python 一个figure上显示多个图像
方法一:主要是inshow()函数的使用
首先基本的画图流程为:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#创建新的figure
fig = plt.figure()
#必须通过add_subplot()创建一个或多个绘图
#ax = fig.add_subplot(221)
#绘制2x2两行两列共四个图,编号从1开始
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(221)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(222)
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(223)
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(224)
#图片的显示
plt.show()然后就会有四个在同一张图上的figure
然后我们可以用python中的Matplotlib库中的,imshow()函数实现绘图。imshow()可以用来绘制热力图
#coding=utf-8
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
points = np.arange(-5,5,0.01)
xs,ys = np.meshgrid(points,points)
z = np.sqrt(xs**2 + ys**2)
#创建新的figure
fig = plt.figure()
#绘制2x2两行两列共四个图,编号从1开始
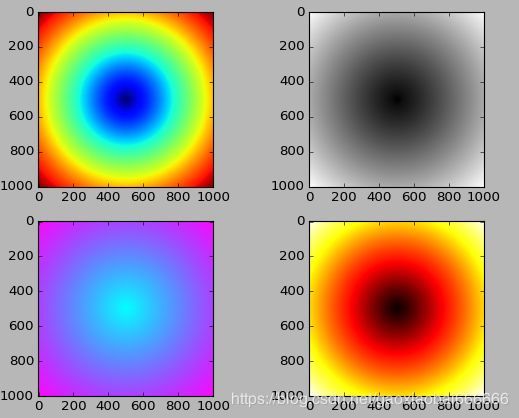
ax = fig.add_subplot(221)
ax.imshow(z)
ax = fig.add_subplot(222)
#使用自定义的colormap(灰度图)
ax.imshow(z,cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax = fig.add_subplot(223)
#使用自定义的colormap
ax.imshow(z,cmap=plt.cm.cool)
ax = fig.add_subplot(224)
#使用自定义的colormap
ax.imshow(z,cmap=plt.cm.hot)
#图片的显示
plt.show()方法二:subplot的使用,在python中,可以用subplot绘制子图。
常用方法:pl.subplot(121)第一个1代表1行,第二个2代表两列,第三个1代表第一个图。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
演示二维插值。
"""
import numpy as np
from scipy import interpolate
import pylab as pl
import matplotlib as mpl
def func(x, y):
return (x+y)*np.exp(-5.0*(x**2 + y**2))
# X-Y轴分为15*15的网格
y,x= np.mgrid[-1:1:15j, -1:1:15j]
fvals = func(x,y) # 计算每个网格点上的函数值 15*15的值
print len(fvals[0])
#三次样条二维插值
newfunc = interpolate.interp2d(x, y, fvals, kind='cubic')
# 计算100*100的网格上的插值
xnew = np.linspace(-1,1,100)#x
ynew = np.linspace(-1,1,100)#y
fnew = newfunc(xnew, ynew)#仅仅是y值 100*100的值
# 绘图
# 为了更明显地比较插值前后的区别,使用关键字参数interpolation='nearest'
# 关闭imshow()内置的插值运算。
pl.subplot(121)
im1=pl.imshow(fvals, extent=[-1,1,-1,1], cmap=mpl.cm.hot, interpolation='nearest', origin="lower")#pl.cm.jet
#extent=[-1,1,-1,1]为x,y范围 favals为
pl.colorbar(im1)
pl.subplot(122)
im2=pl.imshow(fnew, extent=[-1,1,-1,1], cmap=mpl.cm.hot, interpolation='nearest', origin="lower")
pl.colorbar(im2)
pl.show() 以上的代码为二维插值中画图的演示。绘图如下: