基于tensorflow_gpu 1.9.0实现的第三个神经网络:对波士顿的房价预测(回归问题)
示例来源于Tensorflow的官方教程。
基于tensorflow_gpu 1.9.0实现的第三个神经网络:对波士顿的房价预测(回归问题),代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
print(tf.__version__)
boston_housing = keras.datasets.boston_housing
(train_data, train_labels), (test_data, test_labels) = boston_housing.load_data()
# Shuffle the training set
order = np.argsort(np.random.random(train_labels.shape))
train_data = train_data[order]
train_labels = train_labels[order]
# The dataset contains 13 different features:
# Per capita crime rate.
# The proportion of residential land zoned for lots over 25,000 square feet.
# The proportion of non-retail business acres per town.
# Charles River dummy variable (= 1 if tract bounds river; 0 otherwise).
# Nitric oxides concentration (parts per 10 million).
# The average number of rooms per dwelling.
# The proportion of owner-occupied units built before 1940.
# Weighted distances to five Boston employment centers.
# Index of accessibility to radial highways.
# Full-value property-tax rate per $10,000.
# Pupil-teacher ratio by town.
# 1000 * (Bk - 0.63) ** 2 where Bk is the proportion of Black people by town.
# Percentage lower status of the population.
# Each one of these input data features is stored using a different scale. Some
# features are represented by a proportion between 0 and 1, other features are
# ranges between 1 and 12, some are ranges between 0 and 100, and so on. This is
# often the case with real-world data, and understanding how to explore and
# clean such data is an important skill to develop.
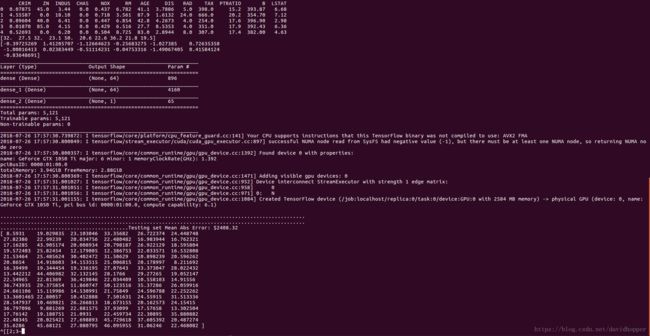
print("Training set: {}".format(train_data.shape)) # 404 examples, 13 features
print("Testing set: {}".format(test_data.shape)) # 102 examples, 13 features
print(train_data[0])
column_names = ['CRIM', 'ZN', 'INDUS', 'CHAS', 'NOX', 'RM', 'AGE', 'DIS', 'RAD',
'TAX', 'PTRATIO', 'B', 'LSTAT']
df = pd.DataFrame(train_data, columns=column_names)
print(df.head())
print(train_labels[0:10]) # Display first 10 entries.
# Normalize features
# Test data is *not* used when calculating the mean and std.
mean = train_data.mean(axis=0)
std = train_data.std(axis=0)
train_data = (train_data - mean) / std
test_data = (test_data - mean) / std
print(train_data[0]) # First training sample, normalized.
# Create the model
def build_model():
model = keras.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(64, activation=tf.nn.relu,
input_shape=(train_data.shape[1], )),
keras.layers.Dense(64, activation=tf.nn.relu),
keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
optimizer = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(0.001)
model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=optimizer, metrics=['mae'])
return model
model = build_model()
model.summary()
# Train the model
# Display training progress by printing a single dot for each completed epoch.
class PrintDot(keras.callbacks.Callback):
def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs):
if epoch % 100 == 0:
print('')
print('.', end='')
# The patience parameter is the amount of epochs to check for improvement.
early_stop = keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', patience=20)
EPOCHS = 500
# Store training stats
history = model.fit(train_data, train_labels, epochs=EPOCHS,
validation_split=0.2, verbose=0,
callbacks=[early_stop, PrintDot()])
# Evaluate the model
[loss, mae] = model.evaluate(test_data, test_labels, verbose=0)
print("Testing set Mean Abs Error: ${:7.2f}".format(mae * 1000))
# Predict
test_predictions = model.predict(test_data).flatten()
print(test_predictions)
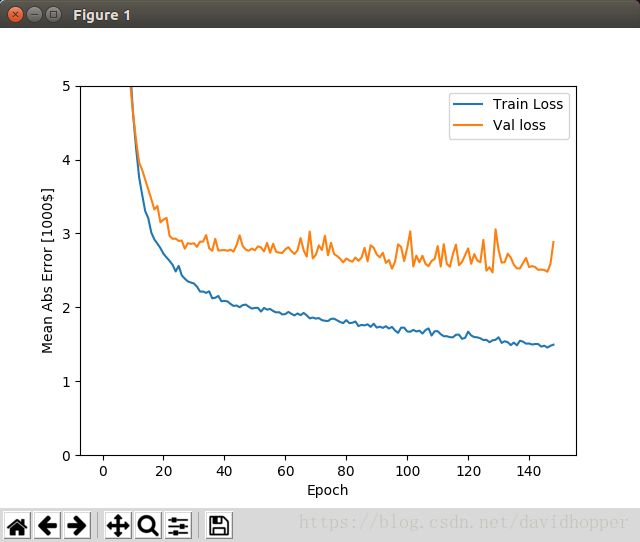
def plot_history(history):
plt.figure()
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Mean Abs Error [1000$]')
plt.plot(history.epoch, np.array(history.history['mean_absolute_error']),
label='Train Loss')
plt.plot(history.epoch, np.array(history.history['val_mean_absolute_error']),
label='Val loss')
plt.legend()
plt.ylim([0, 5])
plt.show()
plot_history(history)
运行该程序之前,需要先根据我的另一篇博客《Ubuntu 16.04安装tensorflow_gpu 1.9.0的方法》,安装tensorflow_gpu 1.9.0,然后安装numpy、pandas、matplotlib等工具包,此外还需要安装python-tk,命令如下:
sudo pip install numpy
sudo pip install pandas
sudo pip install matplotlib
sudo apt-get install python-tk