Text-CNN 文本分类
1.简介
TextCNN 是利用卷积神经网络对文本进行分类的算法,由 Yoon Kim 在 “Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification” 一文 (见参考[1]) 中提出. 是2014年的算法.
合理性:
深度学习模型在计算机视觉与语音识别方面取得了卓越的成就. 在 NLP 也是可以的.
卷积具有局部特征提取的功能, 所以可用 CNN 来提取句子中类似 n-gram 的关键信息.
2.参数与超参数
- sequence_length
Q: 对于CNN, 输入与输出都是固定的,可每个句子长短不一, 怎么处理?
A: 需要做定长处理, 比如定为n, 超过的截断, 不足的补0. 注意补充的0对后面的结果没有影响,因为后面的max-pooling只会输出最大值,补零的项会被过滤掉. - num_classes
多分类, 分为几类. - vocabulary_size
语料库的词典大小, 记为|D|. - embedding_size
将词向量的维度, 由原始的 |D| 降维到 embedding_size. - filter_size_arr
多个不同size的filter.
3.Embedding Layer
通过一个隐藏层, 将 one-hot 编码的词 投影 到一个低维空间中.
本质上是特征提取器,在指定维度中编码语义特征. 这样, 语义相近的词, 它们的欧氏距离或余弦距离也比较近.
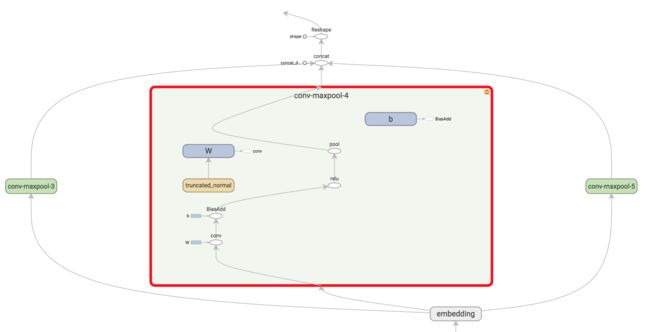
4.Convolution Layer
为不同尺寸的 filter 都建立一个卷积层. 所以会有多个 feature map.
图像是像素点组成的二维数据, 有时还会有RGB三个通道, 所以它们的卷积核至少是二维的.
从某种程度上讲, word is to text as pixel is to image, 所以这个卷积核的 size 与 stride 会有些不一样.
- xi x i
xi∈Rk x i ∈ R k , 一个长度为n的句子中, 第 i 个词语的词向量, 维度为k. - xi:j x i : j
xi:j=xi⊕xi+1⊕...⊕xj x i : j = x i ⊕ x i + 1 ⊕ . . . ⊕ x j
表示在长度为n的句子中, 第 [i,j] 个词语的词向量的拼接. - h h
卷积核所围窗口中单词的个数, 卷积核的尺寸其实就是 hk h k . - w w
w∈Rhk w ∈ R h k , 卷积核的权重矩阵. - ci c i
ci=f(w⋅xi:i+h−1+b) c i = f ( w ⋅ x i : i + h − 1 + b ) , 卷积核在单词i位置上的输出. b∈RK b ∈ R K , 是 bias. f f 是双曲正切之类的激活函数. - c=[c1,c2,...,cn−h+1] c = [ c 1 , c 2 , . . . , c n − h + 1 ]
filter在句中单词上进行所有可能的滑动, 得到的 feature map f e a t u r e m a p .
5.Max-Pooling Layer
max-pooling只会输出最大值, 对输入中的补0 做过滤.
6.SoftMax 分类 Layer
最后接一层全连接的 softmax 层,输出每个类别的概率。
7.小的变种
在 word representation 处理上会有一些变种.
- CNN-rand
设计好 embedding_size 这个 Hyperparameter 后, 对不同单词的向量作随机初始化, 后续BP的时候作调整. - static
拿 pre-trained vectors from word2vec, FastText or GloVe 直接用, 训练过程中不再调整词向量. 这也算是迁移学习的一种思想. - non-static
pre-trained vectors + fine tuning , 即拿word2vec训练好的词向量初始化, 训练过程中再对它们微调. - multiple channel
类比于图像中的RGB通道, 这里也可以用 static 与 non-static 搭两个通道来搞.
一些结果表明,max-pooling 总是优于 average-pooling ,理想的 filter sizes 是重要的,但具体任务具体考量,而用不用正则化似乎在NLP任务中并没有很大的不同。
8. Text CNN 的tf实现
参见[4], [6]. 挺详细的。
需要注意的细节有。
tf.nn.embedding_lookup() creates the actual embedding operation. The result of the embedding operation is a 3-dimensional tensor of shape [None, sequence_length, embedding_size].
TensorFlow’s convolutional conv2d operation expects a 4-dimensional tensor with dimensions corresponding to batch, width, height and channel. The result of our embedding doesn’t contain the channel dimension, so we add it manually, leaving us with a layer of shape [None, sequence_length, embedding_size, 1].
9. 与 LeNet 作比较
# LeNet5
conv1_weights = tf.get_variable(
"weight",
[CONV1_SIZE, CONV1_SIZE, NUM_CHANNELS, CONV1_DEEP],
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1))
tf.nn.conv2d(
input_tensor,
conv1_weights,
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1],
padding='SAME')
tf.nn.max_pool(
relu1,
ksize = [1,POOL1_SIZE,POOL1_SIZE,1],
strides=[1,POOL1_SIZE,POOL1_SIZE,1],
padding="SAME")#TextCNN
conv1_weights = tf.get_variable(
"weight",
[FILTER_SIZE, EMBEDDING_SIZE, 1, NUM_FILTERS],
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1))
tf.nn.conv2d(
self.embedded_chars_expanded,
conv1_weights,
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1],
padding="VALID")
tf.nn.max_pool(
h,
ksize=[1, SEQUENCE_LENGTH - FILTER_SIZE + 1, 1, 1],
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1],
padding='VALID')先来比较卷积
LeNet 的 filter 是正方形的, 且每一层都只用了同一种尺寸的卷积核. Text-CNN中, filter 是矩形, 矩形的长度有好几种, 一般取 (2,3,4), 而矩形的宽度是定长的, 同 word 的 embedding_size 相同. 每种尺寸都配有 NUM_FILTERS 个数目, 类比于LeNet中的output_depth,所以得到的feature_map是长条状, 宽度为1.
因为是卷积, 所以stride每个维度都是1.
再说池化层.
池化处理, 也叫下采样. 这里依旧可以对比 LeNet 网络.
LeNet 的 kernel 是正方形, 一般也是2*2等, 所以会把卷积后的feature_map尺寸缩小一半.
Text-CNN 的 kernel 依旧是长方形, 将整个feature_map 映射到一个点上. 一步到位, 只有一个池化层.
全连接层
都是多分类, 这一步的处理比较类似. 将池化后的矩阵 reshape为二维, 用 tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits() 计算损失.
10. TextCNN 论文中的网络结构
windows size 分别取 (3,4,5), 每个尺寸都会有100个filter.
3.1 Hyperparameters and Training
For all datasets we use: rectified linear units, filter
windows (h) of 3, 4, 5 with 100 feature maps each,
dropout rate (p) of 0.5, l2 constraint (s) of 3, and
mini-batch size of 50. These values were chosen
via a grid search on the SST-2 dev set.参考
- Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification
- Tensorflow版TextCNN主要代码解析
- Recurrent Neural Network for Text Classification with Multi-Task Learning
- implementing-a-cnn-for-text-classification-in-tensorflow
- understanding-convolutional-neural-networks-for-nlp
- textcnn实现-github