RTP 使用 udp 进行数据传输,udp 是不能保证,数据包一定可以到达的,也不提供时序。同时还有 MTU 限制。
RTCP 用来配合 RTP 提供,传输报告,会话建立和退出。
一大批参考规范
1 * [RFC 1321](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc1321) - The MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm 2 * [RFC 1886](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc1886) - DNS Extensions to support IP version 6 3 * [RFC 2032](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2032) - RTP Payload Format for H.261 Video Streams 4 * [RFC 2616](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2616) - Hypertext Transfer Protocol -- HTTP/1.1 5 * [RFC 2617](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2617) - HTTP Authentication: Basic and Digest Access Authentication 6 * [RFC 2782](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2782) - A DNS RR for Specifying the Location of Services (DNS SRV) 7 * [RFC 2915](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2915) - The Naming Authority Pointer (NAPTR) DNS Resource Record 8 * [RFC 3261](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3261) - SIP: Session Initiation Protocol 9 * [RFC 3263](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3263) - Locating SIP Servers 10 * [RFC 3264](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3264) - An Offer/Answer Model with SDP 11 * [RFC 3265](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3265) - SIP-Specific Event Notification 12 * [RFC 3327](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3327) - SIP Extension Header Field for Registering Non-Adjacent Contacts 13 * [RFC 3428](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3428) - SIP Extension for Instant Messaging 14 * [RFC 3489](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3489) - STUN - Simple Traversal of UDP Through NATs 15 * [RFC 3515](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3515) - The SIP Refer Method 16 * [RFC 3550](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3550) - RTP: A Transport Protocol for Real-Time Applications 17 * [RFC 3551](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3551) - RTP Profile for Audio and Video Conferences with Minimal Control 18 * [RFC 3555](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3555) - MIME Type Registration of RTP Payload Formats 19 * [RFC 3556](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3556) - SDP Bandwidth Modifiers for RTCP Bandwidth 20 * [RFC 3581](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3581) - An Extension to SIP for Symmetric Response Routing 21 * [RFC 3605](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3605) - RTCP attribute in SDP 22 * [RFC 3711](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3711) - The Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP) 23 * [RFC 3969](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3969) - The IANA URI Parameter Registry for SIP 24 * [RFC 3994](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3994) - Indication of Message Composition for Instant Messaging 25 * [RFC 4346](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4346) - The TLS Protocol Version 1.1 26 * [RFC 4566](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4566) - SDP: Session Description Protocol 27 * [RFC 4582](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4582) - The Binary Floor Control Protocol (BFCP) 28 * [RFC 4582bis](https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-bfcpbis-rfc4582bis-08) - The Binary Floor Control Protocol (BFCP) 29 * [RFC 4585](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4585) - Extended RTP Profile for RTCP-Based Feedback 30 * [RFC 4733](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4733) - RTP Payload for DTMF Digits, Telephony Tones, and Teleph. Signals 31 * [RFC 4961](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4961) - Symmetric RTP / RTP Control Protocol (RTCP) 32 * [RFC 5118](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5118) - SIP Torture Test Messages for IPv6 33 * [RFC 5245](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5245) - Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE) 34 * [RFC 5389](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5389) - Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN) 35 * [RFC 5626](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5626) - Managing Client-Initiated Connections in SIP 36 * [RFC 5761](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5761) - Multiplexing RTP Data and Control Packets on a Single Port 37 * [RFC 5766](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5766) - Traversal Using Relays around NAT (TURN) 38 * [RFC 5768](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5768) - Indicating Support for ICE in SIP 39 * [RFC 5769](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5769) - Test vectors for STUN 40 * [RFC 5780](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5780) - NAT Behaviour Discovery Using STUN 41 * [RFC 6026](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6026) - Correct Transaction Handling for 2xx Resp. to SIP INVITE Requests 42 * [RFC 6156](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6156) - TURN Extension for IPv6 43 * [RFC 6188](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6188) - The Use of AES-192 and AES-256 in Secure RTP 44 * [RFC 6455](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6455) - The WebSocket Protocol 45 * [RFC 7159](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7159) - JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) 46 * [RFC 7350](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7350) - DTLS as Transport for STUN 47 * [RFC 7714](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7714) - AES-GCM Authenticated Encryption in SRTP
有几关键问题:
1,udp 怎么建立
2, 声音定时器多少时间传输入一次
3, 丢包问题 jitter buffer
下面使用 Wireshark 对比 Baresip 源码来进行分析。
/** * \page GenericAudioStream Generic Audio Stream * * Implements a generic audio stream. The application can allocate multiple * instances of a audio stream, mapping it to a particular SDP media line. * The audio object has a DSP sound card sink and source, and an audio encoder * and decoder. A particular audio object is mapped to a generic media * stream object. Each audio channel has an optional audio filtering chain. * ** write read * | /|\ * \|/ | * .------. .---------. .-------. * |filter|<--| audio |--->|encoder| * '------' | | |-------| * | object |--->|decoder| * '---------' '-------' * | /|\ * | | * \|/ | * .------. .-----. * |auplay| |ausrc| * '------' '-----' **/ /** * Audio transmit/encoder * * \verbatim Processing encoder pipeline: . .-------. .-------. .--------. .--------. .--------. | | | | | | | | | | | |O-->| ausrc |-->| aubuf |-->| resamp |-->| aufilt |-->| encode |---> RTP | | | | | | | | | | | ' '-------' '-------' '--------' '--------' '--------' \endverbatim * */ /** * Audio receive/decoder * \verbatim Processing decoder pipeline: .--------. .-------. .--------. .--------. .--------. |\ | | | | | | | | | | | |<--| auplay |<--| aubuf |<--| resamp |<--| aufilt |<--| decode |<--- RTP |/ | | | | | | | | | | '--------' '-------' '--------' '--------' '--------' \endverbatim */
RTCP 的端口号是 RTP 的端口号加1 。
libre 源码分析
1, 建立udp socket 非阻塞方式
2, 初始化 epoll 注册回调函数 udp_read()
3, 接收到数据 内核通知 epoll 调用 udp_read() 初始化 mbuf
4, call helpers 回调每一个注册的 helper
baresip 声音相关结构体:
1 /** Audio Source parameters */ 2 struct ausrc_prm { 3 uint32_t srate; /**< Sampling rate in [Hz] */ 4 uint8_t ch; /**< Number of channels */ 5 uint32_t ptime; /**< Wanted packet-time in [ms] */ 6 int fmt; /**< Sample format (enum aufmt) */ 7 };
打印的日志:alsa: reset: srate=8000, ch=1, num_frames=160, pcmfmt=S16_LE
默认 8000hz 1ch 10ms 16bit
8000*1*16/8/1000*10 = 160
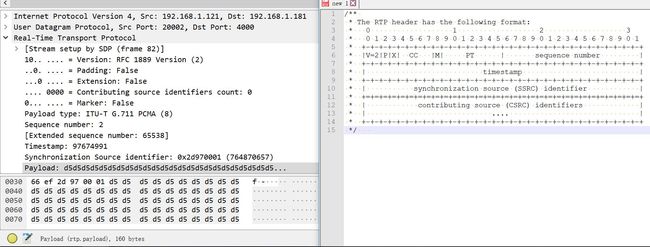
RTP 头信息
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3550#section-5.1
payload type 在这里看 https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3551#page-32
我把常用的给标了红色 PCMU PCMA G722 G729
PT encoding media type clock rate channels name (Hz) ___________________________________________________ 0 PCMU A 8,000 1 1 reserved A 2 reserved A 3 GSM A 8,000 1 4 G723 A 8,000 1 5 DVI4 A 8,000 1 6 DVI4 A 16,000 1 7 LPC A 8,000 1 8 PCMA A 8,000 1 9 G722 A 8,000 1 10 L16 A 44,100 2 11 L16 A 44,100 1 12 QCELP A 8,000 1 13 CN A 8,000 1 14 MPA A 90,000 (see text) 15 G728 A 8,000 1 16 DVI4 A 11,025 1 17 DVI4 A 22,050 1 18 G729 A 8,000 1
RTP 12个字节的头信息:
SSRC 以后就是 payload 。
开始的包:
刚一开始,Marker 是1 。
声音参数配置
8bit sample rate 8000 2 channel ,间隔 20ms 。
测试了基本可用,但回声,和同步,丢包还未实现。