Mybatis数据源和连接池的学习总结
一、数据源DataSource的分类
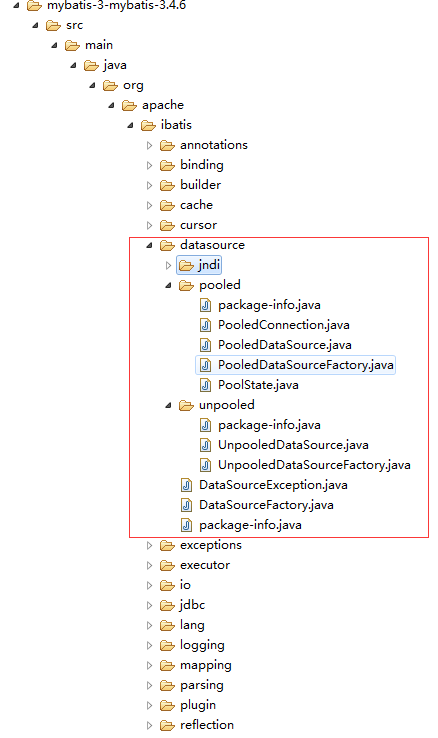
Mybatis的数据实现都在datasource这个包内:
即:
Mybatis把数据源分为了三类:
JNDI:使用JNDI实现数据源(这里不介绍这种)
UNPOOLED:不使用连接池的数据源()
POOLED:使用连接池的数据源
注:我着重学习的是POOLED和UNPOOLED的两种类型
即:
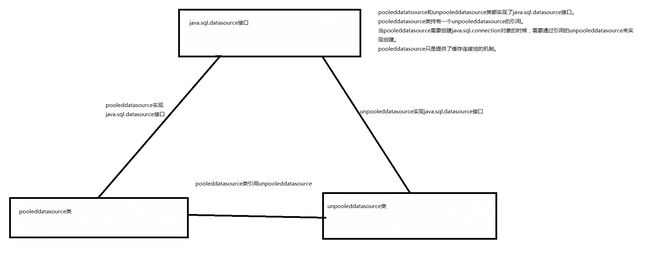
Mybatis内部分别定义实现了java.sql.datasource接口的UNPOOLEDDataSource和POOLEDDataSource类表示UNPOOLED和POOLED类型。如下图:
二、数据源DataSource的创建过程
Mybatis的数据源DataSource对象的创建发生在Mybatis的初始化的时候。我们看一下Mybatis初始化时候如何创建数据源DataSource。
在Mybatis的配置文件configuration-mybatis.xml文件中配置
在Mybatis初始化DataSource时候通过判断type的类型来初始化不同的数据源。
type=”POOLED” Mybatis会创建PooledDataSource实例
type=”UNPOOLED” Mybatis会创建UnPooledDataSource实例
type=”JNDI” MyBatis会从JNDI服务上查找DataSource实例,然后返回使用
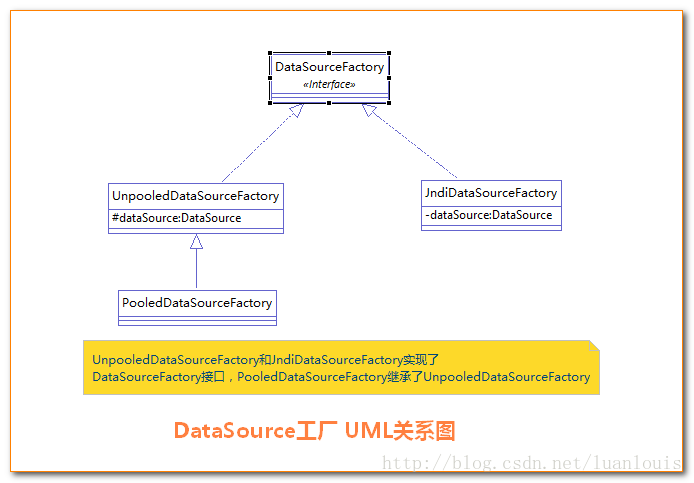
注意:Mybatis是通过工厂模式来创建数据源DataSource的,Mybatis定义了抽象工厂接口:org.apache.ibatis.datasource.DataSourceFactory的getDataSource()方法来获取数据源。
源码图:
package org.apache.ibatis.datasource;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public interface DataSourceFactory {
void setProperties(Properties props);
DataSource getDataSource();
}下图是三种数据源之间的关系:(了解即可)
三、DataSource数据源是什么时候创建Connection对象(这个是重点)
当我们创建了SQLSession之后,通过SqlSession执行sql语句的时候,Mybatis才会调用DataSource数据源去创建Connection对象。
我们使用mybatis完成数据库查询的例子:
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("Configuration-Mybatis.xml");
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder ssfb = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory ssf = ssfb.build(is);
SqlSession ss = ssf.openSession();
ss.selectList("select * from a");
}我们分析如下:
在为执行selectList()方法之前Mybatis还没有为我们创建Connection对象。
protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
}
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
if (level != null) {
connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel());
}
setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommmit);
} 四、在使用UnpooledDataSource数据源例子
当我们的Mybatis配置文件Configuration-mybatis.xml中的
例子:
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return doGetConnection(username, password);
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return doGetConnection(username, password);
}
private Connection doGetConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
Properties props = new Properties();
if (driverProperties != null) {
props.putAll(driverProperties);
}
if (username != null) {
props.setProperty("user", username);
}
if (password != null) {
props.setProperty("password", password);
}
return doGetConnection(props);
}
private Connection doGetConnection(Properties properties) throws SQLException {
//1.初始化驱动
initializeDriver();
//2.从DriverManager中获取连接,获取新的Connection对象
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
//3.配置connection属性
configureConnection(connection);
return connection;
}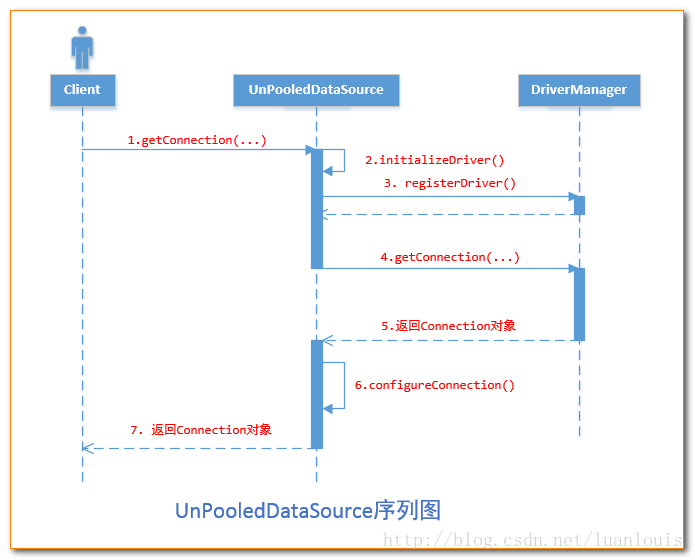
如上述的代码,UnpooledDataSource数据源会做一下事情:
1、 初始化驱动
2、使用DriverManager.getConnection(url,properties);获取一个新的连接。
3、配置Connection对象
4、返回Connection对象
总结:如上述的流程显示,用户每一次调用getConnection()方法,UnpooledDataSource数据源都会通过DriverManager创建新的Connection对象。
五、使用PooledDataSource数据源
PooledDataSource数据源在上面我就介绍了它拥有连接池的数据源。现在我们看一下PooledDataSource的基本原理:PooledDataSource数据源将Connection对象包裹成了PooledConnection对象放到PoolState容器中进行维护。MyBatis将连接池中的PooledConnection分为两种状态: 空闲状态(idle)和活动状态(active),这两种状态的PooledConnection对象分别被存储到PoolState容器内的idleConnections和activeConnections两个List集合中:
idleConnections:空闲(idle)状态PooledConnection对象被放置到此集合中,表示当前闲置的没有被使用的PooledConnection集合,调用PooledDataSource的getConnection()方法时,会优先从此集合中取PooledConnection对象。当用完一个java.sql.Connection对象时,MyBatis会将其包裹成PooledConnection对象放到此集合中。
activeConnections:活动(active)状态的PooledConnection对象被放置到名为activeConnections的ArrayList中,表示当前正在被使用的PooledConnection集合,调用PooledDataSource的getConnection()方法时,会优先从idleConnections集合中取PooledConnection对象,如果没有,则看此集合是否已满,如果未满,PooledDataSource会创建出一个PooledConnection,添加到此集合中,并返回。
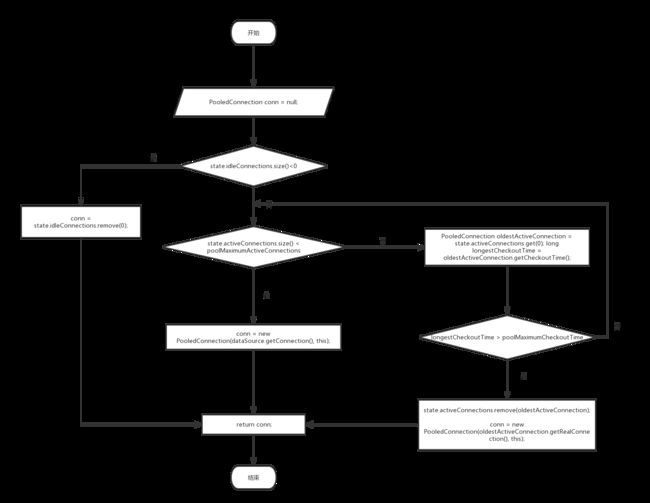
六、PooledDataSource数据源获取Connection连接的过程
public class PooledDataSource implements DataSource {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(PooledDataSource.class);
private final PoolState state = new PoolState(this);
private final UnpooledDataSource dataSource; //这里引用了UnpooledDataSource
// OPTIONAL CONFIGURATION FIELDS
protected int poolMaximumActiveConnections = 10; //最大的活跃连接数量
protected int poolMaximumIdleConnections = 5; //最大的空前连接数量
protected int poolMaximumCheckoutTime = 20000; //连接池内连接的最大校验时间,大于这个时间就可以认为它已经过期
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return popConnection(dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword()).getProxyConnection();
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return popConnection(username, password).getProxyConnection();
}
private PooledConnection popConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
boolean countedWait = false;
PooledConnection conn = null;
long t = System.currentTimeMillis();
int localBadConnectionCount = 0;
//判断PooledConnection是否是第一次创建
while (conn == null) {
synchronized (state) {
//判断连接池内是否有空闲的连接
if (!state.idleConnections.isEmpty()) {
//判断连接池内有空闲连接 就直接返回一个可用的PooledConnection对象
conn = state.idleConnections.remove(0);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Checked out connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " from pool.");
}
} else {
//连接池内没有空闲连接 2.这里也是第二部
// 查看活动状态的PooledConnection池activeConnections是否已满 (这里比较当前活跃连接池内连接数量与活跃连接池的最大数量)
if (state.activeConnections.size() < poolMaximumActiveConnections) {
// 当前活跃连接池还没满,创建一个新的PooledConnection对象,然后放到activeConnections池中,然后返回此PooledConnection对象
conn = new PooledConnection(dataSource.getConnection(), this);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Created connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// 当前活跃连接池已经满了,
PooledConnection oldestActiveConnection = state.activeConnections.get(0); //state.activeConnections.get(0):获取最先进入活跃连接池内的连接
long longestCheckoutTime = oldestActiveConnection.getCheckoutTime(); //oldestActiveConnection.getCheckoutTime():计算这个连接的校验时间
//看最先进入activeConnections池中的PooledConnection对象是否已经过期
if (longestCheckoutTime > poolMaximumCheckoutTime) {
//已经过期,从activeConnections池中移除此对象, 然后创建一个新的PooledConnection对象,添加到activeConnections中,然后将此对象返回
state.claimedOverdueConnectionCount++;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections += longestCheckoutTime;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += longestCheckoutTime;
state.activeConnections.remove(oldestActiveConnection);
if (!oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
try {
oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().rollback();
} catch (SQLException e) {
/*
Just log a message for debug and continue to execute the following
statement like nothing happend.
Wrap the bad connection with a new PooledConnection, this will help
to not intterupt current executing thread and give current thread a
chance to join the next competion for another valid/good database
connection. At the end of this loop, bad {@link @conn} will be set as null.
*/
log.debug("Bad connection. Could not roll back");
}
}
conn = new PooledConnection(oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection(), this);
conn.setCreatedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getCreatedTimestamp());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getLastUsedTimestamp());
oldestActiveConnection.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Claimed overdue connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// 没有过期,线程等待
try {
if (!countedWait) {
state.hadToWaitCount++;
countedWait = true;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Waiting as long as " + poolTimeToWait + " milliseconds for connection.");
}
long wt = System.currentTimeMillis();
state.wait(poolTimeToWait);
state.accumulatedWaitTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - wt;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
}
}
//如果获取PooledConnection成功,则更新其信息
if (conn != null) {
// ping to server and check the connection is valid or not
if (conn.isValid()) {
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
conn.setConnectionTypeCode(assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), username, password));
conn.setCheckoutTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
state.activeConnections.add(conn);
state.requestCount++;
state.accumulatedRequestTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - t;
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") was returned from the pool, getting another connection.");
}
state.badConnectionCount++;
localBadConnectionCount++;
conn = null;
if (localBadConnectionCount > (poolMaximumIdleConnections + poolMaximumLocalBadConnectionTolerance)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
}
}
}
}
if (conn == null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
return conn;
}
}PooledDataSource数据源获取Connection对象是通过引用UnPooledDataSource方法来获取的。
获取的步骤大致分为四部:
1.判断连接池内是否有空闲PooledConnection连接,有直接取出空闲的PooledConnection连接,返回。如果没有走第二步。
2.判断连接池内活跃连接集合是否已经满了,若果没有满,创建一个Connection连接,放入活跃连接集合内。如果已经满了走第三步。
3.这个时候我们查下看活跃连接集合(activeConnections)当中最先创建活跃连接是否过期,若果过期就把它从活跃连接集合中移除,创建一个新的连接放入活跃连接集合。如果没过期走第四步。
4.这个时候只能做线程等待。等来活跃连接过期,完事循环第二步。
流程图如下: