
putchar(ich);
}
fflush(stdout);
exit(0);
}
//输出文件相关的详细属性信息,包括日期和时间
static void file_infos(char *dir, char *name)
{
static char encoded_name[N];
static char path[N];
char timestr[16];
struct stat sb;
strencode(encoded_name, sizeof(encoded_name), name);
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s", dir, name);
if (lstat(path, &sb) < 0)
//设置显示格式,"-"表示左对齐,不加"-"即为右对齐;-32表示显示内容占32列不足用空格补齐;32s表输出字符串的32个字符.
printf("<a href=\"%s\">%-32.32s</a> ???\n", encoded_name, name);
else {
strftime(timestr, sizeof(timestr), "%d%b%Y %H:%M", localtime(&sb.st_mtime));
printf("<a href=\"%s\">%-32.32s</a> %15s %14lld\n", encoded_name, name, timestr, (int64_t)sb.st_size);
}
/*
*size_t strftime(char *s, size_t max, const char *format,
const struct tm *tm);
* 将当前系统的绝对时间,按格式输出。
* format以百分号(%)开始的格式命令集合,格式化输出结果放在s中。
*
* %d 十进制表示的日期(01~31)
* %b 月份英文单词的简写
* %Y 带世纪部分的十进制年份
* %H 24小时制的小时
* %M 十进制表示的分钟数(00~59)
*/
}
/*
*出错时,发送错误相应信息,返回出错页面
*
*status:错误号 title:错误名 text:错误描述
*extra_header:附加描述(特殊情况302时不退出程序,而直接显示正常页面)
*/
static void send_error(int status, char* title, char* extra_header, char* text)
{
send_headers(status, title, extra_header, "text/html", -1, -1);
printf("<html><head><title>%d %s</title></head>\n<body bgcolor=\"#cc9999\"><h4>%d %s</h4>\n",
status, title, status, title);
printf("%s\n", text);
printf("<hr>\n<address><a href=\"%s\">%s</a></address>\n</body></html>\n", SERVER_URL, SERVER_NAME);
fflush(stdout);
exit( 1 );
}
/*
*每个HTTP传送都包含一个首部、一个空行和要发送的数据项。
*Content-Type: 数据项的类型(必选项)
*Content-length: 数据项的大小
*Content-Encoding: 数据项使用的编码方式
*Content-Language: 数据项使用的语言
*
*首部中的每一行都包含一个关键字、一个冒号和信息。
*e.g.
*Content-Type: text/html; charset=iso-8859-1 指明属性的首部
*Content-Length: 508
* 这是一行空行
*<html> 文档内容 </html> 数据项
*/
static void
send_headers(int status, char* title, char* extra_header, char* mime_type, off_t length, time_t mod)
{
time_t now;
char timebuf[100];
printf("%s %d %s\r\n", PROTOCOL, status, title);//HTTP/1.0 200 OK
printf("Server: %s\r\n", SERVER_NAME);//Server: xhttpd
now = time((time_t*)0);
strftime(timebuf, sizeof(timebuf), FORMAT_DATE, gmtime(&now));
printf("Date: %s\r\n", timebuf);
// Date: Fri, 18 Jul 2014 14:34:26 GMT
if (extra_header != NULL)
printf("%s\r\n", extra_header);
if (mime_type != NULL)
printf("Content-Type: %s\r\n", mime_type);
if (length >= 0)
printf("Content-Length: %lld\r\n", (int64_t)length);
if (mod != (time_t)-1) { //强转
strftime(timebuf, sizeof(timebuf), FORMAT_DATE, gmtime(&mod));
printf("Last-Modified: %s\r\n", timebuf);
}
printf("Connection: close\r\n");
printf("\r\n");
}
static char *get_mime_type(char *name)
{
char* dot;
dot = strrchr(name, '.'); //自右向左查找‘.’字符;如不存在返回NULL
/*
*charset=iso-8859-1 西欧的编码,说明网站采用的编码是英文;
*charset=gb2312 说明网站采用的编码是简体中文;
*charset=utf-8 代表世界通用的语言编码;
* 可以用到中文、韩文、日文等世界上所有语言编码上
*charset=euc-kr 说明网站采用的编码是韩文;
*charset=big5 说明网站采用的编码是繁体中文;
*
*以下是依据传递进来的文件名,使用后缀判断是何种文件类型
*将对应的文件类型按照http定义的关键字发送回去
*/
if (dot == (char*)0)
return "text/plain; charset=iso-8859-1";
if (strcmp(dot, ".html") == 0 || strcmp(dot, ".htm") == 0)
return "text/html; charset=iso-8859-1";
if (strcmp(dot, ".jpg") == 0 || strcmp(dot, ".jpeg") == 0)
return "image/jpeg";
if (strcmp(dot, ".gif") == 0)
return "image/gif";
if (strcmp(dot, ".png") == 0)
return "image/png";
if (strcmp(dot, ".css") == 0)
return "text/css";
if (strcmp(dot, ".au") == 0)
return "audio/basic";
if (strcmp( dot, ".wav") == 0)
return "audio/wav";
if (strcmp(dot, ".avi") == 0)
return "video/x-msvideo";
if (strcmp(dot, ".mov") == 0 || strcmp(dot, ".qt") == 0)
return "video/quicktime";
if (strcmp(dot, ".mpeg") == 0 || strcmp(dot, ".mpe") == 0)
return "video/mpeg";
if (strcmp(dot, ".vrml") == 0 || strcmp(dot, ".wrl") == 0)
return "model/vrml";
if (strcmp(dot, ".midi") == 0 || strcmp(dot, ".mid") == 0)
return "audio/midi";
if (strcmp(dot, ".mp3") == 0)
return "audio/mpeg";
if (strcmp(dot, ".ogg") == 0)
return "application/ogg";
if (strcmp(dot, ".pac") == 0)
return "application/x-ns-proxy-autoconfig";
return "text/plain; charset=iso-8859-1";
}
/*
* 处理URL中%20之类的东西!是"解码"过程。
* %20 URL编码中的‘ ’(space)
* %21 '!' %22 '"' %23 '#' %24 '$'
* %25 '%' %26 '&' %27 ''' %28 '('......
*
* 相关知识html中的‘ ’(space)是
*/
static void strdecode(char *to, char *from)
{
for ( ; *from != '\0'; ++to, ++from) {
if (from[0] == '%' && isxdigit(from[1]) && isxdigit(from[2])) {
*to = hexit(from[1])*16 + hexit(from[2]);
from += 2;//移过已经处理的两个字符(%21指针指向1),表达式3的++from还会再向后移一个字符
} else
*to = *from;
}
*to = '\0';
}
//16进制数转化为10进制, return 0不会出现
static int hexit(char c)
{
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9')
return c - '0';
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'f')
return c - 'a' + 10;
if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'F')
return c - 'A' + 10;
return 0;
}
//"编码",用作回写浏览器的时候,将除字母数字及/_.-~以外的字符转义后回写。
//strencode(encoded_name, sizeof(encoded_name), name);
static void strencode(char* to, size_t tosize, const char* from)
{
int tolen;
for (tolen = 0; *from != '\0' && tolen + 4 < tosize; ++from) {
if (isalnum(*from) || strchr("/_.-~", *from) != (char*)0) {
*to = *from;
++to;
++tolen;
} else {
sprintf(to, "%%%02x", (int) *from & 0xff);
to += 3;
tolen += 3;
}
}
*to = '\0';
}