linux——shell变量及函数
shell变量
1.变量定义:
变量即在程序运行过程中它的值是允许改变的量,变量是用一串固定的字符来标志不固定的值的一种方法,变量是一种使用方便的占位符,用于引用计算机内存地址,该地址可以存储scripts运行时可更改的程序信息。在shell 中变量是不可能永久保存在系统中的,必须在文件中声明。
2.变量分类
在shell中变量分为环境级变量,用户级变量,系统级变量, 环境级变量只在当前shell中生效,shell关闭变量丢失, 用户级变量写在用户的骨文件中,只针对当前用户有效, 系统级变量被写在系统的配置文件/etc/profile中 变量即在程序运行时保存在内存中。 硬盘永久,内存临时的。
3.变量名称的规范
变量名称中通常包含大小写字母,数字,下划线
变量名称格式:
WESTOS——LINUX
Westos_Linux
westos_linux
4.变量的定义方法
环境级:
export A=1
用户级:
vim ~/.bash_profile
export A=1
系统级:
vim /etc/profile
export A=1
4.1 环境级
[root@client ~]# echo $PATH //查看环境变量
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
[root@client ~]# a=1 //定义变量a为1
[root@client ~]# echo $a //在当前的进程中输出
1
[root@client ~]# ps
PID TTY TIME CMD
1778 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
1816 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
[root@client ~]# sh //进入另一个进程
sh-4.2# ps
PID TTY TIME CMD
1852 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
1891 pts/0 00:00:00 sh
1892 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
sh-4.2# echo $a
//输出a,此时没有值,是因为这种定义只能用于当前的进程中,后一个进程与前一个进程的分配的内存段不同,无法访问a的值
sh-4.2#
[root@client ~]# export a=1 //声明a=1,将其变为公共
[root@client ~]# echo $a
1
[root@client ~]# ps
PID TTY TIME CMD
1778 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
1817 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
[root@client ~]# sh
sh-4.2# ps
PID TTY TIME CMD
1778 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
1826 pts/0 00:00:00 sh
1827 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
sh-4.2# echo $a
1 //此时别的进程也就可以访问了,但这种定义时临时的,退出进程后就会失效。4.2 用户级
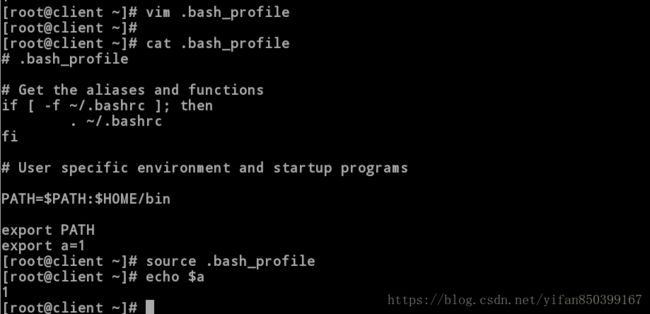
[root@client ~]# vim .bash_profile //编辑用户文件
[root@client ~]# cat .bash_profile
# .bash_profile
# Get the aliases and functions
if [ -f ~/.bashrc ]; then
. ~/.bashrc
fi
# User specific environment and startup programs
PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin
export PATH
export a=1 //添加内容
[root@client ~]# source .bash_profile //刷新文件
[root@client ~]# echo $a
1
[root@client ~]# su - student //切换到student用户中
Last login: Fri Jun 22 17:52:25 EDT 2018 on pts/0
[student@client ~]$ echo $a
//此时变量a无值,查看不到变量的值是因为是不同的shell环境,新的shell会加载不同的配置文件覆盖原来的
4.3 系统级
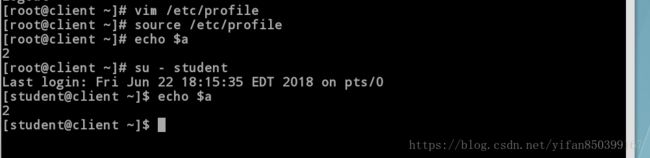
[root@client ~]# vim /etc/profile //编辑系统文件
>---添加内容----<
export=2
[root@client ~]# source /etc/profile //刷新
[root@client ~]# echo $a //此时输出变量值,对比用户文件,我们给root的a=1,也能说明系统级变量比用户级变量的级别高。
2
[root@client ~]# su - student //切换用户
Last login: Fri Jun 22 18:15:35 EDT 2018 on pts/0
[student@client ~]$ echo $a //可以访问
25.临时修改路径
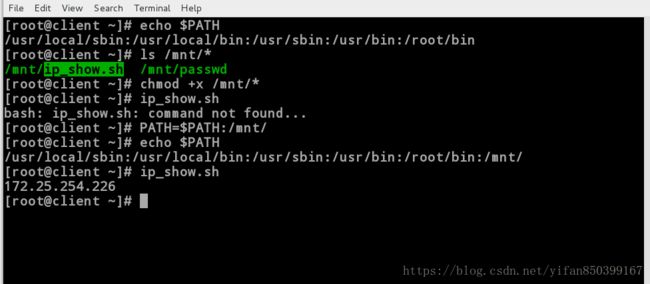
[root@client ~]# echo $PATH //查看系统环境变量
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
[root@client ~]# ls /mnt/*
/mnt/ip_show.sh /mnt/passwd
[root@client ~]# chmod +x /mnt/*
[root@client ~]# ip_show.sh //此时不能执行,因为不是绝对路径
bash: ip_show.sh: command not found...
[root@client ~]# PATH=$PATH:/mnt/ //临时添加/mnt为环境变量,退出当前shell后后失效
[root@client ~]# echo $PATH
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin:/mnt/
[root@client ~]# ip_show.sh //此时可以用相对路径执行成功
172.25.254.2266.字符的转译变量的声明
\ 转译单个字符
” ” 是弱引用,批量转译,不能转义“!”,“/” ,“ ` ”,“$”
’ ’ 是强引用,批量转译 ’ ‘中出现的字符
$() 变量声明,和` `没有区别
$[] 等同于(())
${} 系统声明
echo 1+1 显示结果为1+1,其中1+1是可变长字符
echo $[1+1] 显示结果为2,是整形字符
[root@client ~]# a=hello world //中间的空格需要转译
bash: world: command not found...
[root@client ~]# a=hello\ world
[root@client ~]# echo $a
hello world
[root@client ~]# a="hello hello" //弱转译,但可以转译空格
[root@client ~]# echo $a
hello hello
[root@client ~]# a=1
[root@client ~]# echo $ab
[root@client ~]# echo $a b
1 b
[root@client ~]# echo 1+1
1+1
[root@client ~]# echo $[1+1]
27.变量值传递
| “$”变量值的传递 | |
|---|---|
| $0 | 所运行脚本的名称 |
| $1 | 脚本后的第一串字符串 |
| $2 | 脚本后的第二块字符串 |
| $3 | 脚本后的第三串字符串 |
| $# | 脚本后所跟字符串的个数 |
| $* | 脚本后跟的所有字符串,模式为“1,2,3”,一串 |
| $@ | 脚本后跟的所有字符串,模式为“1’,”2”,”3”,三串 |
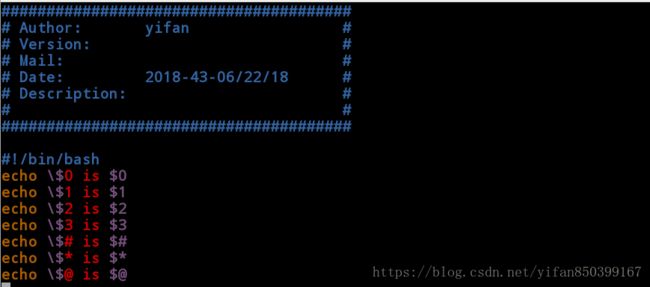
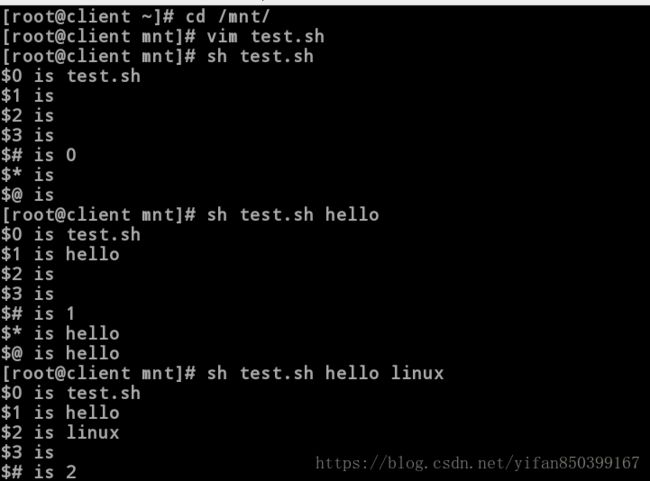
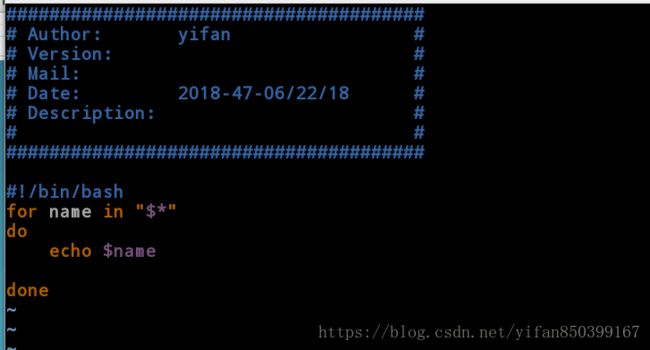
[root@client mnt]# cat test.sh
######################################
# Author: yifan #
# Version: #
# Mail: #
# Date: 2018-49-06/17/18 #
# Description: #
# #
######################################
#!/bin/bash
echo \$0 is $0
echo \$1 is $1
echo \$2 is $2
echo \$3 is $3
echo \$# is $#
echo \$* is $*
echo \$@ is $@
[root@client mnt]# sh test.sh //不加输入
$0 is test.sh
$1 is
$2 is
$3 is
$# is 0
$* is
$@ is
[root@client mnt]# sh test.sh hello //一个输入
$0 is test.sh
$1 is hello
$2 is
$3 is
$# is 1
$* is hello
$@ is hello
[root@client mnt]# sh test.sh hello westos //两个输入
$0 is test.sh
$1 is hello
$2 is westos
$3 is
$# is 2
$* is hello westos
$@ is hello westos
[root@client mnt]# sh test.sh hello westos kill //三个输入
$0 is test.sh
$1 is hello
$2 is westos
$3 is kill
$# is 3
$* is hello westos kill
$@ is hello westos kill//证明“$*”模式为一串字符,“$@”为模式为所跟字符个数串字符。
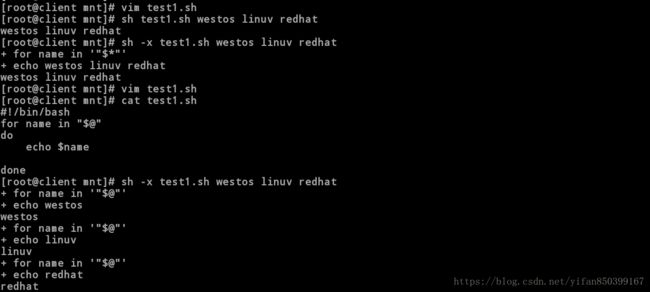
[root@client mnt]# vim test1.sh
#!/bin/bash //脚本内容
for name in "$*"
do
echo $name
done
[root@client mnt]# sh -x test1.sh westos linux redhat //只执行一次
+ for name in '"$*"'
+ echo westos linux redhat
westos linuv redhat
[root@client mnt]# vim test1.sh
[root@client mnt]# cat test1.sh
#!/bin/bash //脚本内容
for name in "$@"
do
echo $name
done
[root@client mnt]# sh -x test1.sh westos linux redhat //执行三次
+ for name in '"$@"'
+ echo westos
westos
+ for name in '"$@"'
+ echo linux
linux
+ for name in '"$@"'
+ echo redhat
redhat8.read交互式变量传递
Read westos
Read -s westos 隐藏输入字符
Read -p westos 显示提示,-p打印
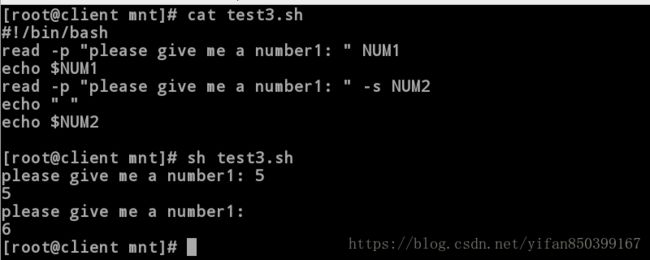
[root@client mnt]# cat test3.sh
#!/bin/bash
read -p "please give me a number1: " NUM1
echo $NUM1
read -p "please give me a number1: " -s NUM2 //加密输出NUM2
echo " " //输出空行,换行
echo $NUM2
[root@client mnt]# sh test3.sh
please give me a number1: 5
5
please give me a number1:
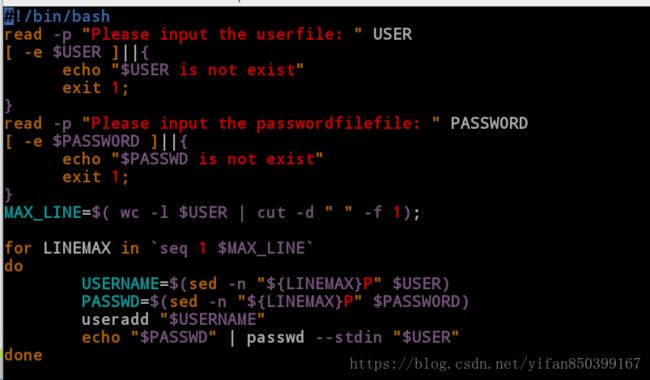
6练习:编写脚本,提示输入用户名和密码的存放文件,并判断文件是否存在,若不存在,提示不存在,若存在则建立用户
[root@client mnt]# vim user_creat.sh
#!/bin/bash
read -p "Please input the userfile: " USER //提示用户输入userfile文件
[ -e $USER ]||{
echo "$USER is not exist" //判断文件是否存在
exit 1;
}
read -p "Please input the passwordfilefile: " PASSWORD //提示用户输入passwdfile文件
[ -e $PASSWORD ]||{
echo "$PASSWD is not exist" //判断文件是否存在
exit 1;
}
MAX_LINE=$( wc -l $USER | cut -d " " -f 1); //统计行数
for LINEMAX in `seq 1 $MAX_LINE` //循环添加
do
USERNAME=$(sed -n "${LINEMAX}P" $USER) //取出第i行内容
PASSWD=$(sed -n "${LINEMAX}P" $PASSWORD)
useradd "$USERNAME"
echo "$PASSWD" | passwd --stdin "$USER" //建立用户
done9.系统命令别名的设定——alias
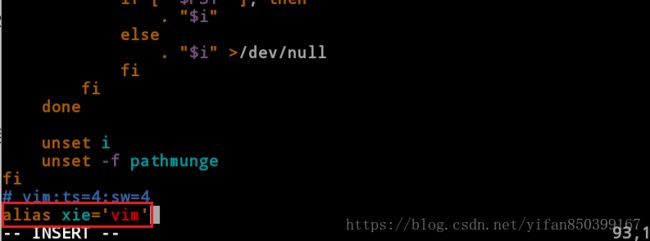
alias xie=’vim’ //临时设定命令别名
vim .bashrc //永久设定用户级别的命令别名
vim /etc/bashrc //永久设定系统级别的命令别名
unalias xie //删除系统命令别名
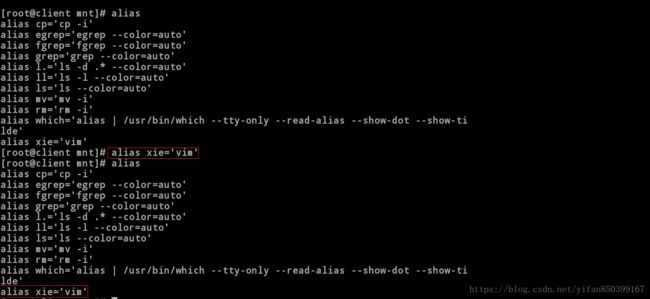
9.1alias xie=’vim’ //临时设定命令别名
[root@client mnt]# alias //查看系统命令设置的别名
alias cp='cp -i'
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
alias l.='ls -d .* --color=auto'
alias ll='ls -l --color=auto'
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
alias mv='mv -i'
alias rm='rm -i'
alias which='alias | /usr/bin/which --tty-only --read-alias --show-dot --show-tilde'
alias xie='vim'
root@client mnt]# alias xie='vim' //临时设定系统命令别名
[root@client mnt]# alias
alias cp='cp -i'
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
alias l.='ls -d .* --color=auto'
alias ll='ls -l --color=auto'
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
alias mv='mv -i'
alias rm='rm -i'
alias which='alias | /usr/bin/which --tty-only --read-alias --show-dot --show-tilde'
alias xie='vim' //此时添加成功
[root@client mnt]# xie //此时执行xie可以调用vim命令
~
~ VIM - Vi IMproved
~
~ version 7.4.160
~ by Bram Moolenaar et al.
~ Modified by @redhat.com>
~ Vim is open source and freely distributable
~
~ Sponsor Vim development!
~ type :help sponsor for information
~
~ type :q to exit
~ type :help or for on-line help
~ type :help version7 for version info
~
~
~
[root@client mnt]# exit
logout
Connection to 172.25.254.171 closed.
[kiosk@foundation26 ~]$ ssh root@172.25.254.171 //退出当前shell
root@172.25.254.171's password:
Last login: Sun Jun 17 20:51:09 2018 from 172.25.254.26
[root@client ~]# xie //此时命令会失效
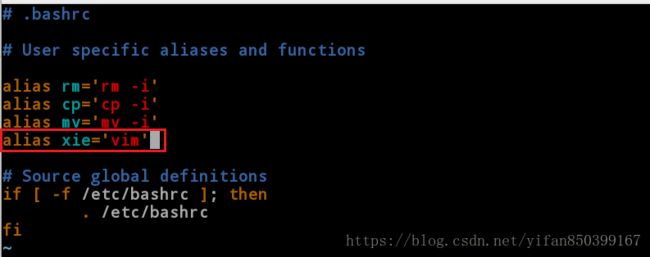
bash: xie: command not found... 9.2.vim .bashrc //永久设定用户级别的命令别名
[root@client ~]# vim .bashrc //编辑用户文件,永久的设定用户系统命令的别名
>---添加内容----<
alias xie=’vim’
[root@client ~]# source .bashrc //刷新文件
[root@client ~]# xie //此时可以调用vim命令
[root@client ~]# su - student //切换到student用户,此时无法使用
Last login: Sun Jun 17 04:47:27 EDT 2018 on pts/1
[student@client ~]$ xie
bash: xie: command not found...
[student@client ~]$ su - root
Password:
Last login: Sun Jun 17 22:22:37 EDT 2018 from 172.25.254.26 on pts/0
9.3.vim /etc/bashrc //永久设定系统级别的命令别名
[root@client ~]# vim /etc/bashrc //修改系统的配置文件,设置系统级命令的别名
>---添加内容----<
alias xie=’vim’
[root@client ~]# source /etc/bashrc
[root@client ~]# su - student //此时student用户也可使用
Last login: Sun Jun 17 22:23:54 EDT 2018 on pts/0
[student@client ~]$ xie
9.4.unalias xie //删除系统命令别名
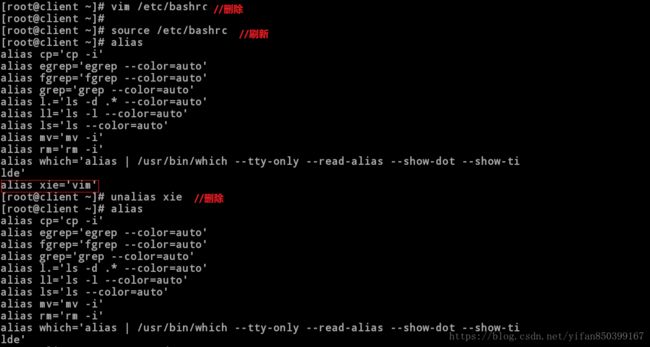
[root@client ~]# vim /etc/bashrc //删除配置文件中添加的内容
[root@client ~]# source /etc/bashrc //刷新
[root@client ~]# alias
alias cp='cp -i'
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
alias l.='ls -d .* --color=auto'
alias ll='ls -l --color=auto'
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
alias mv='mv -i'
alias rm='rm -i'
alias which='alias | /usr/bin/which --tty-only --read-alias --show-dot --show-tilde'
alias xie='vim' //此时系统中还存在这个命令,因为内存缓存中还有
[root@client ~]# unalias xie //删除缓存中命令
[root@client ~]# alias //此时这个命令就会失效
alias cp='cp -i'
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
alias l.='ls -d .* --color=auto'
alias ll='ls -l --color=auto'
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
alias mv='mv -i'
alias rm='rm -i'
alias which='alias | /usr/bin/which --tty-only --read-alias --show-dot --show-tilde'
[root@client ~]# xie
bash: xie: command not found...10.利用命令执行结果设定变量
HOSTNAME=$(hostname) //将hostname执行结果赋值给变量HOSTNAME
HOSTNAME=`hostname`
$? //退出值,默认的退出值是命令在执行完成之后产生的退出值
退出值范围:[0-255],0表示正确,1表示错误,2表示方法不得当
退出值可以用exit命令执行,
例如:exit 6 ,输入echo $? 时显示的是6
[root@client ~]# HOSTNAME=$(hostname) //将hostname执行结果赋值给变量HOSTNAME
[root@client ~]# echo $HOSTNAME
client.example
[root@client ~]# HOSTNAME=`hostname`
[root@client ~]# echo $HOSTNAME
client.example
[root@client ~]# sadlasjcal //错误退出
bash: sadlasjcal: command not found...
[root@client ~]# echo $? //退出值为127
127
[root@client ~]# ping 172.25.254.71 //正确退出
PING 172.25.254.71 (172.25.254.71) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 172.25.254.71: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.127 ms
64 bytes from 172.25.254.71: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.144 ms
C64 bytes from 172.25.254.71: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.212 ms
64 bytes from 172.25.254.71: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.296 ms
C64 bytes from 172.25.254.71: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.172 ms
^C
--- 172.25.254.71 ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 5 received, 0% packet loss, time 4005ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.127/0.190/0.296/0.060 ms
[root@client ~]# echo $? //正确退出值
0
练习:写一个利用exit退出值判断ip是否通;
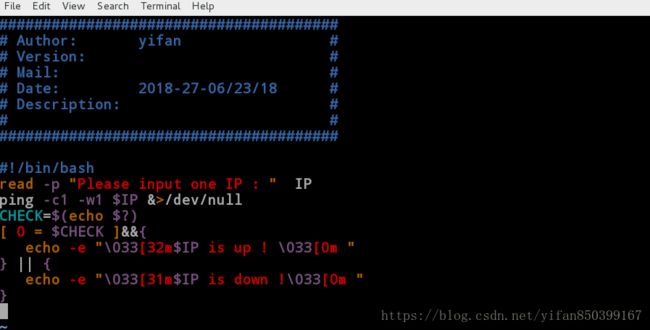
[root@client mnt]# vim ping_test.sh
#!/bin/bash
read -p "Please input one IP : " IP //提示用户输入IP
ping -c1 -w1 $IP &>/dev/null //ping IP ,输出导入垃圾桶中
CHECK=$(echo $?) //定义变量CHECK,用来存储ping命令退出值
[ 0 = $CHECK ]&&{ //判断退出值是否为0,0即ping同,否则失败
echo -e "\033[32m$IP is up ! \033[0m "
} || {
echo -e "\033[31m$IP is down !\033[0m "
}
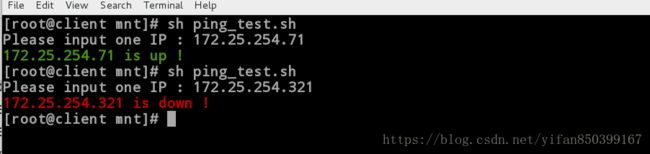
[root@client mnt]# sh ping_test.sh //执行脚本
Please input one IP : 172.25.254.71
172.25.254.71 is up !
[root@client mnt]# sh ping_test.sh
Please input one IP : 172.25.254.321
172.25.254.321 is down !
[root@client mnt]# vim ping_test.sh
函数
脚本中的函数是把一个复杂的语句块定义成一个字符串的方法,可以确保命令的循环执行,简化脚本长度
利用函数循环格式:
Host_Message(){
命令
Host_Message //循环
}
Host_Message //调用函数
实验一:编写脚本利用函数循环,不断使用ping命令
[root@client mnt]# vim test.sh
#!/bin/bash
PING() //定义函数
{
read -p " Please input a ipaddress: " IP
ping -c1 -w1 $IP &> /dev/null
PING //循环
}
PING //调用函数
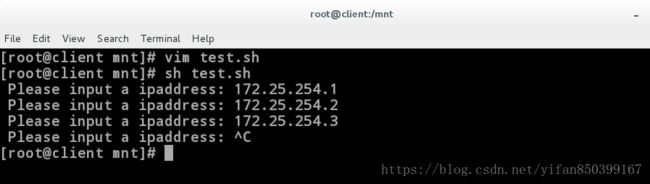
[root@client mnt]# sh test.sh
Please input a ipaddress: 172.25.254.1
Please input a ipaddress: 172.25.254.2
Please input a ipaddress: 172.25.254.3
Please input a ipaddress: ^C //一直循环实验二:编写脚本利用函数循环,不断使用ping命令,当输入exit后退出
[root@client mnt]# vim test.sh
#!/bin/bash
PING()
{
read -p " Please input a ipaddress: " IP
[ "$IP" = exit ] && { //判断输入为exit时退出
echo bye
exit 0
}
ping -c1 -w1 $IP &> /dev/null
PING
}
PING
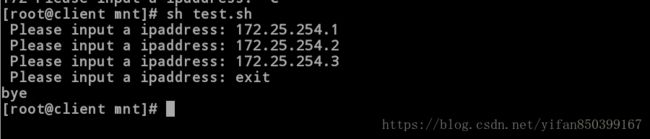
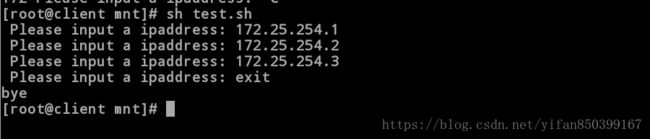
[root@client mnt]# sh test.sh
Please input a ipaddress: 172.25.254.1
Please input a ipaddress: 172.25.254.2
Please input a ipaddress: 172.25.254.3
Please input a ipaddress: exit //输入后退出
Bye
练习:编写脚本,利用函数检测文件类型
[root@client mnt]# vim file_check.sh
#!/bin/bash
FILE_CHECK() //定义函数,函数内变量为函数本身变量,调用时要赋值
{
[ "$1" "$2" ]&& {
echo $2 is a $3 !
exit 0
}
}
[ -e "$1" ]|| {
echo $1 is not exist !!
}
FILE_CHECK -L $1 link //调用函数
FILE_CHECK -f $1 file
FILE_CHECK -b $1 block
FILE_CHECK -c $1 character
FILE_CHECK -d $1 directory
FILE_CHECK -S $1 socket
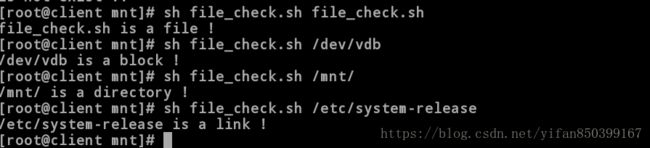
[root@client mnt]# sh file_check.sh file_check.sh
file_check.sh is a file !
[root@client mnt]# sh file_check.sh /dev/vdb
/dev/vdb is a block !
[root@client mnt]# sh file_check.sh /mnt/
/mnt/ is a directory !
[root@client mnt]# sh file_check.sh /etc/system-release
/etc/system-release is a link !