pandas 计算工具
统计函数
增长率pct_change
序列(Series)、数据框(DataFrame)和Panel(面板)都有pct_change方法来计算增长率(需要先使用fill_method来填充空值)
Series.pct_change(periods=1, fill_method=’pad’, limit=None, freq=None, **kwargs)
periods参数控制步长
In [1]: ser = pd.Series(np.random.randn(8))
In [2]: ser.pct_change()
Out[2]:
0 NaN
1 -1.602976
2 4.334938
3 -0.247456
4 -2.067345
5 -1.142903
6 -1.688214
7 -9.759729
dtype: float64协方差Covariance
序列Series对象有cov方法来计算协方差
Series.cov(other, min_periods=None)
In [5]: s1 = pd.Series(np.random.randn(1000))
In [6]: s2 = pd.Series(np.random.randn(1000))
In [7]: s1.cov(s2)
Out[7]: 0.00068010881743108746数据框DataFrame对象的cov方法
DataFrame.cov(min_periods=None)
In [8]: frame = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(1000, 5), columns=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'])
In [9]: frame.cov()
Out[9]:
a b c d e
a 1.000882 -0.003177 -0.002698 -0.006889 0.031912
b -0.003177 1.024721 0.000191 0.009212 0.000857
c -0.002698 0.000191 0.950735 -0.031743 -0.005087
d -0.006889 0.009212 -0.031743 1.002983 -0.047952
e 0.031912 0.000857 -0.005087 -0.047952 1.042487相关系数Correlation
相关系数有三种计算方法
| Method name | Description |
|---|---|
| pearson?(default) | Standard correlation coefficient |
| kendall | Kendall Tau correlation coefficient |
| spearman | Spearman rank correlation coefficient |
Series.corr(other, method=’pearson’, min_periods=None)
DataFrame.corr(method=’pearson’, min_periods=1)
In [15]: frame = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(1000, 5), columns=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'])
In [19]: frame.corr()
Out[19]:
a b c d e
a 1.000000 0.013479 -0.049269 -0.042239 -0.028525
b 0.013479 1.000000 -0.020433 -0.011139 0.005654
c -0.049269 -0.020433 1.000000 0.018587 -0.054269
d -0.042239 -0.011139 0.018587 1.000000 -0.017060
e -0.028525 0.005654 -0.054269 -0.017060 1.000000DataFrame.corrwith(other, axis=0, drop=False)
数据排名
Series.rank(axis=0, method=’average’, numeric_only=None, na_option=’keep’, ascending=True, pct=False)
In [31]: s = pd.Series(np.random.np.random.randn(5), index=list('abcde'))
In [32]: s['d'] = s['b'] # so there's a tie
In [33]: s.rank()
Out[33]:
a 5.0
b 2.5
c 1.0
d 2.5
e 4.0
dtype: float64DataFrame.rank(axis=0, method=’average’, numeric_only=None, na_option=’keep’, ascending=True, pct=False)
axis=0则是按行排序,axis=1按列排序
ascending=True为升序,False为降序
In [34]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.np.random.randn(10, 6))
In [35]: df[4] = df[2][:5] # some ties
In [36]: df
Out[36]:
0 1 2 3 4 5
0 -0.904948 -1.163537 -1.457187 0.135463 -1.457187 0.294650
1 -0.976288 -0.244652 -0.748406 -0.999601 -0.748406 -0.800809
2 0.401965 1.460840 1.256057 1.308127 1.256057 0.876004
3 0.205954 0.369552 -0.669304 0.038378 -0.669304 1.140296
4 -0.477586 -0.730705 -1.129149 -0.601463 -1.129149 -0.211196
5 -1.092970 -0.689246 0.908114 0.204848 NaN 0.463347
6 0.376892 0.959292 0.095572 -0.593740 NaN -0.069180
7 -1.002601 1.957794 -0.120708 0.094214 NaN -1.467422
8 -0.547231 0.664402 -0.519424 -0.073254 NaN -1.263544
9 -0.250277 -0.237428 -1.056443 0.419477 NaN 1.375064
In [37]: df.rank(1)
Out[37]:
0 1 2 3 4 5
0 4.0 3.0 1.5 5.0 1.5 6.0
1 2.0 6.0 4.5 1.0 4.5 3.0
2 1.0 6.0 3.5 5.0 3.5 2.0
3 4.0 5.0 1.5 3.0 1.5 6.0
4 5.0 3.0 1.5 4.0 1.5 6.0
5 1.0 2.0 5.0 3.0 NaN 4.0
6 4.0 5.0 3.0 1.0 NaN 2.0
7 2.0 5.0 3.0 4.0 NaN 1.0
8 2.0 5.0 3.0 4.0 NaN 1.0
9 2.0 3.0 1.0 4.0 NaN 5.0窗口函数
窗口函数介绍rolling
Series.rolling(window, min_periods=None, freq=None, center=False, win_type=None, on=None, axis=0)
window:移动窗口的大小
min_periods:??
center:是否在中间设置标签,默认False
win type=??
In [38]: s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(1000), index=pd.date_range('1/1/2000', periods=1000))
r = s.rolling(window=60)
In [42]: r
Out[42]: Rolling [window=60,center=False,axis=0]
In [43]: r.mean()
Out[43]:
2000-01-01 NaN
2000-01-02 NaN
2000-01-03 NaN
2000-01-04 NaN
2000-01-05 NaN
2000-01-06 NaN
2000-01-07 NaN
...
2002-09-20 -62.694135
2002-09-21 -62.812190
2002-09-22 -62.914971
2002-09-23 -63.061867
2002-09-24 -63.213876
2002-09-25 -63.375074
2002-09-26 -63.539734
Freq: D, dtype: float64
In [44]: s.plot(style='k--')
Out[44]: 0x7ff282080dd0>
In [45]: r.mean().plot(style='k')
Out[45]: 0x7ff282080dd0> 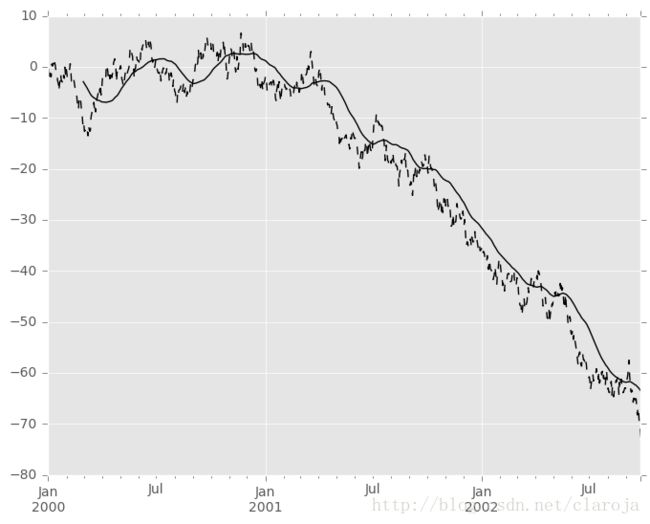
在数据框汇总将会作用于每一列
DataFrame.rolling(window, min_periods=None, freq=None, center=False, win_type=None, on=None, axis=0)
In [46]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(1000, 4),
....: index=pd.date_range('1/1/2000', periods=1000),
....: columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'])
....:
In [47]: df = df.cumsum()
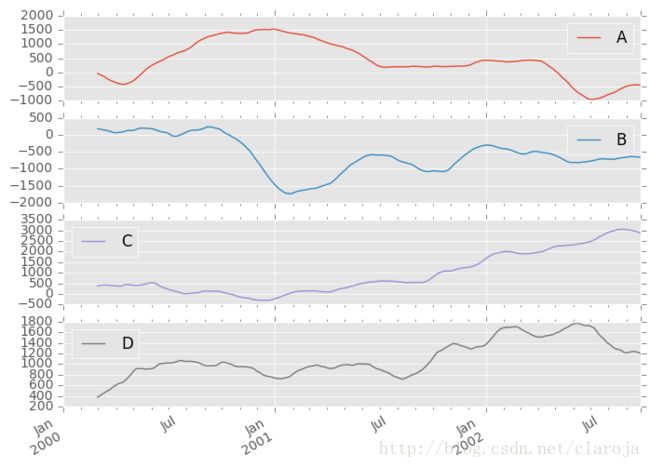
In [48]: df.rolling(window=60).sum().plot(subplots=True)计算方法总结
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| count() | Number of non-null observations |
| sum() | Sum of values |
| mean() | Mean of values |
| median() | Arithmetic median of values |
| min() | Minimum |
| max() | Maximum |
| std() | Bessel-corrected sample standard deviation |
| var() | Unbiased variance |
| skew() | Sample skewness (3rd moment) |
| kurt() | Sample kurtosis (4th moment) |
| quantile() | Sample quantile (value at %) |
| apply() | Generic apply |
| cov() | Unbiased covariance (binary) |
| corr() | Correlation (binary) |
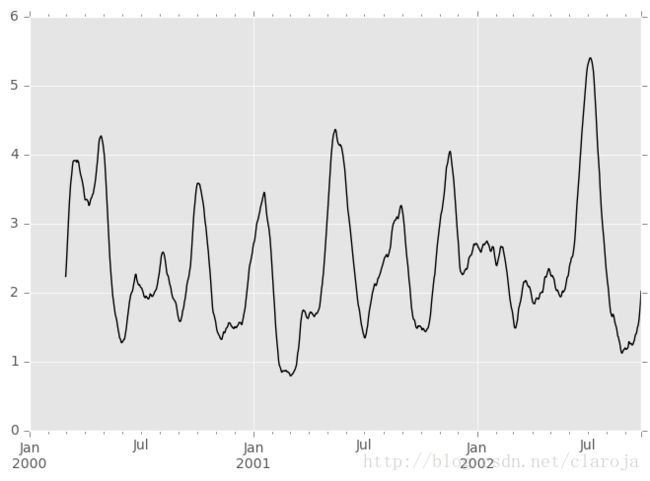
apply()方法可以应用在滚动窗口中。apply()的参数函数必须是指产生一个值,假设我们需要计算均值绝对离差:
In [49]: mad = lambda x: np.fabs(x - x.mean()).mean()
In [50]: s.rolling(window=60).apply(mad).plot(style='k')