JavaScript高级程序设计——知识点整理(Part 3)
理解对象
属性类型
数据属性,包含一个数据值的位置
- [[Configurable]]表示能否通过delete删除属性,能否修改属性的特性,能否把属性修改为访问器属性
- [[Enumerable]]表示能否通过for-in循环返回属性
- [[Writable]]表示能否修改属性的值
- [[Value]]包含这个属性的数据值
- 修改默认属性的特性Object.defineProperty()
var person = {}; Object.defineProperty(person, "name", { writable: false, value: "Nicholas" }); alert(person.name); //"Nicholas" person.name = "Greg"; alert(person.name); //"Nicholas"可以多次调用Object.defineProperty()修改同一个属性,但把configurable设置为false之后,就只能修改writable特性,修改 其他会报错
- 字面量方法定义属性,该属性的数据属性默认值如下:configurable、enumerable、writable为true,value为undefined
- Object.defineProperty()如果不指定,该属性的数据属性默认值如下:configurable、enumerable、writable为false,value为 undefined
访问器属性,不包含数据值
- [[Configurable]]表示能否通过delete删除属性,能否修改属性的特性,能否把属性修改为数据属性
- [[Enumerable]]表示能否通过for-in循环返回属性
- [[Get]]在读取属性时调用的函数
- [[Set]]在写入属性时调用的函数
- 访问器属性不能直接定义,必须使用Object.defineProperty()来定义
var book = { _year: 2004, edition: 1 }; Object.defineProperty(book, "year", { get: function() { return this._year; }, set: function(newValue) { if (newValue > 2004) { this._year = newValue; this.edition += newValue - 2004; } } }); book.year = 2005; alert(book.edition); //2- 下划线用于表示只能通过对象方法访问的属性
- 不一定要同时指定getter和setter,不指定表示不能读或者不能写
定义多个属性
var book = {};
Object.defineProperties(book, {
_year: {
value: 2004
},
edition: {
value: 1
},
year: {
get: function() {
return this._year;
},
set: function(newValue) {
if (newValue > 2004) {
this._year = newValue;
this.edition += newValue - 2004;
}
}
}
});
book.year = 2005;
alert(book.edition); //2读取属性的特性
- Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor()
var descriptor = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(book, "_year"); //数据属性 alert(descriptor.value); //2004 alert(descriptor.configurable); //false alert(typeof descriptor.get); //"undefined" var descriptor = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(book, "year"); //访问器属性 alert(descriptor.value); //undefined alert(descriptor.enumerable); //false alert(typeof descriptor.get); //"function"
创建对象
工厂模式
function createPerson(name, age, job) { var o = new Object(); o.name = name; o.age = age; o.job = job; o.sayName = function(){ alert(this.name); }; return o; } var person1 = createPerson("Nicholas", 29, "Software Engineer"); var person2 = createPerson("Greg", 27, "Doctor"); person1.sayName(); //"Nicholas" person2.sayName(); //"Greg"- 解决了创建多个相似对象的问题,但却没有解决对象识别的问题(即怎样知道一个对象的类型)
构造函数模式
function Person(name, age, job) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.job = job; this.sayName = function() { alert(this.name); }; } // 当作构造函数使用 var person = new Person("Nicholas", 29, "Software Engineer"); person.sayName(); //"Nicholas" // 作为普通函数调用 Person("Greg", 27, "Doctor"); //添加到window window.sayName(); //"Greg" // 在另一个对象的作用域中调用 var o = new Object(); Person.call(o, "Kristen", 25, "Nurse"); o.sayName(); //"Kristen"- 两个对象都有一个constructor(构造函数)属性,该属性指向Person
- 缺陷在于:每个对象都有一个名为sayName()的方法,但这些方法又不是同一个Function的实例
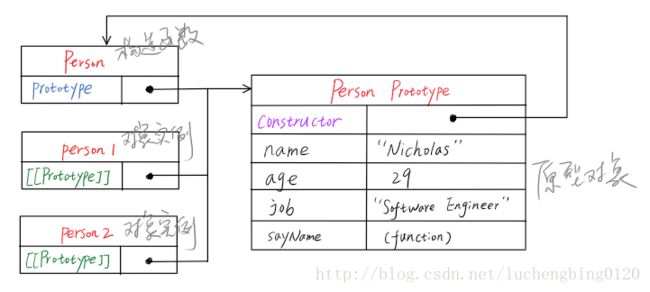
原型模式
function Person(){ } Person.prototype.name = "Nicholas"; Person.prototype.age = 29; Person.prototype.job = "Software Engineer"; Person.prototype.sayName = function(){ alert(this.name); }; var person1 = new Person(); person1.sayName(); //"Nicholas" var person2 = new Person(); person2.sayName(); //"Nicholas" alert(person1.sayName == person2.sayName); //true-
- 实例的[[Prototype]]指向原型对象,而不是构造函数;构造函数的prototype属性也指向原型对象;而原型对象的constructor属性指 向构造函数
- isPrototypeOf()表示参数的[[Prototype]]是否指向调用者,即调用者是不是参数的原型对象
- Object.getPrototypeOf()返回[[Prototype]]的值,即原型对象
- 当为对象实例添加一个属性时,这个属性就会屏蔽原型对象中保存的同名属性;使用delete操作符可以删除实例属性,使我们能够重 新访问原型中的属性
- hasOwnProperty()可以检测一个属性是存在与实例中还是存在于原型中
- 原型与in操作符
- 单独使用in操作符,会在通过对象能够访问给定属性时返回true,无论该属性存在于实例中还是原型中
- 使用for-in循环时,返回的是所有能够通过对象访问的、可枚举的(enumerable)属性,包括实例和原型中的
- 要获得对象上所有可枚举的实例属性,可以使用Object.keys()方法,该方法接受一个对象作为参数,返回一个包含所有可枚举属性的 字符串数组,可作用于原型对象
- Object.getOwnPropertNames()返回所有实例属性,无论它是否可枚举,可作用于原型对象
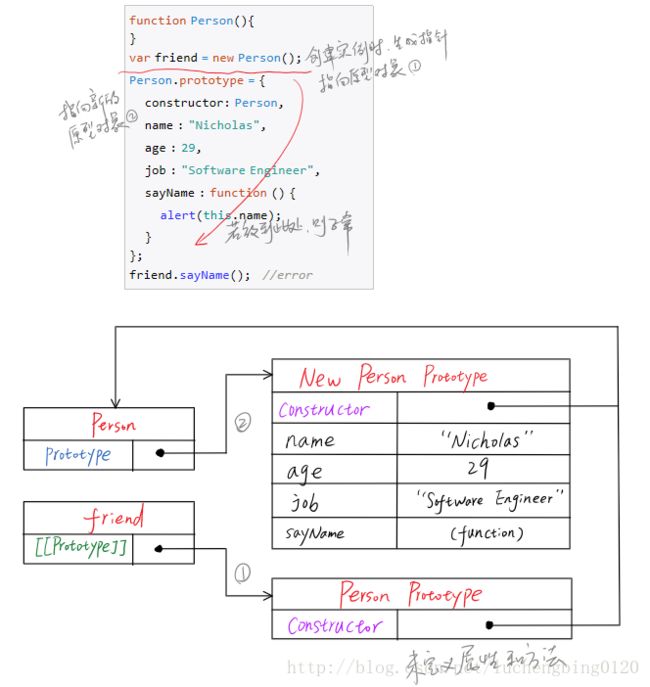
更简单的原型语法
function Person(){ } Person.prototype = { name : "Nicholas", age : 29, job: "Software Engineer", sayName : function () { alert(this.name); } }; var friend = new Person(); alert(friend instanceof Object); //true alert(friend instanceof Person); //true alert(friend.constructor == Person); //false alert(friend.constructor == Object); //true- 重写了默认的prototype对象,因此constructor属性也就变成了新对象的constructor属性(指向Object构造函数),不再指向 Person函数
- 可以特意设置constructor属性的值,但是这样又会导致constructor属性的[[Enumerable]]特性被设置为true,默认是false的。代码 如下:
function Person(){ } Person.prototype = { constructor : Person, name : "Nicholas", age : 29, job: "Software Engineer", sayName : function () { alert(this.name); } };- 可以使用defineProperty()添加constructor属性,并设置[[Enumerable]]特性为false
原型的动态性
-
组合使用构造函数模式和原型模式
- 构造函数模式用于定义实例属性,而原型模式用于定义方法和共享的属性
function Person(name, age, job){ this.name = name; this.age = age; this.job = job; this.friends = ["Shelby", "Court"]; } Person.prototype = { constructor: Person, sayName : function () { alert(this.name); } }; var person1 = new Person("Nicholas", 29, "Software Engineer"); var person2 = new Person("Greg", 27, "Doctor"); person1.friends.push("Van"); alert(person1.friends); //"Shelby,Court,Van" alert(person2.friends); //"Shelby,Court" alert(person1.friends === person2.friends); //false alert(person1.sayName === person2.sayName); //true动态原型模式
function Person(name, age, job){ //属性 this.name = name; this.age = age; this.job = job; //方法 if (typeof this.sayName != "function"){ Person.prototype.sayName = function(){ alert(this.name); }; } } var friend = new Person("Nicholas", 29, "Software Engineer"); friend.sayName();- sayName()方法不存在的情况下,将它添加到原型中
寄生构造函数模式
function Person(name, age, job){ var o = new Object(); o.name = name; o.age = age; o.job = job; o.sayName = function(){ alert(this.name); }; return o; } var friend = new Person("Nicholas", 29, "Software Engineer"); friend.sayName(); //"Nicholas"- 建议在可以使用其他模式的情况下,不要使用这种模式
稳妥构造函数模式
function Person(name, age, job) { //创建要返回的对象 var o = new Object(); //可以在这里定义私有变量和函数 //添加方法 o.sayName = function() { alert(name); }; //返回对象 return o; } var friend = Person("Nicholas", 29, "Software Engineer"); friend.sayName(); //"Nicholas"- 与寄生构造函数模式的区别在于:
- 新创建对象的实例方法不引用this
- 不适用new操作符调用构造函数
- 变量friend中保存的是一个稳妥对象,而除了调用sayName()方法外,没有别的方法可以访问其数据成员(传入到构造函数中的原始数据)
- 与寄生构造函数模式的区别在于:
继承
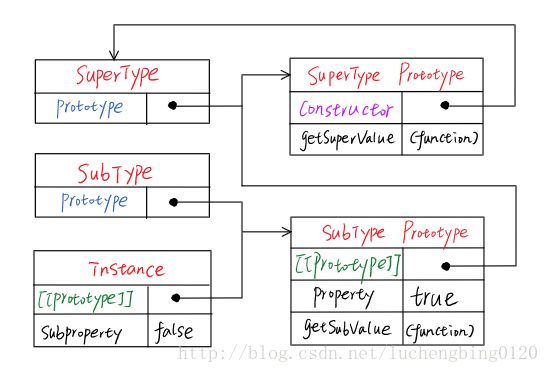
原型链
function SuperType() { this.property = true; } SuperType.prototype.getSuperValue = function() { return this.property; }; function SubType() { this.subproperty = false; } //继承了SuperType SubType.prototype = new SuperType(); SubType.prototype.getSubValue = function () { return this.subproperty; }; var instance = new SubType(); alert(instance.getSuperValue()); //true- 给原型添加方法的代码一定要放在替换原型的语句之后
- 通过原型链实现继承时,不能使用对象字面量创建原型方法,这样会重写原型链
借用构造函数
function SuperType() { this.colors = ["red", "blue", "green"]; } function SubType() { //inherit from SuperType SuperType.call(this); } var instance1 = new SubType(); instance1.colors.push("black"); alert(instance1.colors); //"red,blue,green,black" var instance2 = new SubType(); alert(instance2.colors); //"red,blue,green"组合继承(最常用的继承模式)
- 将原型链和借用构造函数的技术组合到一块
function SuperType(name) { this.name = name; this.colors = ["red", "blue", "green"]; } SuperType.prototype.sayName = function() { alert(this.name); }; function SubType(name, age) { //继承属性 SuperType.call(this, name); this.age = age; } //继承方法 SubType.prototype = new SuperType(); SubType.prototype.sayAge = function() { alert(this.age); }; var instance1 = new SubType("Nicholas", 29); instance1.colors.push("black"); alert(instance1.colors); //"red,blue,green,black" instance1.sayName(); //"Nicholas"; instance1.sayAge(); //29 var instance2 = new SubType("Greg", 27); alert(instance2.colors); //"red,blue,green" instance2.sayName(); //"Greg"; instance2.sayAge(); //27原型式继承
- Object.create()方法,接受两个参数:一个用作新对象原型的对象和(可选的)一个为新对象定义额外属性的对象
var person = { name: "Nicholas", friends: ["Shelby", "Court", "Van"] }; var anotherPerson = Object.create(person, { name: { value: "Greg" } }); alert(anotherPerson.name); //"Greg"寄生式继承
function createAnother(original) { var clone = object(original); //通过调用函数创建一个新对象 clone.sayHi = function() { //以某种方式来增强这个对象 alert("hi"); }; return clone; //返回这个对象 }寄生组合式继承(引用类型最理想的继承范式)
- 在组合继承中,继承方法的语句,会将超类实例的属性添加到子类的原型中,然后在继承属性的语句中,会将超类实例的属性添加到子类的 实例中从而覆盖原型中的属性,所以继承方法的时候不需要实例的属性,修改为使用object函数创建对象
function object(o){ function F(){} F.prototype = o; return new F(); } function inheritPrototype(subType, superType){ var prototype = object(superType.prototype); //创建对象 prototype.constructor = subType; //增强对象 subType.prototype = prototype; //指定对象 } function SuperType(name){ this.name = name; this.colors = ["red", "blue", "green"]; } SuperType.prototype.sayName = function(){ alert(this.name); }; function SubType(name, age){ SuperType.call(this, name); this.age = age; } inheritPrototype(SubType, SuperType); SubType.prototype.sayAge = function(){ alert(this.age); }; var instance1 = new SubType("Nicholas", 29); instance1.colors.push("black"); alert(instance1.colors); //"red,blue,green,black" instance1.sayName(); //"Nicholas"; instance1.sayAge(); //29 var instance2 = new SubType("Greg", 27); alert(instance2.colors); //"red,blue,green" instance2.sayName(); //"Greg"; instance2.sayAge(); //27