生产环境中跨节点隔离网络构架解析
生产环境中跨节点的2层网络组建
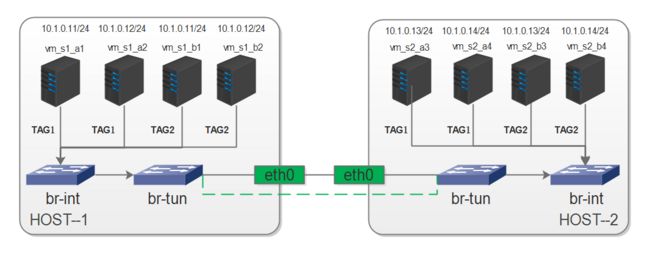
在改图中我们有两个用户,两个物理机,8个虚拟机,A用户与B用户的虚拟机ip时重叠的。
先对该图进行分析:
就租户视觉来看,A租户的4台虚拟机对A来说应该是在一个只有A可以见的一个私有网络环境中,B也一样,二者的IP地址互相重叠。
假设A用户在宿主机之间的tunnel_id为0xb1,在宿主机S1中的tag为1,在宿主机S2中的tag为1。
B用户在宿主机之间的tunnel_id为0xb2,在宿主机S1中的tag为2,在宿主机S2中的tag为2。
模拟实现该环境
接下来的模拟环境我将先叙述分配情况,具体部署我写在一个脚本里面,不再对每一步都做详细说明。
先说下我要做的部署说明吧:
全局配置:
user_1_tunnel_id: 0x101
user_2_tunnel_id:0x102
server_1的配置信息:
ip: 10.180.66.4
user_a_tag: 1
user_b_tag: 2
server_2的配置信息:
ip: 10.180.64.184
user_a_tag: 1
user_b_tag: 2
(这部分可以与server中的tag不一样,只要保证每个用户在每个宿主物理机唯一就行了)
server_1的脚本如下:(在此我们只对脚本一种的每一步进行大体解释)
#!/bin/bash -x
user_a_tunnel_id=0x101
user_b_tunnel_id=0x102
# create two switch and connect then with patch port # 首先我们创建br-int和br-tun,br-int用于宿主机内部交换,br-tun用于通道交换 # 创建两个br之间的通道 ovs-vsctl add-br br-int -- add-br br-tun ovs-vsctl add-port br-int int-tun -- add-port br-tun tun-int ovs-vsctl set interface int-tun type=patch options:peer=tun-int ovs-vsctl set interface tun-int type=patch options:peer=int-tun # init vms # 模拟创建a用户的和B用户的4个云主机 ovs-vsctl add-port br-int vm_s1_a1 -- set port vm_s1_a1 tag=1 -- set interface vm_s1_a1 type=internal ovs-vsctl add-port br-int vm_s1_a2 -- set port vm_s1_a2 tag=1 -- set interface vm_s1_a2 type=internal ovs-vsctl add-port br-int vm_s1_b1 -- set port vm_s1_b1 tag=2 -- set interface vm_s1_b1 type=internal ovs-vsctl add-port br-int vm_s1_b2 -- set port vm_s1_b2 tag=2 -- set interface vm_s1_b2 type=internal ip netns add vm_s1_a1 ip netns add vm_s1_a2 ip netns add vm_s1_b1 ip netns add vm_s1_b2 ip link set vm_s1_a1 netns vm_s1_a1 ip link set vm_s1_a2 netns vm_s1_a2 ip link set vm_s1_b1 netns vm_s1_b1 ip link set vm_s1_b2 netns vm_s1_b2 ip netns exec vm_s1_a1 ifconfig vm_s1_a1 up ip netns exec vm_s1_a2 ifconfig vm_s1_a2 up ip netns exec vm_s1_b1 ifconfig vm_s1_b1 up ip netns exec vm_s1_b2 ifconfig vm_s1_b2 up # 为其分别设置IP ip netns exec vm_s1_a1 ip a a 10.1.0.11/24 dev vm_s1_a1 ip netns exec vm_s1_a2 ip a a 10.1.0.12/24 dev vm_s1_a2 ip netns exec vm_s1_b1 ip a a 10.1.0.11/24 dev vm_s1_b1 ip netns exec vm_s1_b2 ip a a 10.1.0.12/24 dev vm_s1_b2 # =========create gre tunnel with remote ip ===== # 设置GRE的channel,连向对端 ovs-vsctl add-port br-tun gre-tun -- set interface gre-tun type=gre \ options:remote_ip=$1 options:in_key=flow options:out_key=flow # =========init open-flows ====================== # 清理默认的规则,添加我们需要的规则 # ---------clear old flow-rulers of br-tun------- ovs-ofctl del-flows br-tun '' # --------- add rulers ------------------------- # 这个函数是为了获取port 的id编号 function get_port_id () { id=`ovs-vsctl list interface $1 |grep -w ofport |awk '{print $3}'` echo $id } # 获取一对patch的端口的编号 gre_tun_id=`get_port_id gre-tun` tun_int_id=`get_port_id tun-int` #对于用户a的两台虚拟机(判断条件为 tag=1)。抹去tag,设置tunnel_id为0x101然后交给gre_tun转发 ovs-ofctl add-flow br-tun in_port=$tun_int_id,dl_vlan=1,action=strip_vlan,set_tunnel:$user_a_tunnel_id,output:$gre_tun_id # 同上 ovs-ofctl add-flow br-tun in_port=$tun_int_id,dl_vlan=2,action=strip_vlan,set_tunnel:$user_b_tunnel_id,output:$gre_tun_id # 对gre_tun回来的包,如果判断为tunnel_id为0x101,则设置为tag:1转交给tun_int ovs-ofctl add-flow br-tun in_port=$gre_tun_id,tun_id=$user_a_tunnel_id,action=mod_vlan_vid:1,output:$tun_int_id # 同上类似。 ovs-ofctl add-flow br-tun in_port=$gre_tun_id,tun_id=$user_b_tunnel_id,action=mod_vlan_vid:2,output:$tun_int_id从脚本中我们可以看到用法:
./$file_name $remote_ipserver_2的脚本将不详细注释,大同小异,脚本如下:
#!/bin/bash -x
user_a_tunnel_id=0x101
user_b_tunnel_id=0x102
# create two switch and connect then with patch port ovs-vsctl add-br br-int -- add-br br-tun ovs-vsctl add-port br-int int-tun -- add-port br-tun tun-int ovs-vsctl set interface int-tun type=patch options:peer=tun-int ovs-vsctl set interface tun-int type=patch options:peer=int-tun # init vms ovs-vsctl add-port br-int vm_s2_a3 -- set port vm_s2_a3 tag=1 -- set interface vm_s2_a3 type=internal ovs-vsctl add-port br-int vm_s2_a4 -- set port vm_s2_a4 tag=1 -- set interface vm_s2_a4 type=internal ovs-vsctl add-port br-int vm_s2_b3 -- set port vm_s2_b3 tag=2 -- set interface vm_s2_b3 type=internal ovs-vsctl add-port br-int vm_s2_b4 -- set port vm_s2_b4 tag=2 -- set interface vm_s2_b4 type=internal ip netns add vm_s2_a3 ip netns add vm_s2_a4 ip netns add vm_s2_b3 ip netns add vm_s2_b4 ip link set vm_s2_a3 netns vm_s2_a3 ip link set vm_s2_a4 netns vm_s2_a4 ip link set vm_s2_b3 netns vm_s2_b3 ip link set vm_s2_b4 netns vm_s2_b4 ip netns exec vm_s2_a3 ifconfig vm_s2_a3 up ip netns exec vm_s2_a4 ifconfig vm_s2_a4 up ip netns exec vm_s2_b3 ifconfig vm_s2_b3 up ip netns exec vm_s2_b4 ifconfig vm_s2_b4 up ip netns exec vm_s2_a3 ip a a 10.1.0.13/24 dev vm_s2_a3 ip netns exec vm_s2_a4 ip a a 10.1.0.14/24 dev vm_s2_a4 ip netns exec vm_s2_b3 ip a a 10.1.0.13/24 dev vm_s2_b3 ip netns exec vm_s2_b4 ip a a 10.1.0.14/24 dev vm_s2_b4 # =========create gre tunnel with remote ip ===== ovs-vsctl add-port br-tun gre-tun -- set interface gre-tun type=gre \ options:remote_ip=$1 options:in_key=flow options:out_key=flow # =========init open-flows ====================== # ---------clear old flow-rulers of br-tun------- ovs-ofctl del-flows br-tun '' # --------- add rulers ------------------------- function get_port_id () { id=`ovs-vsctl list interface $1 |grep -w ofport |awk '{print $3}'` echo $id } gre_tun_id=`get_port_id gre-tun` tun_int_id=`get_port_id tun-int` ovs-ofctl add-flow br-tun in_port=$tun_int_id,dl_vlan=1,action=strip_vlan,set_tunnel:$user_a_tunnel_id,output:$gre_tun_id ovs-ofctl add-flow br-tun in_port=$tun_int_id,dl_vlan=2,action=strip_vlan,set_tunnel:$user_b_tunnel_id,output:$gre_tun_id ovs-ofctl add-flow br-tun in_port=$gre_tun_id,tun_id=$user_a_tunnel_id,action=mod_vlan_vid:1,output:$tun_int_id ovs-ofctl add-flow br-tun in_port=$gre_tun_id,tun_id=$user_b_tunnel_id,action=mod_vlan_vid:2,output:$tun_int_id在调试过程中,难免会出现错误,在此我也写了一个用于清理现场的脚本,用于在出错的时候清理现场,重新进行调试。
#! /bin/bash -x
ovs-vsctl del-br br-int
ovs-vsctl del-br br-tun
ip netns list | awk '{print "ip netns del " $1}' |bash下面又到了我们开始试验的时候了:
server_1和server_2分别运行个子的初始化脚本,完成初始化环境的测试。
server_1:
./$file_name 10.180.64.184
root@www /home/abaobo/tmp 2015-08-22 20:32:28
# ovs-vsctl show
69581e33-310b-4971-84f3-2c06c4f8a75c
Bridge br-tun
Port tun-int
Interface tun-int
type: patch
options: {peer=int-tun}
Port gre-tun
Interface gre-tun
type: gre
options: {in_key=flow, out_key=flow, remote_ip="10.180.64.184"}
Port br-tun
Interface br-tun
type: internal
Bridge br-int
Port "vm_s1_b2"
tag: 2
Interface "vm_s1_b2"
type: internal
Port "vm_s1_b1"
tag: 2
Interface "vm_s1_b1"
type: internal
Port "vm_s1_a2"
tag: 1
Interface "vm_s1_a2"
type: internal
Port int-tun
Interface int-tun
type: patch
options: {peer=tun-int}
Port br-int
Interface br-int
type: internal
Port "vm_s1_a1"
tag: 1
Interface "vm_s1_a1"
type: internal
ovs_version: "2.4.0"
root@www /home/abaobo/tmp 2015-08-22 20:32:33
# ovs-ofctl dump-flows br-tun
NXST_FLOW reply (xid=0x4):
cookie=0x0, duration=33.027s, table=0, n_packets=12, n_bytes=948, idle_age=23, in_port=1,dl_vlan=1 actions=strip_vlan,set_tunnel:0x101,output:2
cookie=0x0, duration=33.025s, table=0, n_packets=13, n_bytes=1026, idle_age=23, in_port=1,dl_vlan=2 actions=strip_vlan,set_tunnel:0x102,output:2
cookie=0x0, duration=33.022s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=33, tun_id=0x101,in_port=2 actions=mod_vlan_vid:1,output:1
cookie=0x0, duration=33.019s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=33, tun_id=0x102,in_port=2 actions=mod_vlan_vid:2,output:1server_2:
./$file_name 10.180.66.2
root@cnsdev-network-dca5999d-f2e4-4cec-80ac-1e673baa3b90 ~/tmp 20:33:26
# ovs-vsctl show
b77ecdc3-e478-4ae2-9744-194963d9a59d
Bridge br-tun
Port tun-int
Interface tun-int
type: patch
options: {peer=int-tun}
Port gre-tun
Interface gre-tun
type: gre
options: {in_key=flow, out_key=flow, remote_ip="10.180.66.2"}
Port br-tun
Interface br-tun
type: internal
Bridge br-int
Port int-tun
Interface int-tun
type: patch
options: {peer=tun-int}
Port "vm_s2_a4"
tag: 1
Interface "vm_s2_a4"
type: internal
Port "vm_s2_b3"
tag: 2
Interface "vm_s2_b3"
type: internal
Port "vm_s2_a3"
tag: 1
Interface "vm_s2_a3"
type: internal
Port "vm_s2_b4"
tag: 2
Interface "vm_s2_b4"
type: internal
Port br-int
Interface br-int
type: internal
ovs_version: "2.3.0"
root@cnsdev-network-dca5999d-f2e4-4cec-80ac-1e673baa3b90 ~/tmp 20:33:40
# ovs-ofctl dump-flows br-tun
NXST_FLOW reply (xid=0x4):
cookie=0x0, duration=77.363s, table=0, n_packets=14, n_bytes=1116, idle_age=67, in_port=1,dl_vlan=2 actions=strip_vlan,set_tunnel:0x102,output:2
cookie=0x0, duration=77.365s, table=0, n_packets=13, n_bytes=1026, idle_age=67, in_port=1,dl_vlan=1 actions=strip_vlan,set_tunnel:0x101,output:2
cookie=0x0, duration=77.361s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=77, tun_id=0x101,in_port=2 actions=mod_vlan_vid:1,output:1
cookie=0x0, duration=77.359s, table=0, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=77, tun_id=0x102,in_port=2 actions=mod_vlan_vid:2,output:1接下来进行测试:
在server_1中我们的测试结果如下:
root@www /home/abaobo/tmp 2015-08-22 21:01:02
# ip netns exec vm_s1_a1 ping 10.1.0.12 -c 1
PING 10.1.0.12 (10.1.0.12) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.1.0.12: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.526 ms
--- 10.1.0.12 ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.526/0.526/0.526/0.000 ms
root@www /home/abaobo/tmp 2015-08-22 21:01:04
# ip netns exec vm_s1_a1 ping 10.1.0.13 -c 1
PING 10.1.0.13 (10.1.0.13) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.1.0.13: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=3.51 ms
--- 10.1.0.13 ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 3.517/3.517/3.517/0.000 ms
root@www /home/abaobo/tmp 2015-08-22 21:01:08
# ip netns exec vm_s1_a1 ping 10.1.0.14 -c 1
PING 10.1.0.14 (10.1.0.14) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.1.0.14: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=3.24 ms
--- 10.1.0.14 ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 3.240/3.240/3.240/0.000 ms
root@www /home/abaobo/tmp 2015-08-22 21:01:11
#server_1中b租户的虚拟机测试结果在此不再详细列出
server_2中的具体测试结果在此不再详细给出
- 注: 有兴趣的读者可以尝试看下不同命名空间内的arp表,看看不同的变化。
总结
在前面的讲述的和测试用例中,我们用的IP都是手工分配的,目前还不曾涉及到DHCP分配IP地址的问题,
在我们的使用场景中,我们使用的是每一个端口IP地址都是固定的,这个端口我们可能把其绑定到不同宿主物理机的虚拟机上面,以及私有域内的DNS解析服务,
但是,每个用户的私有网络的网络地址空间可能重复,或者私有域名都可能重复,在接下来的一节中我们将讲述该服务实现的细节。