1、thinkphp访问路径拆解
路径:http://www.yftest.com / index.php / admin / test / index
域名· 入口文件 模块 controller action
2、不同的controller之间的访问
不同controller之间方法的访问有三个方法
方法一:使用命名空间
php namespace app\admin\controller; use think\Controller; class Index extends Controller{ public function Index() { //方法一 $test = new \app\admin\controller\Test(); return $test->index(); //也可写作以下写法 return call_user_func([new \app\admin\controller\Test(), 'index']); } }
方法二:使用use的方式
php namespace app\admin\controller; use think\Controller; use app\admin\controller\Test; class Index extends Controller{ public function Index() { //方法二 $test = new Test(); return $test->index(); //也可写作以下写法 return call_user_func([new Test(), 'index']); } }
方法三:使用thinkphp的内置方法
php namespace app\admin\controller; use think\Controller; class Index extends Controller{ public function Index() { //方法三 $test = controller('index/Index'); return $test->index(); return call_user_func([controller('index/Index'), 'index']); //以上表示的是在index模块下的Index控制器里的index这个方法,直接实例化好的 } }
3、调用当前控制器里的方法
php namespace app\admin\controller; use think\Controller; class Index extends Controller{ public function Index() { //方法一 常用 return $this->check(); // //方法二 return self::check(); // //方法三 return Index::check(); // //方法四 常用 return action('check'); } public function check() { return 'this is check page'; } }
如果是跨模块,那么可以使用第四种方法,如下
php namespace app\admin\controller; use think\Controller; class Index extends Controller{ public function Index() { //表示模块/controller/action return action('index/Index/index'); } }
4、thinkphp配置
a、惯例配置
目录:thinkphp\convention.php
读取:config('name'); 以及 \think\Config::get('name') 来获取
注意:惯例配置一般不建议修改
php namespace app\admin\controller; use think\Controller; use think\Config; class Index extends Controller{ public function Index() { //方法一 return config('name'); //方法二 return Config::get('name');
//如果是一个数组,那么可以用以下方法访问
return Config::get('name.prop') //表示是name这个数组下面的prop属性,用方法一也是一样的
} }
php namespace app\admin\controller; use think\Controller; use think\Config; class Index extends Controller{ public function Index() { //判断是否有name这个配置 dump(Config::has('name')); //设置值 Config::set('name', 'haha'); dump(Config::get('name')); //判断是否存在cookie这个配置 dump(config('?cookie')); //设置值 config('name', 'are you ok???'); dump(config('name')); } }
b、应用配置
目录:application\config.php
读取:同惯例配置一样
c、扩展配置
扩展配置其实就是对配置文件进行分目录的管理
目录:application\database.php;
读取:方法同上,如果读取database里的配置用config('database.password');
添加自定义的配置文件
//在application下新建Php文件如extra.php里面的内容如下 return [ 'user' => [ 'name' => 'test', 'pass' => 123 ] ]; //在config.php中把return 改成 $config = [...]; //在config.php后面补充上两句代码 $extra = require_once(APP_PATH.'extra'.EXT); return array_merge($extra, $config); //就可正常使用了 注意顺序,要用$config覆盖自定义的
d、场景配置
目录:application\config.php
如何使用:
1、修改应用配置(...application\config.php)'app_status' => 'home';
2、在应用目录下(application)新建对应的home.php
3、在home.php中书写相关配置,内容示例如下:
php return [ 'database' => [ // 服务器地址 'hostname' => '127.0.0.1', // 数据库名 'database' => 'are you ok???', // 用户名 'username' => 'root', // 密码 'password' => 'haha', ] ];
e、模块配置
目录:application\模块名\ => 下面新建config.php
访问:同上面的访问方法一致
内容:如下示例
php return [ 'today' => 'today is good day' ];
f、动态配置
利用代码进行配置,方法与a点下的方法一致
以上的配置的覆盖顺序:惯例配置 =》 应用配置 =》 场景配置 =》 模块配置 =》 动态配置
g、环境变量配置
目录:在根据目录下新建文件.env 里面的内容如下
name = 'this is env test' [arr] //以下是数组里的值,注意,这里是不能设置中文的 type = 'arrtype' name = 'arrname'
获取:如下示例
php namespace app\admin\controller; use think\Controller; use think\Env; class Index extends Controller{ public function Index() { //获取普通值 return Env::get('name'); //获取数组里的值,这里是获取不到数组的全部值 return Env::get('arr.name'); } }
注意:Env::get('name', default)可以进行默认值设置,这样就可以在里面配置debug等常用配置,在config.php中引入think\Env进行引用
5、thinkphp路由
作用:1、有利于记忆;2、有利于SEO
进行Url美化的步骤(省略书写入口文件)
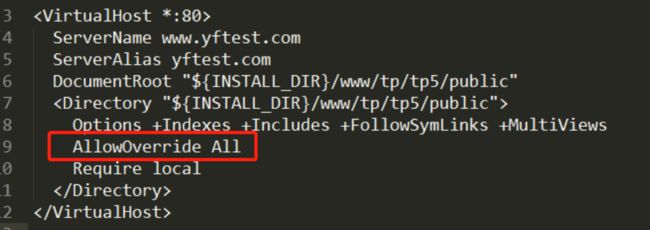
a、打开Apach下的httpd.conf下的重写配置
b、在apach下的httpd-vhosts.conf进行配置
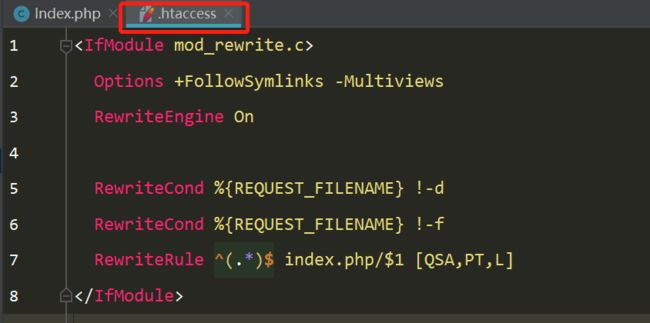
c、在thinkphp的public目录下添加.htacess文件
以上步骤便可以省略掉书写入口文件(但是后台系统不能省略入口文件的书写)
Url地址美化
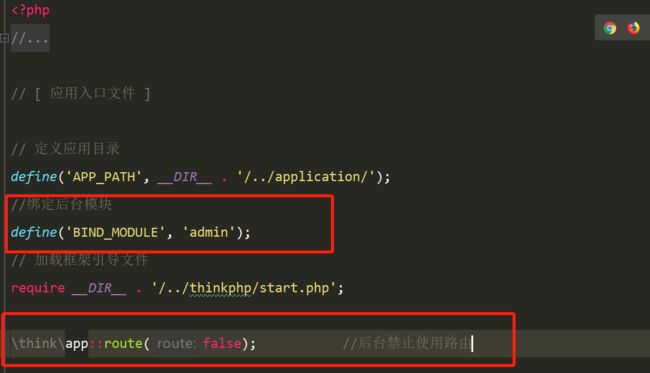
·1、添加一个后台的入口文件内容如下
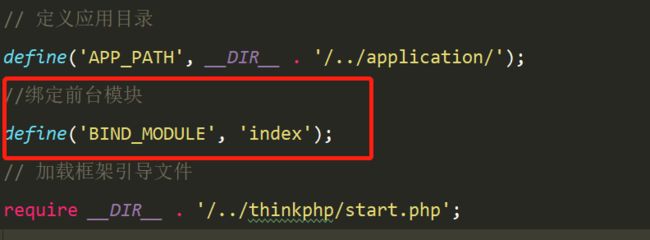
2、给前台的入口文件进行模块绑定
这样前台的访问地址就可以是www.yftest.com/index/index
6、thinkphp的路由模式
a、普通模式
定义:关闭路由,完全使用默认的PATH_INFO方式URL;
形式:http://www.yftest.com/admin.php/index/index;
设置:如下
// 是否开启路由 'url_route_on' => false, // 是否强制使用路由 'url_route_must' => false,
b、混合模式
定义:开启路由,可以使用路由,但也可以使用PATH_INFO方式URL;
设置:如下
// 是否开启路由 'url_route_on' => true, // 是否强制使用路由 'url_route_must' => false,
c、强制模式
定义:开启路由,只能使用路由
设置: 如下
// 是否开启路由 'url_route_on' => true, // 是否强制使用路由 'url_route_must' => true,
7、注册路由规则
a、动态单个注册
路由定义采用\think\Route类的rule方法注册,通常是在应用的路由配置文件 application\route.php进行注册格式是:
Route::rule('路由表达式',‘路由地址’,’请求类型‘,’路由参数(数组)‘,’变量规则(数组)‘)
静态地址路由
//在route.php文件中 use think\Route; Route::rule('/', 'index/index/index'); //表示当访问/的时候路由转到index/index/index这个地址下,注意:尽量写全,如有后台,怕混乱 Route::rule('test', 'index/index/test'); //表示当访问test的时候转到index/index/test这个地址下
带参数路由
//1、带一个参数 Route::rule('test/:id', 'index/index/test'); //表示当访问test的时候转到index/index/test并且传入的参数为id //2、带两个参数,如果设置两个参数,就必需带两个参数 Route::rule('time/:year/:month', 'index/index/time'); //3、可选参数的路由 Route::rule('time/:year/[:month]', 'index/index/time'); //4、全动态的路由,同时又有一个可选的,如果这种情况有一个与之前写的路由匹配的情况,那么会优先匹配之前的路由,所以不建议全动态操作 Route::rule(':a/[:b]', 'index/index/param'); //不建议使用 //5、完全匹配路由,也就是只能http://www.yftest.com/check进行访问,后面不能加任何的/...字符,否则会报错,如果需要全局设置需要开启route_complete_match = true Route::rule('check$', 'index/index/check'); //6、额外的带参数,注意:这种情况是不能用$_GET进行获取的,但是可以用input()进行获取 Route::rule('param', 'index/index/get?name=abc&age=20');
设置请求类型
tp中的请求类型:get,post,put,delete
tp路由默认支持所有的请求方式,为了安全考虑,可以对请求方式进行限制
//同时支持四种类型 Route::rule('type', 'index/index/type', 'get|post|put|delete'); //只支持get Route::rule('type', 'index/index/type', 'get'); Route::get('type', 'index/index/type'); //只支持post Route::rule('type', 'index/index/type', 'post'); Route::post('type', 'index/index/type'); //只支持Put Route::rule('type', 'index/index/type', 'put'); Route::put('type', 'index/index/type'); //只支持delete Route::rule('type', 'index/index/type', 'delete'); Route::delete('type', 'index/index/type'); //支持所有类型 Route::rule('type', 'index/index/type', '*'); Route::any('type', 'index/index/type');
注意:设置路由后就不能用Path_info方式访问了
b、动态批量注册(采用第一类的批量做法)
基本格式:
Route::rule([ '路由规则1' => '路由地址和参数', '路由规则2' => ['路由地址和参数', '匹配参数[数组]', '变量规则(数组)'] ... ], '', '请求类型', '匹配参数(数组)', '变量规则');
Route::rule([ 'test/:id' => 'index/index/test', 'time/:year/[:month]' => 'index/index/time' ], '', 'get'); Route::get([ 'param/:a/:b' => 'index/index/param', 'check' => 'index/index/check' ]);
c、定义文件形式注册
return [ 'test/:id' => 'index/index/test', 'time/:year/[:month]' => 'index/index/time', 'param/:a/:b' => 'index/index/param', 'check' => 'index/index/check' ];
use think\Route; Route::group('abc', [ 'blog' => 'index/blog/index', 'create/:id' => 'index/blog/create', ':id' => 'index/blog/post' ], ['method' => 'get'], ['id' => '\d{1,3}']); //上下两种情况是等价的 return [ '__pattern__' => [ 'id' => '\d{1,3}' ], '[abc]' => [ 'blog' => ['index/blog/index', ['method' => 'get']], //访问的地址是:http://www.yftest.com/abc/blog 'create/:id' => ['index/blog/create', ['method' => 'get']], //访问的址是:http://www.yftest.com/abc/create/123 ':id' => ['index/blog/post', ['method' => 'get']] //访问的地址是:http://www.yftest.com/abc/34 ] ];
//默认首页的路由可以做以下定义
return [ '[]' => [ '' => ['index/index', ['method' => 'get']], 'first' => ['index/first', ['method'=> 'get']] ] ];
8、路由参数变量规则
//以下路由只能用类似该地址访问 //http://www.yftest.com/param/12/abc.html Route::rule('param/:a/:b', 'index/index/param', 'get', ['method' => 'get', 'ext' => 'html'], ['a' => '\d{1,3}', 'b' => '\D{1,3}']);
9、miss路由
use think\Route; //一旦设置了MISS路由,相当于开启了强制路由模式 //当所有的路由规则都没有匹配到后,会路由到 public/miss路由地址。 Route::miss('index/index/test');
10、获取转化后的路由地址
//不带参数 url('index/index/param/12'); use think\Url; Url::build('index/index/param/13'); //带参数 url('index/index/param/12', ['id' => 'abc']); Url::build('index/index/param/13', ['id' => 'abc']);