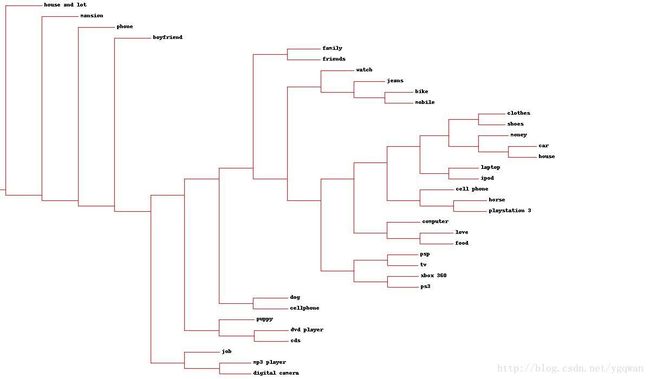
聚类算法反应人们想要的物品(tanimoto相关度)
也就是tanimoto相关度能够很好的解决01关系, 也就是是否关系, 比如是否看过某部电影; 而皮尔逊相关度能够很好的解决一些用程度衡量的, 比如为某部电影打分就是程度
其中用到的数据来自集体智慧编程的作者
只是把距离函数改掉了:
#coding:utf-8
import os
import sys
import chardet
from math import sqrt
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import random
def readFile(fileName):
lines = [line for line in file(fileName)]
colNames = lines[0].strip().split('\t')[1:]
rowNames = []
data = []
for line in lines[1:]:
p = line.strip().split('\t')
rowNames.append(p[0])
data.append([float(x) for x in p[1:]])
return rowNames, colNames, data
def pearsonBeta(v1, v2):
sum1 = sum(v1)
sum2 = sum(v2)
sum1Sq = sum([pow(v, 2) for v in v1])
sum2Sq = sum([pow(v, 2) for v in v2])
pSum = sum([v1[i] * v2[i] for i in range(len(v1))])
nums = pSum - (sum1 * sum2 / len(v1))
den = sqrt((sum1Sq - pow(sum1, 2) / len(v1)) * (sum2Sq - pow(sum2, 2) / len(v2)))
if(den == 0):
return 0
return 1.0 - nums/den
#距离函数
def pearson(v1, v2):
sum1 = sum(v1)
sum2 = sum(v2)
eSum1 = sum1 / len(v1)
eSum2 = sum2 / len(v2)
pSum = sum([(v1[i] - eSum1) * (v2[i] - eSum2) for i in range(len(v1))])
pTmp1 = sqrt(sum([pow(v1[i] -eSum1, 2) for i in range(len(v1))]))
pTmp2 = sqrt(sum([pow(v2[i] -eSum2, 2) for i in range(len(v2))]))
pSqrtSum = pTmp1 * pTmp2
if pSqrtSum == 0:
return 0
return 1 - pSum / pSqrtSum
#距离函数2
def tanimoto(v1, v2):
c1, c2, shr = 0, 0, 0
for i in range(len(v1)):
if v1[i] != 0: c1 += 1
if v2[i] != 0: c2 += 1
if v1[i] != 0 and v2[i] != 0: shr += 1
return 1.0 - float(shr) / (float(c1 + c2 - shr))
class bicluster:
def __init__(self, vec, left = None, right = None, distance = 0.0, id = None):
self.vec = vec
self.left = left
self.right = right
self.distance = distance
self.id = id
def vis(self):
print self.vec
#层次聚类
def hCluster(rows, distanceFunc = pearson):
distances = {}
currentClustId = -1
clust = [bicluster(rows[i], id = i) for i in range(len(rows))]
while len(clust) > 1:
lowestPair = (0, 1)
closest = distanceFunc(clust[0].vec, clust[1].vec)
for i in range(len(clust)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(clust)):
if(clust[i].id, clust[j].id) not in distances:
distances[(clust[i].id, clust[j].id)] = distanceFunc(clust[i].vec, clust[j].vec)
d = distances[(clust[i].id, clust[j].id)] #直接写成了i,j , 害我找了半天
if d < closest:
closest = d
lowestPair = (i, j)
mergevec = [(clust[lowestPair[0]].vec[i] + clust[lowestPair[1]].vec[i]) / 2.0 for i in range(len(clust[0].vec))]
newCluster = bicluster(mergevec, left = clust[lowestPair[0]], right = clust[lowestPair[1]], distance = closest, id = currentClustId)
currentClustId -= 1
del clust[lowestPair[1]] #must first del 1, then 0
del clust[lowestPair[0]]
clust.append(newCluster)
return clust[0]
#k-均值聚类
def kcluster(rows, distanceFunc = pearson, k = 5):
ranges = [(min(row[i] for row in rows), max(row[i] for row in rows)) for i in range(len(rows[0]))]
clusters = [[random.random() * (ranges[i][1] - ranges[i][0]) + ranges[i][0] for i in range(len(rows[0]))] for j in range(k)]
bestMatches = None
for t in range(100):
print "iter is: %d" %(t)
lastMatches = [[] for i in range(k)]
for i in range(len(rows)):
row = rows[i]
lastMatch = 0
for j in range(k):
d = distanceFunc(clusters[j], row)
if d < distanceFunc(rows[lastMatch], row):
lastMatch = j
lastMatches[lastMatch].append(i)
if lastMatches == bestMatches:
break;
bestMatches = lastMatches
#move center
for i in range(k):
if len(bestMatches[i]) > 0:
newRow = []
for j in range(len(rows[0])):
sum = 0
for v in range(len(bestMatches[i])):
sum += rows[v][j]
newRow.append(sum)
for j in range(len(newRow)):
newRow[j] = newRow[j] / len(bestMatches[i])
clusters[i] = newRow
return bestMatches
#以缩进方式打印层次聚类的树
def printClust(clust, labels = None, n = 0):
for i in range(n):print ' ',
if clust.id < 0:
print '-'
else:
if labels == None:
print clust.id
else:
print labels[clust.id]
if clust.left != None:
printClust(clust.left, labels = labels, n = n + 1)
if clust.right != None:
printClust(clust.right, labels = labels, n = n + 1)
def getHeight(clust):
if clust.left == None and clust.right == None:
return 1
return getHeight(clust.left) + getHeight(clust.right)
def getDepth(clust):
if clust.left == None and clust.right == None:
return 1
return max(getDepth(clust.left), getDepth(clust.right)) + clust.distance
def drawnode(draw, clust, x, y, scaling, labels):
if clust.id < 0:
h1 = getHeight(clust.left) * 20
h2 = getHeight(clust.right) * 20
top = y - (h1 + h2) / 2
bottom = y + (h1 + h2) / 2
li = clust.distance * scaling
draw.line((x, top + h1/2, x, bottom - h2/2), fill = (255, 0, 0))
draw.line((x, top + h1/2, x + li, top + h1/2), fill = (255, 0, 0))
draw.line((x ,bottom - h2/2, x + li, bottom - h2/2), fill = (255, 0, 0))
drawnode(draw, clust.left, x + li, top + h1/2, scaling, labels)
drawnode(draw, clust.right, x + li, bottom - h2/2, scaling, labels)
else:
draw.text((x + 5, y - 7), labels[clust.id], (0, 0, 0))
#以属性结构打印层次聚类的关系
def drawdendrogram(clust, labels, jpeg = "zebo2.jpg"):
h = getHeight(clust) * 20
w = 1200
depth = getDepth(clust)
scaling = float(w - 150) / depth
img = Image.new("RGB", (w, h), (255, 255, 255))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
draw.line((0, h/2, 10, h/2), fill = (255, 0, 0))
drawnode(draw, clust, 10, (h/2), scaling, labels)
img.save(jpeg, "JPEG")
(wants, people, data) = readFile("F:\\py\\dataFetch\\julei\\data\\zebo.txt")
clust = hCluster(data, distanceFunc = tanimoto)
#printClust(clust, wants)
drawdendrogram(clust, wants)
#print kcluster(data)
#cluster = hCluster(data, distanceFunc = tanimoto)
#drawdendrogram(cluster, rowNames)
从图中可以看到一些信息: 想要手机的人想拥有一只狗(好像不怎么准), 游戏机被聚在了一起;衣服鞋子也被聚在了一起, 想拥有男朋友的人貌似很普遍