普林斯顿算法课Part 1 Week 1 Analysis of Algorithms
1. Observations
例子:3-SUM
给定N个不同的integer,取三个相加之和为0的有多少种组合。
% more 8ints.txt
8
30 -40 -20 -10 40 0 10 5
% java ThreeSum 8ints.txt
4存在如下几种组合:
30 -40 10
30 -20 -10
-40 40 0
-10 0 10
1.1 3-SUM: brute-force algorithm
public class ThreeSum
{
public static int count(int[] a)
{
int N = a.length;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = i+1; j < N; j++)
for (int k = j+1; k < N; k++)
if (a[i] + a[j] + a[k] == 0)
count++;
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] a = In.readInts(args[0]);
StdOut.println(count(a));
}
}1.2 度量运行时间
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] a = In.readInts(args[0]);
Stopwatch stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
StdOut.println(ThreeSum.count(a));
double time = stopwatch.elapsedTime();
}1.3 经验分析:记录不同输入大小所耗时间
| N | time (seconds) |
|---|---|
| 250 | 0.0 |
| 500 | 0.0 |
| 1,000 | 0.1 |
| 2,000 | 0.8 |
| 4,000 | 6.4 |
| 8,000 | 51.1 |
| 16,000 | ? |

由此得到 T(N)=1.006×10–10×N2.999 T ( N ) = 1.006 × 10 – 10 × N 2.999
1.4 Doubling hypothesis:快速估计指数b的方法
| N | time (seconds) | ratio | lg ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250 | 0.0 | – | |
| 500 | 0.0 | 4.8 | 2.3 |
| 1,000 | 0.1 | 6.9 | 2.8 |
| 2,000 | 0.8 | 7.7 | 2.9 |
| 4,000 | 6.4 | 8.0 | 3.0 |
| 8,000 | 51.1 | 8.0 | 3.0 |
得到b之后可以代入 T(N)=aNb T ( N ) = a N b 求得a。
但注意这种方法无法用来估计存在对数关系的计算复杂度。
2. Mathematical models
总运行时间 = sum of cost × frequency for all operations.
・Need to analyze program to determine set of operations.
・Cost depends on machine, compiler.
・Frequency depends on algorithm, input data.
2.1 例子:1-Sum
How many instructions as a function of input size N ?
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
if (a[i] == 0)
count++;| operation | frequency |
|---|---|
| variable declaration | 2 |
| assignment statement | 2 |
| less than compare | N + 1 |
| equal to compare | N |
| array access | N |
| increment | N to 2 N |
2.2 例子:2-Sum
How many instructions as a function of input size N ?
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = i+1; j < N; j++)
if (a[i] + a[j] == 0)
count++;| operation | frequency |
|---|---|
| variable declaration | 3 |
| assignment statement | 3 |
| less than compare | N+1+(N+N−1+N−2+...+1)=N+1+(N+1)∗N2=(N+1)∗(N+2)2 N + 1 + ( N + N − 1 + N − 2 + . . . + 1 ) = N + 1 + ( N + 1 ) ∗ N 2 = ( N + 1 ) ∗ ( N + 2 ) 2 |
| equal to compare | N−1+N−2+...+1=N∗(N−1)2 N − 1 + N − 2 + . . . + 1 = N ∗ ( N − 1 ) 2 |
| array access | N−1+N−2+...+1=N∗(N−1) N − 1 + N − 2 + . . . + 1 = N ∗ ( N − 1 ) |
| increment | N+N−1+N−2+...+1=N+(N+1)∗(N+2)2toN+N∗(N−1) N + N − 1 + N − 2 + . . . + 1 = N + ( N + 1 ) ∗ ( N + 2 ) 2 t o N + N ∗ ( N − 1 ) |
然而上面这种计数每一个operation的方式非常麻烦,所以可以采用一些简化操作。
2.3 Simplification 1: cost model
Cost model. Use some basic operation as a proxy for running time
比如这里只看进行了多少次array access操作
2.4 Simplification 2: tilde notation
Estimate running time (or memory) as a function of input size N.
Ignore lower order terms.
- when N is large, terms are negligible
- when N is small, we don’t care
抹掉低阶项
| operation | frequency | tilde notation |
|---|---|---|
| variable declaration | N + 2 | ~ N |
| assignment statement | N + 2 | ~ N |
| less than compare | ½ (N + 1) (N + 2) | ~ ½ N2 |
| equal to compare | ½ N (N − 1) | ~ ½ N2 |
| array access | N (N − 1) | ~ N2 |
| increment | ½ N (N − 1) to N (N − 1) | ~ ½ N2 to ~ N2 |
2.5 3-Sum
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = i+1; j < N; j++)
for (int k = j+1; k < N; k++)
if (a[i] + a[j] + a[k] == 0)
count++;3. Order-of-growth classifications
logN,N,NlogN,N2,N3,2N l o g N , N , N l o g N , N 2 , N 3 , 2 N
3.1 Binary search
给定一个有序的数组,和一个key,在数组中找到这个key的index。
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int key)
{
int lo = 0, hi = a.length-1;
while (lo <= hi)
{
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
if (key < a[mid]) hi = mid - 1;
else if (key > a[mid]) lo = mid + 1;
else return mid;
}
return -1;
}Binary search uses at most 1+lgN 1 + l g N key compares to search in
a sorted array of size N.
3.2 An N2logN N 2 l o g N algorithm for 3-SUM
前面我们写了一个order of growth是 N3 N 3 的3-Sum算法,因为我们选择遍历N所有的3个的组合,并挨个判断是否和为0。在有了Binary Search后,一个将这个算法的order of growth降低到 N2logN N 2 l o g N 的方法是:
1. 首先将输入的数组进行排序,insertion sort的order of growth为 N2 N 2
2. 然后遍历数组两个的组合,即两层循环, N2 N 2 ,每一次使用binary search查找两个数字之和的负数, lgN l g N 的order of growth,因此共 N2lgN N 2 l g N
4. Theory of algorithms

Common mistake. Interpreting big-Oh as an approximate model
5. Memory
5.1 Basics
Bit. 0 or 1.
Byte. 8 bits.
Megabyte (MB). 1 million or 220 bytes.
Gigabyte (GB). 1 billion or 230 bytes.
常见数据类型的内存占用:

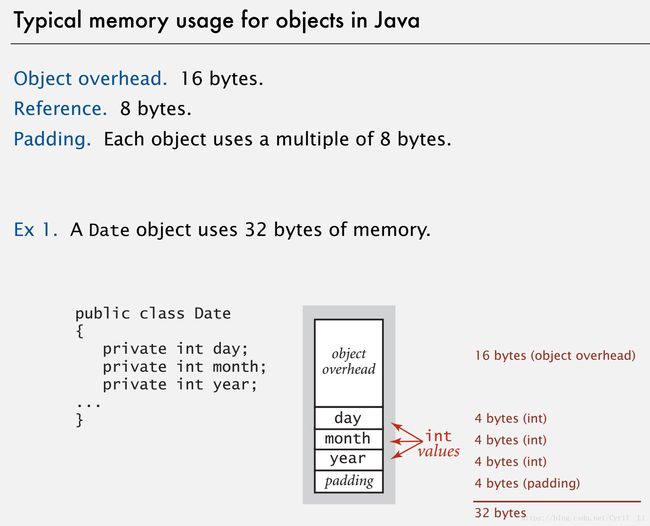
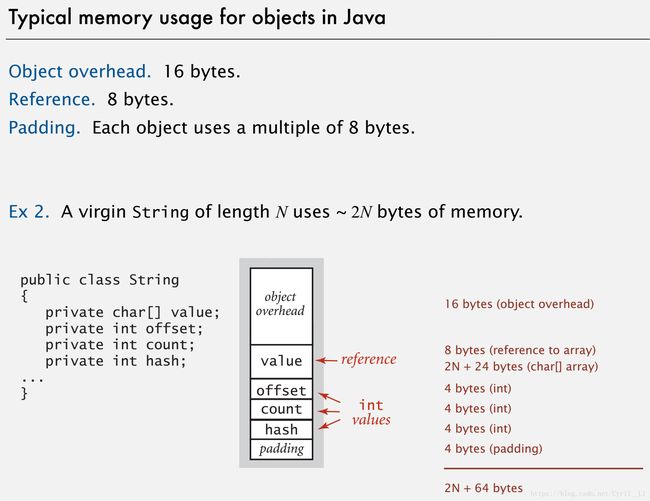
Java Object的内存占用计算:
Object overhead,每个primitive type占用的内存,Object内的array记得还要加上reference的占用,最后加起来的占用要进行padding变成8 bytes的倍数