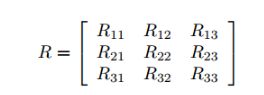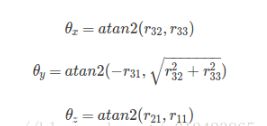欧拉角和旋转矩阵相互转换
(一)变换矩阵/F/H的svd分解或者旋转矩阵、平移矩阵求解
(二)欧拉角和旋转矩阵可同样表示刚体在三维空间的旋转,下面分享这两者互相转换的方法和核心代码
- 欧拉角转旋转矩阵
欧拉角通过将刚体绕过原点的轴(i,j,k)旋转θ,分解成三步,如下图(蓝色是起始坐标系,而红色的是旋转之后的坐标系)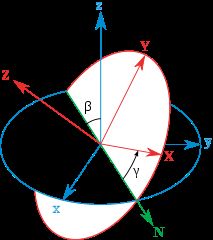
如果将每一个角度用旋转矩阵表示如下: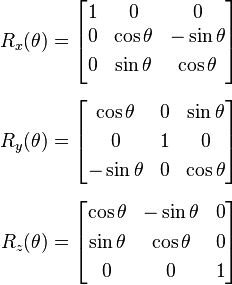
所以,容易得到,欧拉角转旋转矩阵如下: 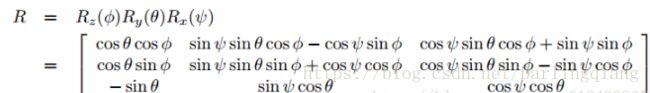
代码
- 欧拉角转旋转矩阵
/**
欧拉角计算对应的旋转矩阵
**/
Mat eulerAnglesToRotationMatrix(Vec3f &theta)
{
// 计算旋转矩阵的X分量
Mat R_x = (Mat_(3,3) <<
1, 0, 0,
0, cos(theta[0]), -sin(theta[0]),
0, sin(theta[0]), cos(theta[0])
);
// 计算旋转矩阵的Y分量
Mat R_y = (Mat_(3,3) <<
cos(theta[1]), 0, sin(theta[1]),
0, 1, 0,
-sin(theta[1]), 0, cos(theta[1])
);
// 计算旋转矩阵的Z分量
Mat R_z = (Mat_(3,3) <<
cos(theta[2]), -sin(theta[2]), 0,
sin(theta[2]), cos(theta[2]), 0,
0, 0, 1);
// 合并
Mat R = R_z * R_y * R_x;
return R;
} - 旋转矩阵转欧拉角
/*** 功能: 检查是否是旋转矩阵**/
bool isRotationMatrix(Mat &R)
{
Mat Rt;
transpose(R, Rt);
Mat shouldBeIdentity = Rt * R;
Mat I = Mat::eye(3,3, shouldBeIdentity.type());
return norm(I, shouldBeIdentity) < 1e-6;
}
/**
* 功能: 通过给定的旋转矩阵计算对应的欧拉角**/
Vec3f rotationMatrixToEulerAngles(Mat &R)
{
assert(isRotationMatrix(R));
float sy = sqrt(R.at(0,0) * R.at(0,0) + R.at(1,0) * R.at(1,0) );
bool singular = sy < 1e-6; // If
float x, y, z;
if (!singular) {
x = atan2(R.at(2,1) , R.at(2,2));
y = atan2(-R.at(2,0), sy);
z = atan2(R.at(1,0), R.at(0,0));
} else {
x = atan2(-R.at(1,2), R.at(1,1));
y = atan2(-R.at(2,0), sy);
z = 0;
}
return Vec3f(x, y, z);
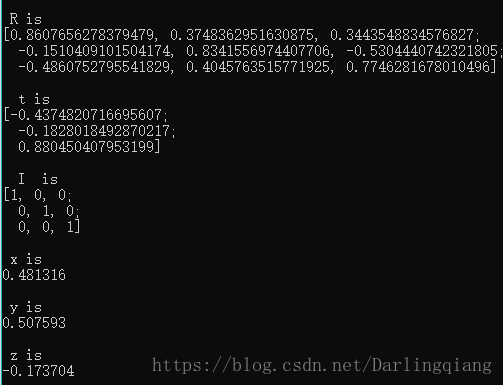
} 程序运行结果展示:
参考
1. 欧拉角详解
暂做记录,后续补充