吴恩达机器学习第三次作业(python实现):多分类与神经网络
多分类
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.io import loadmat
from scipy.optimize import minimize
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
"""
每个训练样本是一个20x20的图像
原始数据是一个字典,字典中的X的shape是(5000,400),y的shape是(5000,1)
X的每一行代表一个数字图像的特征向量(400维,一个像素占一维)
y(1,2,3···9,10)代表数字的值(1,2,3···9,0),共有5000个训练样本
"""
# 获取原始数据
def raw_data(path):
data=loadmat(path)
return data
# 随机生成一张图片
def random_an_image(x,y):
index=np.random.randint(0,5000)
image=x[index]
fig,ax=plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(20,20))
ax.matshow(image.reshape(20,20),cmap='gray_r')
print("this is",y[index])
plt.show()
# 随机生成100张图片
def random_100_image(x):
indexs=np.random.choice(x.shape[0],100)
images=x[indexs]
# 将显示幕布分成10行10列,每一份大小是20x20
fig,axs=plt.subplots(10,10,figsize=(20,20))
for row in range(10):
for col in range(10):
axs[row,col].matshow(images[row*10+col].reshape(20,20),cmap='gray_r')
plt.show()
def sigmoid(z):
return 1/(1+np.exp(-z))
# 代价函数
def cost_function(theta,x,y,lam):
m=x.shape[0]
first=(y.dot(np.log(sigmoid(x.dot(theta))))+(1-y).dot(np.log(1-sigmoid(x.dot(theta)))))/(-m)
theta_reg=theta[1:] # 不惩罚第一项
second=lam*(theta_reg.dot(theta_reg))/(2*m)
j=first+second
return j
# 梯度下降,只需求偏导数即可
def gradient_descent(theta,x,y,lam):
m=x.shape[0]
partial_first=((sigmoid(x.dot(theta))-y).T).dot(x)/m
partial_second=lam*theta/m
partial_second[0]=0
partial=partial_first+partial_second
return partial
# 生成theta矩阵,其中每一行代表一个数字的theta向量(401维),一共10个数字,所以一共10行
def one_to_all(x,y,lam,k):
theta_all=np.zeros((k,x.shape[1]))
# print(theta_all.shape) #(10,401)
for i in range(1,k+1):
# 获取每一个数字的y向量
y_i=np.array([1 if num==i else 0 for num in y])
# 逐个训练theta向量
theta_i=theta_all[i-1]
result=minimize(fun=cost_function,args=(x,y_i,lam),x0=theta_i,method='tnc',jac=gradient_descent)
# 合并theta向量
theta_all[i-1]=result.x
return theta_all
# 获得预测结果矩阵
def predict(theta_all,x):
h=sigmoid(x.dot(theta_all.T))
h_max=np.argmax(h,axis=1) # 获取h每一行的最大值元素下标
# 因为下标从0开始,所以加1
h_max=h_max+1
# print(h_max.shape) # (5000,)
return h_max
def main():
rawdata=raw_data('venv/lib/dataset/ex3data1.mat')
x1=rawdata['X']
x=np.c_[np.ones(x1.shape[0]),x1]
y=rawdata['y'].ravel() # 降维,方便之后计算
# print(x.shape,y.shape) # (5000, 401) (5000,)
# random_an_image(x1, y)
random_100_image(x1)
theta_all=one_to_all(x,y,1,10)
y_predict=predict(theta_all,x)
report=classification_report(y_predict,y)
print(report)
main()
随机100张图片

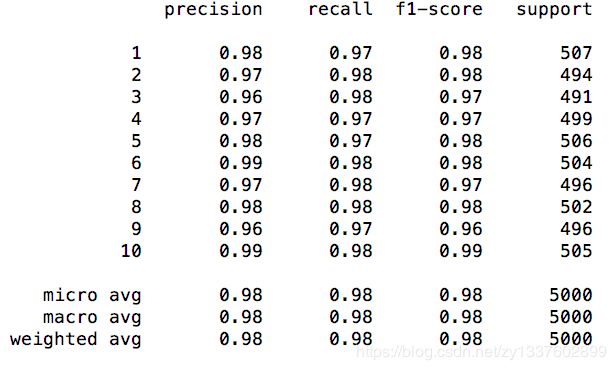
report结果,大概94%多的样子
关于report结果,如果不会看的话,看这里classification_report结果说明
神经网络
这里只做前向传播,权值已经给出
import numpy as np
from scipy.io import loadmat
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
"""
不需要计算权值,仅做前向传播
"""
def raw_data(path):
data=loadmat(path)
return data
def sigmoid(z):
return 1/(1+np.exp(-z))
def predict(y):
h_max=np.argmax(y,axis=1)
h_max=h_max+1
return h_max
def main():
rawdata=raw_data('venv/lib/dataset/ex3data1.mat')
weight=raw_data('venv/lib/dataset/ex3weights.mat')
x1=rawdata['X']
x=np.c_[np.ones(x1.shape[0]),x1]
y=rawdata['y'].ravel()
theta1=weight['Theta1']
theta2 = weight['Theta2']
# print(x.shape,y.shape,theta1.shape,theta2.shape) # (5000, 401) (5000,) (25, 401) (10, 26)
a1=x
z2=a1.dot(theta1.T)
a2=sigmoid(z2)
a2=np.c_[np.ones(a2.shape[0]),a2]
z3=a2.dot(theta2.T)
a3=sigmoid(z3)
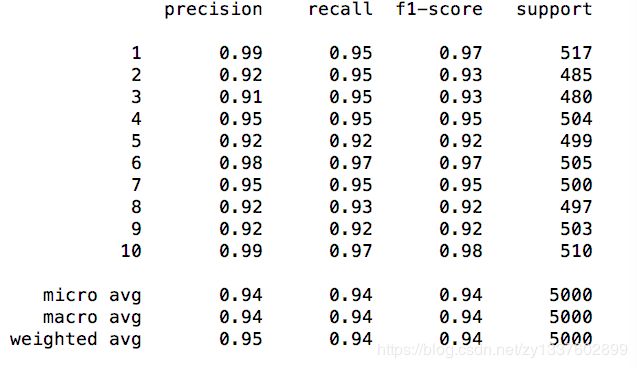
report=classification_report(predict(a3),y)
print(report)
main()