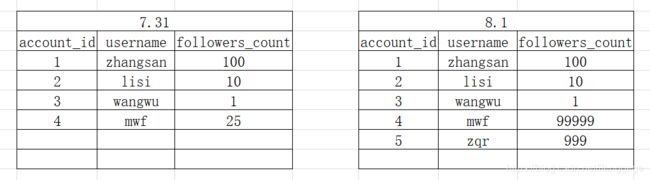
数据仓库历史数据存储 - 拉链表
假如我们有一个账号account表,我们需要在hive中存储(数据是从线上mysql读取binlog同步来的,是有明细变化的)
account表结构:account_id, username, followers_count, modified_at
我们经常使用的存储方式有快照表和流水表。快照表就是以时间为粒度(比如天),生成每个时间的全量数据快照;流水表则是记录数据的每一条具体的改变。
现在有一个需求:需要记录账号的历史变更情况
快照表实现
这里以天为粒度,对每天账号最终的状态进行存储即可。
在hive中,以天为分区存储,我们需要访问某天的历史状态,直接指定分区即可访问
-- 访问20190801时某个账号的状态
select * from account_snapshot where ds = "20190801" and account_id = xxx
快照表的缺点是:当单表的数据量比较大时,每天存储全量的快照,会导致不必要的资源开支
流水表实现
流水表记录数据的每一条变化,来一条插入一条
这种存储方法对数据的使用者不太友好
-- 查询20190801时某个账号的状态
select * from (
select
*,
row_number over(partition by account_id order by modified_at desc) as ro
from account where modified_at <= "2019-08-02 00:00:00" and account_id = xxx
) where ro = 1
以上的两种方式,多多少少都存在问题,接下来介绍拉链表的使用
拉链表
拉链表是维护历史状态、以及最新状态的一种方式。
拉链表对快照表进行了优化,根据拉链粒度(一般为时间)的不同,去除了在粒度范围内不变的数据。
拉链表可以维护两个时间(start_time, end_time),来标识当前记录是否还有效,以及更好的定位历史数据
实现前提:
首先要有某一时刻的全量数据,作为起始表
其次要有流水表或者快照表两者其一,作为变化的依据
实现:
-- 原始数据
create table account(
account int ,
username varchar,
followers_count int ,
modified_at timestamp
)
-- 创建拉链表
create table account_zip(
account int ,
username varchar,
followers_count int ,
modified_at timestamp ,
start_time timestamp, -- 记录的有效起始时间
end_time timestamp, -- 记录的有效结束时间
)
今天是8.1,我们从7.31号的数据开始记录
首先我们将7.31号的数据导入我们的拉链表中
insert into account_zip
select
*,
"2019-07-31 00:00:00" as start_time ,
"9999-12-31 00:00:00" as end_time
from
account ;
这里的start_time指的是这条记录是在7.31改变生效的,end_time是指这条记录在9999-12-31前是有效的。导入拉链表后,表内的记录如下所示,
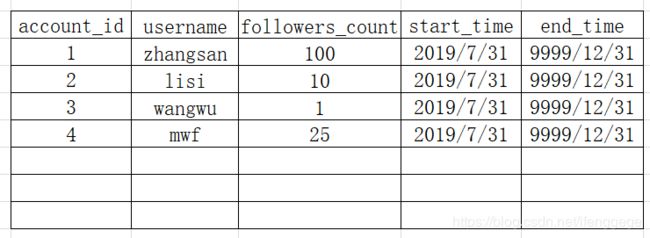
接下来,我们在8.1的时候,对账号进行修改和新增
我们可以看到8.1进行了一条记录的修改(修改mwf的followers_account)和一条记录的新增(新增account_id为5的用户)
针对修改来说:
在拉链中已经存在mwf的信息,8.1对他进行修改,
我们可以将之前那条记录的end_time修改为8.1,表示他在8.1之后失效了
然后将8.1的这次操作写入拉链表,他的start_time为8.1,end_time为9999-12-31
针对新增来说:
我们直接将它写入拉链表,start_time为8.1,end_time为9999-12-31
8.1过后,我们的拉链表变为了如下版本:
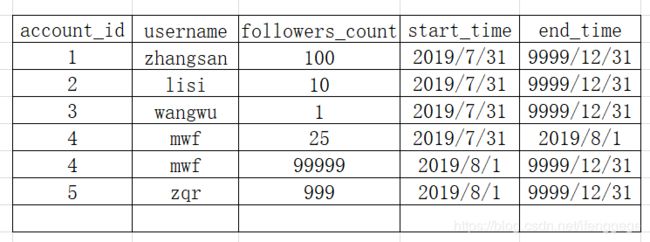
以上我们就实现了一个拉链表
查询记录
- 查询当前的有效记录
select * from account_zip where end_time = "9999-12-31 00:00:00"
- 如查询2019-07-31时的历史快照
-- 在7.31号前开始生效,且在7.31号当天时还没有失效, 此处通过两个时间刚好限定了范围
select * from account_zip
where start_time <= "2019-07-31 00:00:00" and end_time >= "2019-07-31 00:00:00"
基于快照表生成拉链表
insert into account_zip_tmp
-- 联合两个表,写入临时的拉链表中
select * from (
-- 改变原有拉链表中 失效的数据
-- 这里用到了md5来比较数据是否相同
select
bak.account_id,
bak.username ,
bak.followers_count ,
bak.modified_at,
bak.start_time
case
when bak.end_time = "9999-12-31 00:00:00" and md5(concat(
coalesce(bak.username, 'NULL'),
coalesce(bak.followers_count, 'NULL'),
coalesce(bak.modified_at, 'NULL')
)) != md5(concat(
coalesce(new.username, 'NULL'),
coalesce(new.followers_count, 'NULL'),
coalesce(new.modified_at, 'NULL')
))
then "2019-07-31 00:00:00"
else bak.end_time
end as end_time
from account_zip as bak
left join (
select * from account_snapshot where ds = "20190801"
) as new on bak.account_id = new.account_id
union
-- 写入修改或新增的数据
select
a.account_id,
a.username ,
a.followers_count ,
a.modified_at,
"2019-07-31 00:00:00" as start_time,
"9999-12-31 00:00:00" as end_time
from (
select * from account_snapshot where ds = "20190801"
) as a
left join (
select
*
from account_zip
where end_time = "9999-12-31 00:00:00"
) on a.account_id = b.account_id
where md5(concat(
coalesce(a.username, 'NULL'),
coalesce(a.followers_count, 'NULL'),
coalesce(a.modified_at, 'NULL')
)) != md5(concat(
coalesce(b.username, 'NULL'),
coalesce(b.followers_count, 'NULL'),
coalesce(b.modified_at, 'NULL')
))
);
-- 将临时拉链表写回拉链表
insert overwrite table account_zip
select * from account_zip_tmp
参考
https://www.jianshu.com/p/799252156379
实践出真知 !