深度学习: Non-Maximum Supression (非极大值抑制)
NMS (Non-Maximum Supression)
NMS来 选取那些邻域里分数最高的窗口,同时抑制那些分数低的窗口 。
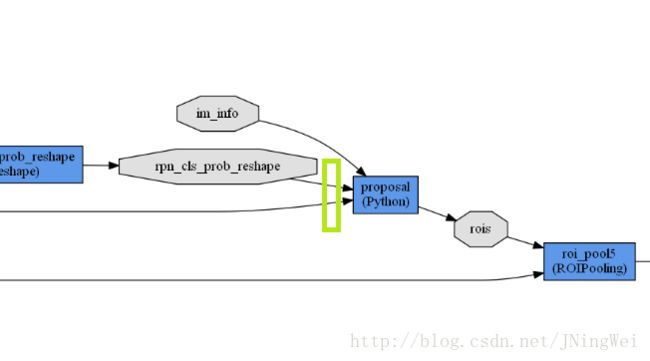
由 论文可见,在 Faster R-CNN 中,NMS算法被放在RPN网络的末段,用于 协助 剔除低得分的box:

Note:
-
所有NMS算法都是在每个类内分别独立进行NMS。
-
NMS算法略显粗暴,直接将和得分最大的box的IOU大于某个阈值的box的 得分置零 或者 丢弃box 。后续的改良版——Soft NMS,改用稍低一点的分数 ( score*(1-iou) ) 来代替原有的分数,而不是直接置零。
Test
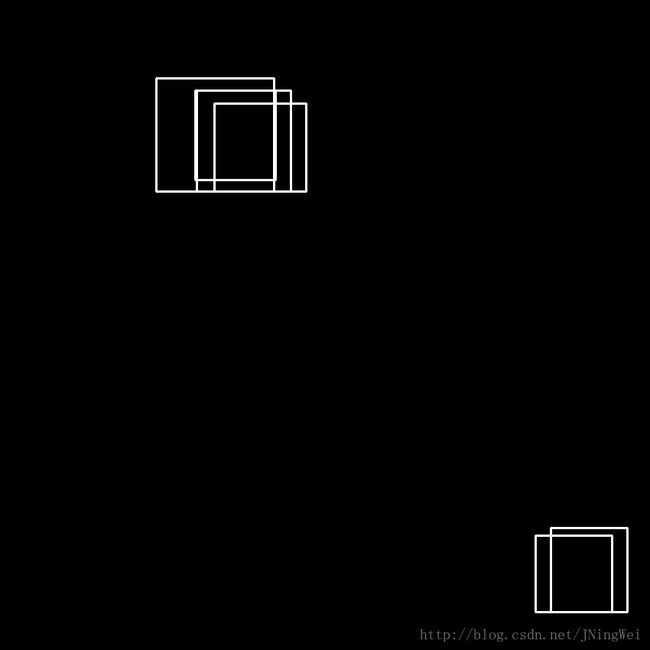
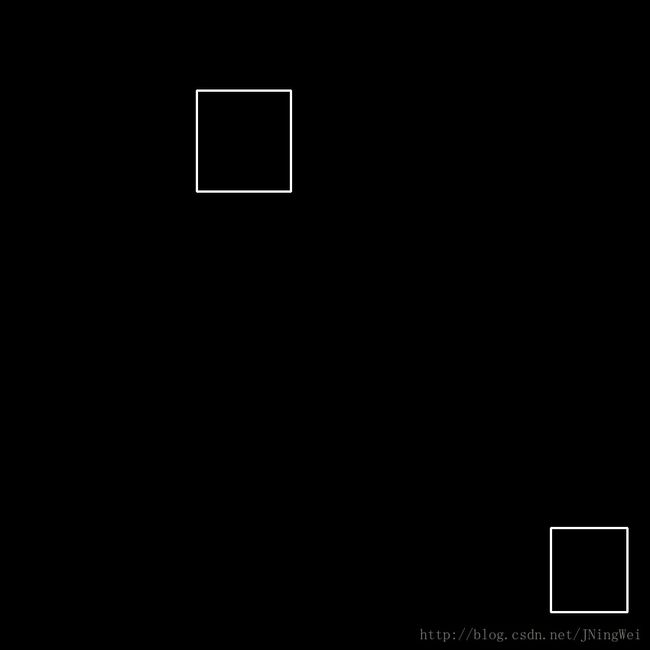
我经过动手实验,成功复现了 NMS 的处理过程。
Code
效果图所对应的源码如下:
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
import cv2
def nms(bboxs, thresh):
x1, y1, x2, y2, scores = list([bboxs[:, i] for i in range(len(bboxs[0]))])
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1) # 每块 bbox 面积
order = scores.argsort()[::-1] # 所有 bbox 根据置信度 进行 index排序
keep = [] # 筛选后 要留下来的 bbox
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0] # 置信度最高的bbox 的 index
keep.append(i) # 先 留下 剩下的bbox 中 置信度最高的bbox 的index
# 选择大于x1,y1和小于x2,y2的区域
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
# 当前bbox 与 每个剩余的 bbox 分别的 重叠区域
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h # [ 12272. 11716. 13566. 0. 0.] [ 8181.]
# 交叉区域面积 / (bbox + 某区域面积 - 交叉区域面积)
overlap = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter) # [ 0.73362028 0.62279396 0.52134814 0. 0. ] [ 0.61832061]
# 保留交集小于一定阈值的boundingbox
idxs = np.where(overlap <= thresh)[0] # [3 4] []
order = order[idxs + 1] # [0 3] []
return keep
def draw_bbox(bboxs, pic_name):
pic = np.zeros((850, 850), np.uint8)
for bbox in bboxs:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, bbox[:-1])
pic = cv2.rectangle(pic, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.imwrite('./{}.jpg'.format(pic_name), pic)
if __name__ == "__main__":
bboxs = np.array([
[720, 690, 820, 800, 0.5],
[204, 102, 358, 250, 0.5],
[257, 118, 380, 250, 0.8],
[700, 700, 800, 800, 0.4],
[280, 135, 400, 250, 0.7],
[255, 118, 360, 235, 0.7]])
thresh = 0.3
draw_bbox(bboxs, "Before_NMS")
keep = nms(bboxs, thresh) # [2, 0]
draw_bbox(bboxs[keep], "After_NMS")
算法缺陷
NMS算法的 核心思想 是:在 假设 实例之间均为不重叠或低重叠的 前提 下,去除高重叠bbox。
该核心思想也导致了NMS不可避免地会对 高重叠的实例 产生 漏检 。