Tensorflow学习笔记(第四天)—递归神经网络
一、首先下载来源于 Tomas Mikolov 网站上的 PTB 数据集
http://www.fit.vutbr.cz/~imikolov/rnnlm/simple-examples.tgz
二、需要的代码:
这里只简单的放了一些代码,具体解释可以看官方文档。还有这篇文章我觉得不错:
https://blog.csdn.net/mydear_11000/article/details/52440115
reader.py代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Copyright 2015 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
"""Utilities for parsing PTB text files."""
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import collections
import os
import sys
import tensorflow as tf
Py3 = sys.version_info[0] == 3
def _read_words(filename):
with tf.gfile.GFile(filename, "r") as f:
if Py3:
return f.read().replace("\n", "").split()
else:
return f.read().decode("utf-8").replace("\n", "").split()
def _build_vocab(filename):
data = _read_words(filename)
counter = collections.Counter(data)
count_pairs = sorted(counter.items(), key=lambda x: (-x[1], x[0]))
words, _ = list(zip(*count_pairs))
word_to_id = dict(zip(words, range(len(words))))
return word_to_id
def _file_to_word_ids(filename, word_to_id):
data = _read_words(filename)
return [word_to_id[word] for word in data if word in word_to_id]
def ptb_raw_data(data_path=None):
"""Load PTB raw data from data directory "data_path".
Reads PTB text files, converts strings to integer ids,
and performs mini-batching of the inputs.
The PTB dataset comes from Tomas Mikolov's webpage:
http://www.fit.vutbr.cz/~imikolov/rnnlm/simple-examples.tgz
Args:
data_path: string path to the directory where simple-examples.tgz has
been extracted.
Returns:
tuple (train_data, valid_data, test_data, vocabulary)
where each of the data objects can be passed to PTBIterator.
"""
train_path = os.path.join(data_path, "ptb.train.txt")
valid_path = os.path.join(data_path, "ptb.valid.txt")
test_path = os.path.join(data_path, "ptb.test.txt")
word_to_id = _build_vocab(train_path)
train_data = _file_to_word_ids(train_path, word_to_id)
valid_data = _file_to_word_ids(valid_path, word_to_id)
test_data = _file_to_word_ids(test_path, word_to_id)
vocabulary = len(word_to_id)
return train_data, valid_data, test_data, vocabulary
def ptb_producer(raw_data, batch_size, num_steps, name=None):
"""Iterate on the raw PTB data.
This chunks up raw_data into batches of examples and returns Tensors that
are drawn from these batches.
Args:
raw_data: one of the raw data outputs from ptb_raw_data.
batch_size: int, the batch size.
num_steps: int, the number of unrolls.
name: the name of this operation (optional).
Returns:
A pair of Tensors, each shaped [batch_size, num_steps]. The second element
of the tuple is the same data time-shifted to the right by one.
Raises:
tf.errors.InvalidArgumentError: if batch_size or num_steps are too high.
"""
with tf.name_scope(name, "PTBProducer", [raw_data, batch_size, num_steps]):
raw_data = tf.convert_to_tensor(raw_data, name="raw_data", dtype=tf.int32)
data_len = tf.size(raw_data)
batch_len = data_len // batch_size
data = tf.reshape(raw_data[0 : batch_size * batch_len],
[batch_size, batch_len])
epoch_size = (batch_len - 1) // num_steps
assertion = tf.assert_positive(
epoch_size,
message="epoch_size == 0, decrease batch_size or num_steps")
with tf.control_dependencies([assertion]):
epoch_size = tf.identity(epoch_size, name="epoch_size")
i = tf.train.range_input_producer(epoch_size, shuffle=False).dequeue()
x = tf.strided_slice(data, [0, i * num_steps],
[batch_size, (i + 1) * num_steps])
x.set_shape([batch_size, num_steps])
y = tf.strided_slice(data, [0, i * num_steps + 1],
[batch_size, (i + 1) * num_steps + 1])
y.set_shape([batch_size, num_steps])
return x, y
ptb_word_lm.py代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Copyright 2015 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
# Copyright 2015 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
"""Example / benchmark for building a PTB LSTM model.
Trains the model described in:
(Zaremba, et. al.) Recurrent Neural Network Regularization
http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.2329
There are 3 supported model configurations:
===========================================
| config | epochs | train | valid | test
===========================================
| small | 13 | 37.99 | 121.39 | 115.91
| medium | 39 | 48.45 | 86.16 | 82.07
| large | 55 | 37.87 | 82.62 | 78.29
The exact results may vary depending on the random initialization.
The hyperparameters used in the model:
- init_scale - the initial scale of the weights
- learning_rate - the initial value of the learning rate
- max_grad_norm - the maximum permissible norm of the gradient
- num_layers - the number of LSTM layers
- num_steps - the number of unrolled steps of LSTM
- hidden_size - the number of LSTM units
- max_epoch - the number of epochs trained with the initial learning rate
- max_max_epoch - the total number of epochs for training
- keep_prob - the probability of keeping weights in the dropout layer
- lr_decay - the decay of the learning rate for each epoch after "max_epoch"
- batch_size - the batch size
- rnn_mode - the low level implementation of lstm cell: one of CUDNN,
BASIC, or BLOCK, representing cudnn_lstm, basic_lstm, and
lstm_block_cell classes.
The data required for this example is in the data/ dir of the
PTB dataset from Tomas Mikolov's webpage:
$ wget http://www.fit.vutbr.cz/~imikolov/rnnlm/simple-examples.tgz
$ tar xvf simple-examples.tgz
To run:
$ python ptb_word_lm.py --data_path=simple-examples/data/
"""
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import time
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import reader
import util
from tensorflow.python.client import device_lib
flags = tf.flags
logging = tf.logging
flags.DEFINE_string(
"model", "small",
"A type of model. Possible options are: small, medium, large.")
flags.DEFINE_string("data_path", None,
"Where the training/test data is stored.")
flags.DEFINE_string("save_path", None,
"Model output directory.")
flags.DEFINE_bool("use_fp16", False,
"Train using 16-bit floats instead of 32bit floats")
flags.DEFINE_integer("num_gpus", 1,
"If larger than 1, Grappler AutoParallel optimizer "
"will create multiple training replicas with each GPU "
"running one replica.")
flags.DEFINE_string("rnn_mode", None,
"The low level implementation of lstm cell: one of CUDNN, "
"BASIC, and BLOCK, representing cudnn_lstm, basic_lstm, "
"and lstm_block_cell classes.")
FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
BASIC = "basic"
CUDNN = "cudnn"
BLOCK = "block"
def data_type():
return tf.float16 if FLAGS.use_fp16 else tf.float32
class PTBInput(object):
"""The input data."""
def __init__(self, config, data, name=None):
self.batch_size = batch_size = config.batch_size
self.num_steps = num_steps = config.num_steps
self.epoch_size = ((len(data) // batch_size) - 1) // num_steps
self.input_data, self.targets = reader.ptb_producer(
data, batch_size, num_steps, name=name)
class PTBModel(object):
"""The PTB model."""
def __init__(self, is_training, config, input_):
self._is_training = is_training
self._input = input_
self._rnn_params = None
self._cell = None
self.batch_size = input_.batch_size
self.num_steps = input_.num_steps
size = config.hidden_size
vocab_size = config.vocab_size
with tf.device("/cpu:0"):
embedding = tf.get_variable(
"embedding", [vocab_size, size], dtype=data_type())
inputs = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding, input_.input_data)
if is_training and config.keep_prob < 1:
inputs = tf.nn.dropout(inputs, config.keep_prob)
output, state = self._build_rnn_graph(inputs, config, is_training)
softmax_w = tf.get_variable(
"softmax_w", [size, vocab_size], dtype=data_type())
softmax_b = tf.get_variable("softmax_b", [vocab_size], dtype=data_type())
logits = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(output, softmax_w, softmax_b)
# Reshape logits to be a 3-D tensor for sequence loss
logits = tf.reshape(logits, [self.batch_size, self.num_steps, vocab_size])
# Use the contrib sequence loss and average over the batches
loss = tf.contrib.seq2seq.sequence_loss(
logits,
input_.targets,
tf.ones([self.batch_size, self.num_steps], dtype=data_type()),
average_across_timesteps=False,
average_across_batch=True)
# Update the cost
self._cost = tf.reduce_sum(loss)
self._final_state = state
if not is_training:
return
self._lr = tf.Variable(0.0, trainable=False)
tvars = tf.trainable_variables()
grads, _ = tf.clip_by_global_norm(tf.gradients(self._cost, tvars),
config.max_grad_norm)
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(self._lr)
self._train_op = optimizer.apply_gradients(
zip(grads, tvars),
global_step=tf.train.get_or_create_global_step())
self._new_lr = tf.placeholder(
tf.float32, shape=[], name="new_learning_rate")
self._lr_update = tf.assign(self._lr, self._new_lr)
def _build_rnn_graph(self, inputs, config, is_training):
if config.rnn_mode == CUDNN:
return self._build_rnn_graph_cudnn(inputs, config, is_training)
else:
return self._build_rnn_graph_lstm(inputs, config, is_training)
def _build_rnn_graph_cudnn(self, inputs, config, is_training):
"""Build the inference graph using CUDNN cell."""
inputs = tf.transpose(inputs, [1, 0, 2])
self._cell = tf.contrib.cudnn_rnn.CudnnLSTM(
num_layers=config.num_layers,
num_units=config.hidden_size,
input_size=config.hidden_size,
dropout=1 - config.keep_prob if is_training else 0)
params_size_t = self._cell.params_size()
self._rnn_params = tf.get_variable(
"lstm_params",
initializer=tf.random_uniform(
[params_size_t], -config.init_scale, config.init_scale),
validate_shape=False)
c = tf.zeros([config.num_layers, self.batch_size, config.hidden_size],
tf.float32)
h = tf.zeros([config.num_layers, self.batch_size, config.hidden_size],
tf.float32)
self._initial_state = (tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMStateTuple(h=h, c=c),)
outputs, h, c = self._cell(inputs, h, c, self._rnn_params, is_training)
outputs = tf.transpose(outputs, [1, 0, 2])
outputs = tf.reshape(outputs, [-1, config.hidden_size])
return outputs, (tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMStateTuple(h=h, c=c),)
def _get_lstm_cell(self, config, is_training):
if config.rnn_mode == BASIC:
return tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(
config.hidden_size, forget_bias=0.0, state_is_tuple=True,
reuse=not is_training)
if config.rnn_mode == BLOCK:
return tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMBlockCell(
config.hidden_size, forget_bias=0.0)
raise ValueError("rnn_mode %s not supported" % config.rnn_mode)
def _build_rnn_graph_lstm(self, inputs, config, is_training):
"""Build the inference graph using canonical LSTM cells."""
# Slightly better results can be obtained with forget gate biases
# initialized to 1 but the hyperparameters of the model would need to be
# different than reported in the paper.
def make_cell():
cell = self._get_lstm_cell(config, is_training)
if is_training and config.keep_prob < 1:
cell = tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(
cell, output_keep_prob=config.keep_prob)
return cell
cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell(
[make_cell() for _ in range(config.num_layers)], state_is_tuple=True)
self._initial_state = cell.zero_state(config.batch_size, data_type())
state = self._initial_state
# Simplified version of tf.nn.static_rnn().
# This builds an unrolled LSTM for tutorial purposes only.
# In general, use tf.nn.static_rnn() or tf.nn.static_state_saving_rnn().
#
# The alternative version of the code below is:
#
# inputs = tf.unstack(inputs, num=self.num_steps, axis=1)
# outputs, state = tf.nn.static_rnn(cell, inputs,
# initial_state=self._initial_state)
outputs = []
with tf.variable_scope("RNN"):
for time_step in range(self.num_steps):
if time_step > 0: tf.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables()
(cell_output, state) = cell(inputs[:, time_step, :], state)
outputs.append(cell_output)
output = tf.reshape(tf.concat(outputs, 1), [-1, config.hidden_size])
return output, state
def assign_lr(self, session, lr_value):
session.run(self._lr_update, feed_dict={self._new_lr: lr_value})
def export_ops(self, name):
"""Exports ops to collections."""
self._name = name
ops = {util.with_prefix(self._name, "cost"): self._cost}
if self._is_training:
ops.update(lr=self._lr, new_lr=self._new_lr, lr_update=self._lr_update)
if self._rnn_params:
ops.update(rnn_params=self._rnn_params)
for name, op in ops.items():
tf.add_to_collection(name, op)
self._initial_state_name = util.with_prefix(self._name, "initial")
self._final_state_name = util.with_prefix(self._name, "final")
util.export_state_tuples(self._initial_state, self._initial_state_name)
util.export_state_tuples(self._final_state, self._final_state_name)
def import_ops(self):
"""Imports ops from collections."""
if self._is_training:
self._train_op = tf.get_collection_ref("train_op")[0]
self._lr = tf.get_collection_ref("lr")[0]
self._new_lr = tf.get_collection_ref("new_lr")[0]
self._lr_update = tf.get_collection_ref("lr_update")[0]
rnn_params = tf.get_collection_ref("rnn_params")
if self._cell and rnn_params:
params_saveable = tf.contrib.cudnn_rnn.RNNParamsSaveable(
self._cell,
self._cell.params_to_canonical,
self._cell.canonical_to_params,
rnn_params,
base_variable_scope="Model/RNN")
tf.add_to_collection(tf.GraphKeys.SAVEABLE_OBJECTS, params_saveable)
self._cost = tf.get_collection_ref(util.with_prefix(self._name, "cost"))[0]
num_replicas = FLAGS.num_gpus if self._name == "Train" else 1
self._initial_state = util.import_state_tuples(
self._initial_state, self._initial_state_name, num_replicas)
self._final_state = util.import_state_tuples(
self._final_state, self._final_state_name, num_replicas)
@property
def input(self):
return self._input
@property
def initial_state(self):
return self._initial_state
@property
def cost(self):
return self._cost
@property
def final_state(self):
return self._final_state
@property
def lr(self):
return self._lr
@property
def train_op(self):
return self._train_op
@property
def initial_state_name(self):
return self._initial_state_name
@property
def final_state_name(self):
return self._final_state_name
class SmallConfig(object):
"""Small config."""
init_scale = 0.1
learning_rate = 1.0
max_grad_norm = 5
num_layers = 2
num_steps = 20
hidden_size = 200
max_epoch = 4
max_max_epoch = 13
keep_prob = 1.0
lr_decay = 0.5
batch_size = 20
vocab_size = 10000
rnn_mode = BLOCK
class MediumConfig(object):
"""Medium config."""
init_scale = 0.05
learning_rate = 1.0
max_grad_norm = 5
num_layers = 2
num_steps = 35
hidden_size = 650
max_epoch = 6
max_max_epoch = 39
keep_prob = 0.5
lr_decay = 0.8
batch_size = 20
vocab_size = 10000
rnn_mode = BLOCK
class LargeConfig(object):
"""Large config."""
init_scale = 0.04
learning_rate = 1.0
max_grad_norm = 10
num_layers = 2
num_steps = 35
hidden_size = 1500
max_epoch = 14
max_max_epoch = 55
keep_prob = 0.35
lr_decay = 1 / 1.15
batch_size = 20
vocab_size = 10000
rnn_mode = BLOCK
class TestConfig(object):
"""Tiny config, for testing."""
init_scale = 0.1
learning_rate = 1.0
max_grad_norm = 1
num_layers = 1
num_steps = 2
hidden_size = 2
max_epoch = 1
max_max_epoch = 1
keep_prob = 1.0
lr_decay = 0.5
batch_size = 20
vocab_size = 10000
rnn_mode = BLOCK
def run_epoch(session, model, eval_op=None, verbose=False):
"""Runs the model on the given data."""
start_time = time.time()
costs = 0.0
iters = 0
state = session.run(model.initial_state)
fetches = {
"cost": model.cost,
"final_state": model.final_state,
}
if eval_op is not None:
fetches["eval_op"] = eval_op
for step in range(model.input.epoch_size):
feed_dict = {}
for i, (c, h) in enumerate(model.initial_state):
feed_dict[c] = state[i].c
feed_dict[h] = state[i].h
vals = session.run(fetches, feed_dict)
cost = vals["cost"]
state = vals["final_state"]
costs += cost
iters += model.input.num_steps
if verbose and step % (model.input.epoch_size // 10) == 10:
print("%.3f perplexity: %.3f speed: %.0f wps" %
(step * 1.0 / model.input.epoch_size, np.exp(costs / iters),
iters * model.input.batch_size * max(1, FLAGS.num_gpus) /
(time.time() - start_time)))
return np.exp(costs / iters)
def get_config():
"""Get model config."""
config = None
if FLAGS.model == "small":
config = SmallConfig()
elif FLAGS.model == "medium":
config = MediumConfig()
elif FLAGS.model == "large":
config = LargeConfig()
elif FLAGS.model == "test":
config = TestConfig()
else:
raise ValueError("Invalid model: %s", FLAGS.model)
if FLAGS.rnn_mode:
config.rnn_mode = FLAGS.rnn_mode
if FLAGS.num_gpus != 1 or tf.__version__ < "1.3.0" :
config.rnn_mode = BASIC
return config
def main(_):
if not FLAGS.data_path:
raise ValueError("Must set --data_path to PTB data directory")
gpus = [
x.name for x in device_lib.list_local_devices() if x.device_type == "GPU"
]
if FLAGS.num_gpus > len(gpus):
raise ValueError(
"Your machine has only %d gpus "
"which is less than the requested --num_gpus=%d."
% (len(gpus), FLAGS.num_gpus))
raw_data = reader.ptb_raw_data(FLAGS.data_path)
train_data, valid_data, test_data, _ = raw_data
config = get_config()
eval_config = get_config()
eval_config.batch_size = 1
eval_config.num_steps = 1
with tf.Graph().as_default():
initializer = tf.random_uniform_initializer(-config.init_scale,
config.init_scale)
with tf.name_scope("Train"):
train_input = PTBInput(config=config, data=train_data, name="TrainInput")
with tf.variable_scope("Model", reuse=None, initializer=initializer):
m = PTBModel(is_training=True, config=config, input_=train_input)
tf.summary.scalar("Training Loss", m.cost)
tf.summary.scalar("Learning Rate", m.lr)
with tf.name_scope("Valid"):
valid_input = PTBInput(config=config, data=valid_data, name="ValidInput")
with tf.variable_scope("Model", reuse=True, initializer=initializer):
mvalid = PTBModel(is_training=False, config=config, input_=valid_input)
tf.summary.scalar("Validation Loss", mvalid.cost)
with tf.name_scope("Test"):
test_input = PTBInput(
config=eval_config, data=test_data, name="TestInput")
with tf.variable_scope("Model", reuse=True, initializer=initializer):
mtest = PTBModel(is_training=False, config=eval_config,
input_=test_input)
models = {"Train": m, "Valid": mvalid, "Test": mtest}
for name, model in models.items():
model.export_ops(name)
metagraph = tf.train.export_meta_graph()
if tf.__version__ < "1.1.0" and FLAGS.num_gpus > 1:
raise ValueError("num_gpus > 1 is not supported for TensorFlow versions "
"below 1.1.0")
soft_placement = False
if FLAGS.num_gpus > 1:
soft_placement = True
util.auto_parallel(metagraph, m)
with tf.Graph().as_default():
tf.train.import_meta_graph(metagraph)
for model in models.values():
model.import_ops()
sv = tf.train.Supervisor(logdir=FLAGS.save_path)
config_proto = tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=soft_placement)
with sv.managed_session(config=config_proto) as session:
for i in range(config.max_max_epoch):
lr_decay = config.lr_decay ** max(i + 1 - config.max_epoch, 0.0)
m.assign_lr(session, config.learning_rate * lr_decay)
print("Epoch: %d Learning rate: %.3f" % (i + 1, session.run(m.lr)))
train_perplexity = run_epoch(session, m, eval_op=m.train_op,
verbose=True)
print("Epoch: %d Train Perplexity: %.3f" % (i + 1, train_perplexity))
valid_perplexity = run_epoch(session, mvalid)
print("Epoch: %d Valid Perplexity: %.3f" % (i + 1, valid_perplexity))
test_perplexity = run_epoch(session, mtest)
print("Test Perplexity: %.3f" % test_perplexity)
if FLAGS.save_path:
print("Saving model to %s." % FLAGS.save_path)
sv.saver.save(session, FLAGS.save_path, global_step=sv.global_step)
if __name__ == "__main__":
tf.app.run()
三、运行
python E:\tensorflow_data\ptb_word_lm\ptb_word_lm.py --data_path=E:\tensorflow_data\ptb_word_lm\simple-examples\simple-examples\data --model small
这里只运行了一个小模型
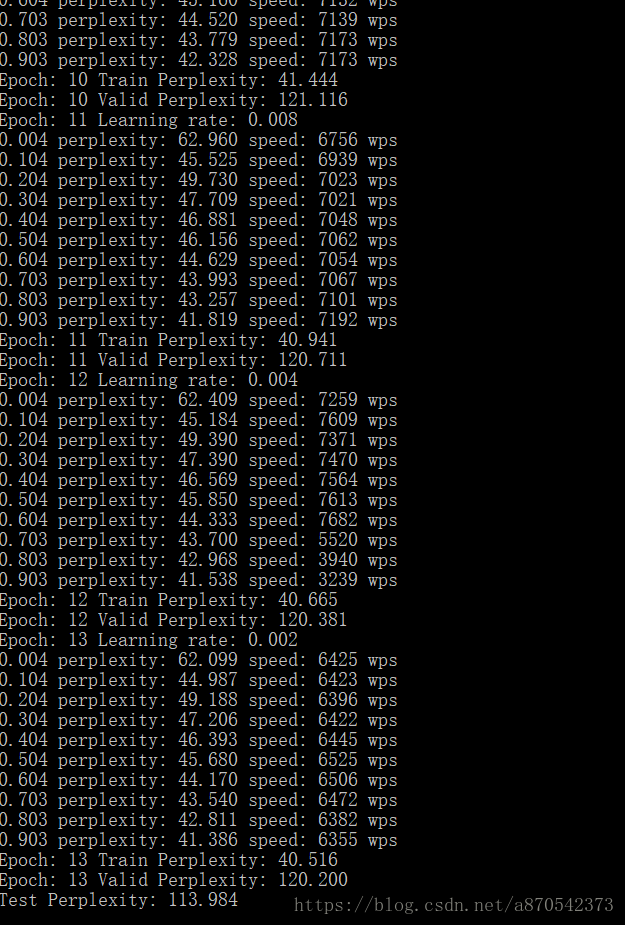
运行结果:
在13个epoch时,我们的测试perplexity为113.984