前言
在Andrroid开发中,网络请求十分常用
而在Android网络请求库中,Retrofit是当下最热的一个网络请求库
今天,我将献上一份非常详细Retrofit v2.0的使用教程,希望你们会喜欢。
如果对Retrofit v2.0的源码感兴趣,可看文章:Android:手把手带你深入剖析 Retrofit 2.0 源码
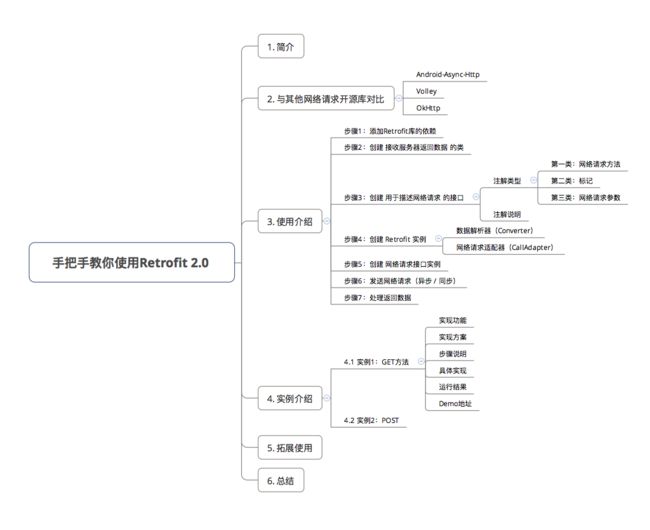
目录
1. 简介
特别注意:
准确来说,Retrofit 是一个 RESTful 的 HTTP 网络请求框架的封装。
原因:网络请求的工作本质上是 OkHttp 完成,而 Retrofit 仅负责 网络请求接口的封装
App应用程序通过 Retrofit 请求网络,实际上是使用 Retrofit 接口层封装请求参数、Header、Url 等信息,之后由 OkHttp 完成后续的请求操作
在服务端返回数据之后,OkHttp 将原始的结果交给 Retrofit,Retrofit根据用户的需求对结果进行解析
2. 与其他开源请求库对比
除了Retrofit,如今Android中主流的网络请求框架有:
Android-Async-Http
Volley
OkHttp
下面是简单介绍:
一图让你了解全部的网络请求库和他们之间的区别!
附:各个主流网络请求库的Github地址
Android-Async-Http
Volley
OkHttp
Retrofit
3. 使用介绍
使用 Retrofit 的步骤共有7个:
步骤1:添加Retrofit库的依赖
步骤2:创建 接收服务器返回数据 的类
步骤3:创建 用于描述网络请求 的接口
步骤4:创建 Retrofit 实例
步骤5:创建 网络请求接口实例 并 配置网络请求参数
步骤6:发送网络请求(异步 / 同步)
封装了 数据转换、线程切换的操作
步骤7: 处理服务器返回的数据
接下来,我们一步步进行讲解。
步骤1:添加Retrofit库的依赖
1. 在 Gradle加入Retrofit库的依赖
由于Retrofit是基于OkHttp,所以还需要添加OkHttp库依赖
build.gradle
dependencies { compile'com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:2.0.2'// Retrofit库compile'com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:3.1.2'// Okhttp库}
1
2
3
4
5
6
2. 添加 网络权限
AndroidManifest.xml
1
步骤2:创建 接收服务器返回数据 的类
Reception.java
public class Reception {...// 根据返回数据的格式和数据解析方式(Json、XML等)定义 // 下面会在实例进行说明 }
1
2
3
4
5
步骤3:创建 用于描述网络请求 的接口
Retrofit将 Http请求 抽象成 Java接口:采用 注解 描述网络请求参数 和配置网络请求参数
用 动态代理 动态 将该接口的注解“翻译”成一个 Http 请求,最后再执行 Http 请求
注:接口中的每个方法的参数都需要使用注解标注,否则会报错
GetRequest_Interface.interface
publicinterfaceGetRequest_Interface { @GET("openapi.do?keyfrom=Yanzhikai&key=2032414398&type=data&doctype=json&version=1.1&q=car") Call getCall();// @GET注解的作用:采用Get方法发送网络请求// getCall() = 接收网络请求数据的方法// 其中返回类型为Call<*>,*是接收数据的类(即上面定义的Translation类)// 如果想直接获得Responsebody中的内容,可以定义网络请求返回值为Call
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
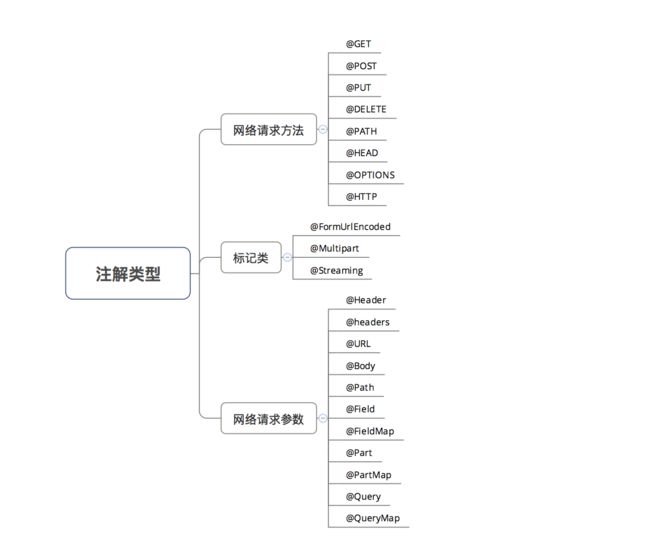
下面详细介绍Retrofit 网络请求接口 的注解类型。
注解类型
注解说明
第一类:网络请求方法
详细说明:
a. @GET、@POST、@PUT、@DELETE、@HEAD
以上方法分别对应 HTTP中的网络请求方式
publicinterfaceGetRequest_Interface { @GET("openapi.do?keyfrom=Yanzhikai&key=2032414398&type=data&doctype=json&version=1.1&q=car") Call getCall();// @GET注解的作用:采用Get方法发送网络请求// getCall() = 接收网络请求数据的方法// 其中返回类型为Call<*>,*是接收数据的类(即上面定义的Translation类)}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
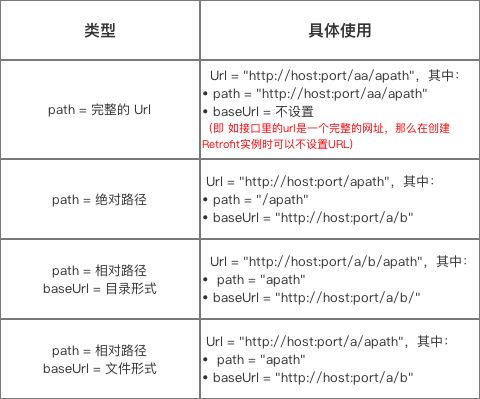
此处特意说明URL的组成:Retrofit把 网络请求的URL 分成了两部分设置:
// 第1部分:在网络请求接口的注解设置@GET("openapi.do?keyfrom=Yanzhikai&key=2032414398&type=data&doctype=json&version=1.1&q=car")Call getCall();// 第2部分:在创建Retrofit实例时通过.baseUrl()设置Retrofit retrofit =newRetrofit.Builder() .baseUrl("http://fanyi.youdao.com/")//设置网络请求的Url地址.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())//设置数据解析器.build();// 从上面看出:一个请求的URL可以通过 替换块 和 请求方法的参数 来进行动态的URL更新。// 替换块是由 被{}包裹起来的字符串构成// 即:Retrofit支持动态改变网络请求根目录
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
网络请求的完整 Url =在创建Retrofit实例时通过.baseUrl()设置 +网络请求接口的注解设置(下面称 “path“ )
具体整合的规则如下:
建议采用第三种方式来配置,并尽量使用同一种路径形式。
b. @HTTP
作用:替换@GET、@POST、@PUT、@DELETE、@HEAD注解的作用 及 更多功能拓展
具体使用:通过属性method、path、hasBody进行设置
publicinterfaceGetRequest_Interface{/**
* method:网络请求的方法(区分大小写)
* path:网络请求地址路径
* hasBody:是否有请求体
*/@HTTP(method ="GET", path ="blog/{id}", hasBody =false) Call getCall(@Path("id")intid);// {id} 表示是一个变量// method 的值 retrofit 不会做处理,所以要自行保证准确}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
第二类:标记
a. @FormUrlEncoded
作用:表示发送form-encoded的数据
每个键值对需要用@Filed来注解键名,随后的对象需要提供值。
b. @Multipart
作用:表示发送form-encoded的数据(适用于 有文件 上传的场景)
每个键值对需要用@Part来注解键名,随后的对象需要提供值。
具体使用如下:
GetRequest_Interface
public interface GetRequest_Interface {/**
*表明是一个表单格式的请求(Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded)
* Field("username") 表示将后面的 String name 中name的取值作为 username 的值
*/@POST("/form")@FormUrlEncodedCall testFormUrlEncoded1(@Field("username") String name,@Field("age") int age);/** * {@linkPart} 后面支持三种类型,{@linkRequestBody}、{@linkokhttp3.MultipartBody.Part} 、任意类型 * 除 {@linkokhttp3.MultipartBody.Part} 以外,其它类型都必须带上表单字段({@linkokhttp3.MultipartBody.Part} 中已经包含了表单字段的信息), */@POST("/form")@MultipartCall testFileUpload1(@Part("name") RequestBody name,@Part("age") RequestBody age,@PartMultipartBody.Part file);}// 具体使用GetRequest_Interface service = retrofit.create(GetRequest_Interface.class);// @FormUrlEncoded Call call1 = service.testFormUrlEncoded1("Carson",24);// @MultipartRequestBody name = RequestBody.create(textType,"Carson"); RequestBody age = RequestBody.create(textType,"24"); MultipartBody.Part filePart = MultipartBody.Part.createFormData("file","test.txt", file); Call call3 = service.testFileUpload1(name, age, filePart);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
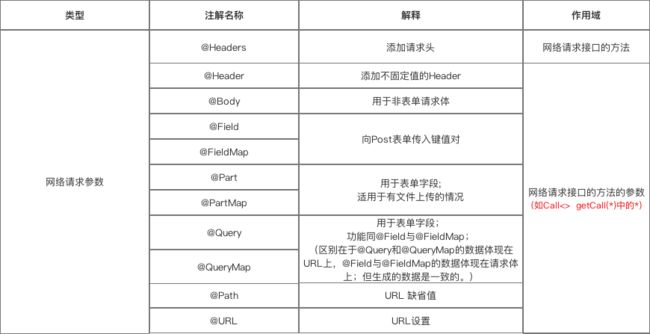
第三类:网络请求参数
详细说明
a. @Header & @Headers
作用:添加请求头 &添加不固定的请求头
具体使用如下:
// @Header@GET("user")Call getUser(@Header("Authorization") String authorization)// @Headers@Headers("Authorization: authorization")@GET("user")Call getUser()// 以上的效果是一致的。// 区别在于使用场景和使用方式// 1. 使用场景:@Header用于添加不固定的请求头,@Headers用于添加固定的请求头// 2. 使用方式:@Header作用于方法的参数;@Headers作用于方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
b. @Body
作用:以 Post方式 传递 自定义数据类型 给服务器
特别注意:如果提交的是一个Map,那么作用相当于 @Field
不过Map要经过 FormBody.Builder 类处理成为符合 Okhttp 格式的表单,如:
FormBody.Builderbuilder = new FormBody.Builder();builder.add("key","value");
1
2
3
c. @Field & @FieldMap
作用:发送 Post请求 时提交请求的表单字段
具体使用:与 @FormUrlEncoded 注解配合使用
publicinterfaceGetRequest_Interface{/**
*表明是一个表单格式的请求(Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded)
* Field("username") 表示将后面的 String name 中name的取值作为 username 的值
*/@POST("/form")@FormUrlEncodedCall testFormUrlEncoded1(@Field("username") String name,@Field("age")intage);/**
* Map的key作为表单的键
*/@POST("/form")@FormUrlEncodedCall testFormUrlEncoded2(@FieldMapMap map);}// 具体使用// @FieldCall call1 = service.testFormUrlEncoded1("Carson",24);// @FieldMap// 实现的效果与上面相同,但要传入MapMap map =newHashMap<>(); map.put("username","Carson"); map.put("age",24); Call call2 = service.testFormUrlEncoded2(map);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
d. @Part & @PartMap
作用:发送 Post请求 时提交请求的表单字段
与@Field的区别:功能相同,但携带的参数类型更加丰富,包括数据流,所以适用于 有文件上传 的场景
具体使用:与 @Multipart 注解配合使用
public interface GetRequest_Interface {/** * {@linkPart} 后面支持三种类型,{@linkRequestBody}、{@linkokhttp3.MultipartBody.Part} 、任意类型 * 除 {@linkokhttp3.MultipartBody.Part} 以外,其它类型都必须带上表单字段({@linkokhttp3.MultipartBody.Part} 中已经包含了表单字段的信息), */@POST("/form")@MultipartCall testFileUpload1(@Part("name") RequestBody name,@Part("age") RequestBody age,@PartMultipartBody.Part file);/** * PartMap 注解支持一个Map作为参数,支持 {@linkRequestBody } 类型, * 如果有其它的类型,会被{@linkretrofit2.Converter}转换,如后面会介绍的 使用{@linkcom.google.gson.Gson} 的 {@linkretrofit2.converter.gson.GsonRequestBodyConverter} * 所以{@linkMultipartBody.Part} 就不适用了,所以文件只能用@PartMultipartBody.Part */@POST("/form")@MultipartCall testFileUpload2(@PartMapMap args,@PartMultipartBody.Part file);@POST("/form")@MultipartCall testFileUpload3(@PartMapMap args);}// 具体使用MediaType textType = MediaType.parse("text/plain"); RequestBody name = RequestBody.create(textType,"Carson"); RequestBody age = RequestBody.create(textType,"24"); RequestBody file = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("application/octet-stream"),"这里是模拟文件的内容");// @PartMultipartBody.Part filePart = MultipartBody.Part.createFormData("file","test.txt", file); Call call3 = service.testFileUpload1(name, age, filePart); ResponseBodyPrinter.printResponseBody(call3);// @PartMap// 实现和上面同样的效果Map fileUpload2Args =newHashMap<>(); fileUpload2Args.put("name", name); fileUpload2Args.put("age", age);//这里并不会被当成文件,因为没有文件名(包含在Content-Disposition请求头中),但上面的 filePart 有//fileUpload2Args.put("file", file);Call call4 = service.testFileUpload2(fileUpload2Args, filePart);//单独处理文件ResponseBodyPrinter.printResponseBody(call4);}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
e. @Query和@QueryMap
作用:用于 @GET 方法的查询参数(Query = Url 中 ‘?’ 后面的 key-value)
如:url = http://www.println.net/?cate=android,其中,Query = cate
具体使用:配置时只需要在接口方法中增加一个参数即可:
@GET("/") Call cate(@Query("cate") String cate);}// 其使用方式同@Field与@FieldMap,这里不作过多描述
1
2
3
4
5
6
f. @Path
作用:URL地址的缺省值
具体使用:
publicinterfaceGetRequest_Interface{@GET("users/{user}/repos") Call getBlog(@Path("user") String user );// 访问的API是:https://api.github.com/users/{user}/repos// 在发起请求时, {user} 会被替换为方法的第一个参数 user(被@Path注解作用)}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
g. @Url
作用:直接传入一个请求的 URL变量 用于URL设置
具体使用:
publicinterfaceGetRequest_Interface{@GETCall testUrlAndQuery(@UrlString url,@Query("showAll")booleanshowAll);// 当有URL注解时,@GET传入的URL就可以省略// 当GET、POST...HTTP等方法中没有设置Url时,则必须使用 {@link Url}提供}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
汇总
步骤4:创建 Retrofit 实例
Retrofit retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder().baseUrl("http://fanyi.youdao.com/") // 设置网络请求的Url地址.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create()) // 设置数据解析器.addCallAdapterFactory(RxJavaCallAdapterFactory.create()) // 支持RxJava平台.build();
1
2
3
4
5
a. 关于数据解析器(Converter)
Retrofit支持多种数据解析方式
使用时需要在Gradle添加依赖
数据解析器Gradle依赖
Gsoncom.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:2.0.2
Jacksoncom.squareup.retrofit2:converter-jackson:2.0.2
Simple XMLcom.squareup.retrofit2:converter-simplexml:2.0.2
Protobufcom.squareup.retrofit2:converter-protobuf:2.0.2
Moshicom.squareup.retrofit2:converter-moshi:2.0.2
Wirecom.squareup.retrofit2:converter-wire:2.0.2
Scalarscom.squareup.retrofit2:converter-scalars:2.0.2
b. 关于网络请求适配器(CallAdapter)
Retrofit支持多种网络请求适配器方式:guava、Java8和rxjava
使用时如使用的是 Android 默认的 CallAdapter,则不需要添加网络请求适配器的依赖,否则则需要按照需求进行添加
Retrofit 提供的 CallAdapter
使用时需要在Gradle添加依赖:
网络请求适配器Gradle依赖
guavacom.squareup.retrofit2:adapter-guava:2.0.2
Java8com.squareup.retrofit2:adapter-java8:2.0.2
rxjavacom.squareup.retrofit2:adapter-rxjava:2.0.2
步骤5:创建 网络请求接口实例
// 创建 网络请求接口 的实例 GetRequest_Interface request = retrofit.create(GetRequest_Interface.class);//对 发送请求 进行封装Callcall= request.getCall();
1
2
3
4
5
步骤6:发送网络请求(异步 / 同步)
封装了 数据转换、线程切换的操作
//发送网络请求(异步)call.enqueue(newCallback() {//请求成功时回调@OverridepublicvoidonResponse(Call call, Response response) {//请求处理,输出结果response.body().show(); }//请求失败时候的回调@OverridepublicvoidonFailure(Call call, Throwable throwable) { System.out.println("连接失败"); } });// 发送网络请求(同步)Response response = call.execute();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
步骤7:处理返回数据
通过response类的 body()对返回的数据进行处理
//发送网络请求(异步)call.enqueue(newCallback() {//请求成功时回调@OverridepublicvoidonResponse(Call call, Response response) {// 对返回数据进行处理response.body().show(); }//请求失败时候的回调@OverridepublicvoidonFailure(Call call, Throwable throwable) { System.out.println("连接失败"); } });// 发送网络请求(同步)Response response = call.execute();// 对返回数据进行处理response.body().show();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
4. 实例讲解
接下来,我将用两个实例分别对 Retrofit GET方式 和 POST方式进行 网络请求 讲解。
4.1 实例1
实现功能:将中文翻译成英文
实现方案:采用Get方法对 金山词霸API 发送网络请求
采用 Gson 进行数据解析
步骤说明
步骤1:添加Retrofit库的依赖
步骤2:创建 接收服务器返回数据 的类
步骤3:创建 用于描述网络请求 的接口
步骤4:创建 Retrofit 实例
步骤5:创建 网络请求接口实例 并 配置网络请求参数
步骤6:发送网络请求(采用最常用的异步方式)
封装了 数据转换、线程切换的操作
步骤7: 处理服务器返回的数据
接下来,我们一步步进行讲解。
具体使用
步骤1:添加Retrofit库的依赖
1. 在 Gradle加入Retrofit库的依赖
由于Retrofit是基于OkHttp,所以还需要添加OkHttp库依赖
build.gradle
dependencies { compile'com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:2.0.2'// Retrofit库compile'com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:3.1.2'// Okhttp库}
1
2
3
4
5
6
2. 添加 网络权限
AndroidManifest.xml
1
步骤2:创建 接收服务器返回数据 的类
金山词霸API 的数据格式说明如下:
//URL模板http://fy.iciba.com/ajax.php// URL实例http://fy.iciba.com/ajax.php?a=fy&f=auto&t=auto&w=hello%20world// 参数说明:// a:固定值 fy// f:原文内容类型,日语取 ja,中文取 zh,英语取 en,韩语取 ko,德语取 de,西班牙语取 es,法语取 fr,自动则取 auto// t:译文内容类型,日语取 ja,中文取 zh,英语取 en,韩语取 ko,德语取 de,西班牙语取 es,法语取 fr,自动则取 auto// w:查询内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
根据 金山词霸API 的数据格式,创建 接收服务器返回数据 的类:
Translation.java
publicclassTranslation {privateintstatus;privatecontent content;privatestaticclasscontent {privateStringfrom;privateString to;privateString vendor;privateStringout;privateinterrNo; }//定义 输出返回数据 的方法publicvoidshow() { System.out.println(status); System.out.println(content.from); System.out.println(content.to); System.out.println(content.vendor); System.out.println(content.out); System.out.println(content.errNo); }}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
步骤3:创建 用于描述网络请求 的接口
采用 注解 描述 网络请求参数。
GetRequest_Interface.java
publicinterfaceGetRequest_Interface { @GET("ajax.php?a=fy&f=auto&t=auto&w=hello%20world") Call getCall();// 注解里传入 网络请求 的部分URL地址// Retrofit把网络请求的URL分成了两部分:一部分放在Retrofit对象里,另一部分放在网络请求接口里// 如果接口里的url是一个完整的网址,那么放在Retrofit对象里的URL可以忽略// getCall()是接受网络请求数据的方法}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
接下来的步骤均在GetRequest.java内实现(看注释)
步骤4:创建Retrofit对象
步骤5:创建 网络请求接口 的实例
步骤6:发送网络请求
以最常用的 异步请求 为例
步骤7:处理返回数据
GetRequest.java
publicclassGetRequestextendsAppCompatActivity{@OverrideprotectedvoidonCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); request();// 使用Retrofit封装的方法}publicvoidrequest() {//步骤4:创建Retrofit对象Retrofit retrofit =newRetrofit.Builder() .baseUrl("http://fy.iciba.com/")// 设置 网络请求 Url.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())//设置使用Gson解析(记得加入依赖).build();// 步骤5:创建 网络请求接口 的实例GetRequest_Interface request = retrofit.create(GetRequest_Interface.class);//对 发送请求 进行封装Call call = request.getCall();//步骤6:发送网络请求(异步)call.enqueue(newCallback() {//请求成功时回调@OverridepublicvoidonResponse(Call call, Response response) {// 步骤7:处理返回的数据结果response.body().show(); }//请求失败时回调@OverridepublicvoidonFailure(Call call, Throwable throwable) { System.out.println("连接失败"); } }); }}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
由于此处采用了 Gson 解析,所以需要在 Gradle加入依赖
build.gradle
compile'com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:2.0.2'
1
运行结果
Demo地址
Carson_Ho的Github:https://github.com/Carson-Ho/RetrofitDemo
4.2 实例2
实现的功能:将 英文 翻译成 中文
实现方法:采用Post方法对 有道API 发送网络请求
采用 Gson 进行数据解析
使用步骤
步骤1:添加Retrofit库的依赖
步骤2:创建 接收服务器返回数据 的类
步骤3:创建 用于描述网络请求 的接口
步骤4:创建 Retrofit 实例
步骤5:创建 网络请求接口实例 并 配置网络请求参数
步骤6:发送网络请求(采用最常用的异步方式)
封装了 数据转换、线程切换的操作
步骤7: 处理服务器返回的数据
接下来,我们一步步进行Retrofit的使用。
具体使用
步骤1:添加Retrofit库的依赖
1. 在 Gradle加入Retrofit库的依赖
由于Retrofit是基于OkHttp,所以还需要添加OkHttp库依赖
build.gradle
dependencies { compile'com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:2.0.2'// Retrofit库compile'com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:3.1.2'// Okhttp库}
1
2
3
4
5
6
2. 添加 网络权限
AndroidManifest.xml
1
步骤2:创建 接收服务器返回数据 的类
API 的数据格式说明如下:
//URLhttp://fanyi.youdao.com/translate// URL实例http://fanyi.youdao.com/translate?doctype=json&jsonversion=&type=&keyfrom=&model=&mid=&imei=&vendor=&screen=&ssid=&network=&abtest=// 参数说明// doctype:json 或 xml// jsonversion:如果 doctype 值是 xml,则去除该值,若 doctype 值是 json,该值为空即可// xmlVersion:如果 doctype 值是 json,则去除该值,若 doctype 值是 xml,该值为空即可// type:语言自动检测时为 null,为 null 时可为空。英译中为 EN2ZH_CN,中译英为 ZH_CN2EN,日译中为 JA2ZH_CN,中译日为 ZH_CN2JA,韩译中为 KR2ZH_CN,中译韩为 ZH_CN2KR,中译法为 ZH_CN2FR,法译中为 FR2ZH_CN// keyform:mdict. + 版本号 + .手机平台。可为空// model:手机型号。可为空// mid:平台版本。可为空// imei:???。可为空// vendor:应用下载平台。可为空// screen:屏幕宽高。可为空// ssid:用户名。可为空// abtest:???。可为空// 请求方式说明// 请求方式:POST// 请求体:i// 请求格式:x-www-form-urlencoded
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
根据 有道API 的数据格式,创建 接收服务器返回数据 的类:
Translation.java
publicclassTranslation1{privateString type;privateinterrorCode;privateintelapsedTime;privateList> translateResult;publicStringgetType() {returntype; }publicvoidsetType(String type) {this.type = type; }publicintgetErrorCode() {returnerrorCode; }publicvoidsetErrorCode(interrorCode) {this.errorCode = errorCode; }publicintgetElapsedTime() {returnelapsedTime; }publicvoidsetElapsedTime(intelapsedTime) {this.elapsedTime = elapsedTime; }publicList>getTranslateResult() {returntranslateResult; }publicvoidsetTranslateResult(List> translateResult) {this.translateResult = translateResult; }publicstaticclassTranslateResultBean{/**
* src : merry me
* tgt : 我快乐
*/publicString src;publicString tgt;publicStringgetSrc() {returnsrc; }publicvoidsetSrc(String src) {this.src = src; }publicStringgetTgt() {returntgt; }publicvoidsetTgt(String tgt) {this.tgt = tgt; } }}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
步骤3:创建 用于描述网络请求 的接口
采用 注解 描述 网络请求参数。
PostRequest_Interface.java
publicinterfacePostRequest_Interface{@POST("translate?doctype=json&jsonversion=&type=&keyfrom=&model=&mid=&imei=&vendor=&screen=&ssid=&network=&abtest=")@FormUrlEncodedCall getCall(@Field("i") String targetSentence);//采用@Post表示Post方法进行请求(传入部分url地址)// 采用@FormUrlEncoded注解的原因:API规定采用请求格式x-www-form-urlencoded,即表单形式// 需要配合@Field 向服务器提交需要的字段}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
接下来的步骤均在PostRequest.java内实现(看注释)
步骤4:创建Retrofit对象
步骤5:创建 网络请求接口 的实例
步骤6:发送网络请求
以最常用的 异步请求 为例
步骤7:处理返回数据
PostRequest.java
publicclassPostRequestextendsAppCompatActivity{@OverrideprotectedvoidonCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); request(); }publicvoidrequest() {//步骤4:创建Retrofit对象Retrofit retrofit =newRetrofit.Builder() .baseUrl("http://fanyi.youdao.com/")// 设置 网络请求 Url.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())//设置使用Gson解析(记得加入依赖).build();// 步骤5:创建 网络请求接口 的实例PostRequest_Interface request = retrofit.create(PostRequest_Interface.class);//对 发送请求 进行封装(设置需要翻译的内容)Call call = request.getCall("I love you");//步骤6:发送网络请求(异步)call.enqueue(newCallback() {//请求成功时回调@OverridepublicvoidonResponse(Call call, Response response) {// 步骤7:处理返回的数据结果:输出翻译的内容System.out.println(response.body().getTranslateResult().get(0).get(0).getTgt()); }//请求失败时回调@OverridepublicvoidonFailure(Call call, Throwable throwable) { System.out.println("请求失败"); System.out.println(throwable.getMessage()); } }); }}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
由于此处采用了 Gson 解析,所以需要在 Gradle 加入依赖
build.gradle
compile'com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:2.0.2'
1
运行结果
Demo地址
Carson_Ho的Github:https://github.com/Carson-Ho/RetrofitDemo
5. Retrofit 的拓展使用
Retrofit的使用场景非常丰富,如支持RxJava和Prototocobuff
具体设置也非常简单 & 方便:
<-- 主要在创建Retrofit对象中设置 -->Retrofit retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder().baseUrl(""http://fanyi.youdao.com/"").addConverterFactory(ProtoConverterFactory.create()) // 支持Prototocobuff解析.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create()) // 支持Gson解析.addCallAdapterFactory(RxJavaCallAdapterFactory.create()) // 支持RxJava.build();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
具体关于 RxJava的使用这里就不展开,请期待下篇关于 Rxjava的文章。
6. 总结
看完本文,相信你已经非常熟悉 Retrofit 2.0 的使用
如果你希望继续阅读 Retrofit 2.0 的源码,请看我写的文章:Android:手把手带你深入剖析 Retrofit 2.0 源码
接下来,我将继续分析与 Retrofit 配合使用的 RxJava,有兴趣可以继续关注Carson_Ho的安卓开发笔记