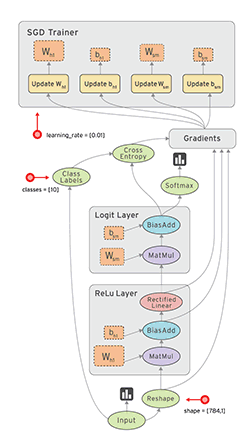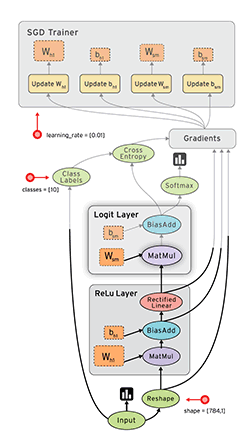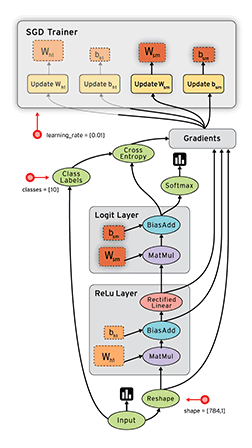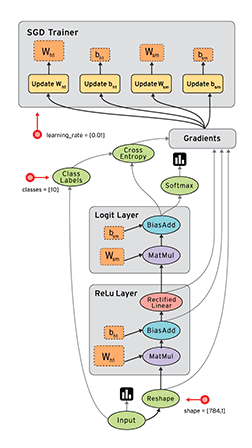
2、TensorFlow 的计算模型、运行模型、数据模型
一、TensorFlow 简介
1. TensorFlow 的定义
Tensor(张量) 意味着 N 维数组,Flow(流) 意味着基于数据流图的计算,TensorFlow 代表着
张量在图中通过运算(op)进行传递和变换
2. TensorFlow 的工作模式
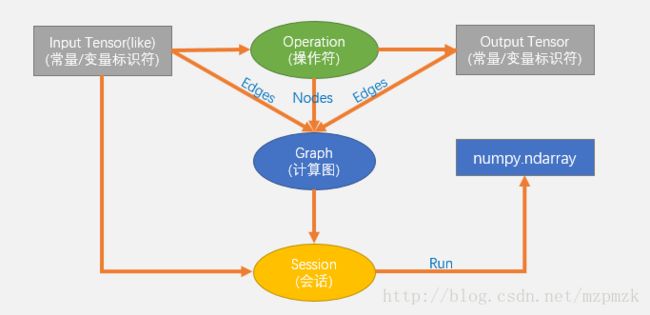
TensorFlow 使用图(Graphs)来表示计算任务,图中的节点称之为 op(Operation),一个 op 可以获得 0 个或多个张量(Tensor),通过创建会话(Session)对象来执行计算,产生 0 个或多个Tensor。所以,TensorFlow 的工作模式分为以下两步:
- Define the
computation graph- Run the graph (with data) in
Session为什么需要提前定义好计算图,然后再去执行运算?
Save computation:only run subgraphs that lead to the values you want to fetchFacilitate distributed computation: spread the work across multiple CPUs, GPUs, or devicesFacilitates auto-differentiation:break computation into small, differential pieces
3. TensorFlow 的特点
- 异步的:一处写,一处读,一处训练
- 全局的:操作添加到全局的
Graph中,监控添加到全局的summary中,参数/损失添加到全局的collection中- 符号式的:创建时没有具体值,运行时才传入
4、TF High-Level API
KerasTFLearnTensorlayertf.contrib.learn:tensorflow 界的 scikit-learntf.contrib.slim:轻量浓缩版本高级接口,可以很方便地定义/训练/评估复杂的网络结构模型
二、TensorFlow 核心概念
- Graph holds operations and tensors, not values.
- Session is where you can run or evaluate operations and tensors.
1. TensorFlow 的计算模型------计算图(Graph)
a、Building a tf.Graph
-
TensorFlow 使用
图来表示计算任务,图(Graphs)是由op 对象和 tensor(like) 对象组成的,所以构建图的过程其实就是:- 创建 op 对象的过程
- 以及如何将这些个 op 对象和 tensor(like) 对象
连接起来的过程
-
获取默认计算图:
tf.get_default_graph() -
重建一张图来代替原来的默认图:
tf.reset_default_graph(),注意,使用该函数时必须保证当前图的资源已经全部释放 -
Graph 类的常用方法
class tf.Graph()
常用方法:
as_default(): Returns a context manager that makes this Graph the default graph.device(device_name_or_function):指定运行计算的设备as_graph_def():Returns aGraphDef protocol bufferget_tensor_by_name(name):返回指定名称(string)的Tensor,等价于 tensor。注意,name 的形式为:: get_operation_by_name(name):返回指定名称(string)的Operation,等价于 tensor.op。 注意,name 的形式为:get_operations():以列表的形式返回图中所有的操作节点。
- 代码实践
import tensorflow as tf c = tf.constant([5], name='c1') d = tf.constant([4], name='d1') e = tf.add(c, d, name='add1') with tf.Session() as sess: print('Tensor name is: %s, Op name is: %s' %(e.name, e.op.name)) # 每个操作节点(Op Node)是一个 NodeDef 对象,包含 name、op、input、device、attr 等属性 node_name_list = [node.name for node in tf.get_default_graph().as_graph_def().node] for node_name in node_name_list: print(node_name) print(sess.run(e)) # 当直接加载 .meta 或 .pb 形式的计算图时,可以使用 Tensor name 来获取相应的值 print(sess.run(tf.get_default_graph().get_tensor_by_name('add1:0'))) # 输出 Tensor name is: add1:0, Op name is: add1 [u'c1', u'd1', u'add1'] [9] [9]
b、Graph structure
- 由
tf.Operation objects(nodes) andtf.Tensor(like) objects(edges) 组成- tf.Operation objects: represent units of computation
- tf.Tensor objects: represent the units of data that flow between operations
c、Graph collections
-
在一个计算图中,可以通过集合(collection)来管理不同类别的资源(张量、变量、队列资源等)。
- 通过
tf.add_to_collection(name, value)函数将资源加入一个或多个集合中 - 通过
tf.get_collection(name, scope=None)获取一个集合里面的所有资源
- 通过
-
tf.add_to_collection(name, value)- name: The key(
any string is a valid collection name) for the collection(即,集合名称). The GraphKeys class contains many standard names for collections. - value: The value to add to the collections.
- name: The key(
-
tf.get_collection(name, scope=None)- Returns a list of values in the collection with the given name.
- Class tf.GraphKeys defines some of the standard keys(即,集合名称),以下是 TF 自动管理的几个最常用的集合
tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLEStf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLEStf.GraphKeys.LOCAL_VARIABLEStf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPStf.GraphKeys.MODEL_VARIABLEStf.GraphKeys.SUMMARIEStf.GraphKeys.REGULARIZATION_LOSSEStf.GraphKeys.QUEUE_RUNNERS- …
eg: tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES),亦可使用 Variable helper functions 中的相关函数取得集合中的值tf.global_variables(scope=None)tf.trainable_variables(scope=None)tf.local_variables(scope=None)tf.model_variables(scope=None)
- 如果想要所定义的变量不可训练(非权重参数)的话,可以使用以下两种方式实现:
# 1、specify trainable=False as an argument to tf.get_variable my_non_trainable = tf.get_variable("my_non_trainable", shape=(), trainable=False) # 2、add it to the tf.GraphKeys.LOCAL_VARIABLES collection my_local = tf.get_variable("my_local", shape=(), collections=[tf.GraphKeys.LOCAL_VARIABLES])
-
tf.add_n(inputs, name=None)- inputs: A list of Tensor objects, each with same shape and type.
- eg:
tf.add_n(tf.get_collection('l2_losses')) # Adds all input tensors element-wise
d、Graph control_denpendencies
tf.control_dependencies(control_inputs)control_inputs: A list of Operation or Tensor objects which must be executed or computed before running the operations defined in the context. Can also be None to clear the control dependencies.- Use
with keywordto specify that all operations constructed within the context should have control dependencies on control_inputs,eg:
with tf.control_dependencies([a, b, c]): # `d` and `e` will only run after `a`, `b`, and `c` have executed. d = ... e = ...
e、Visualize the graph
# 1、Write the graph defination to disk
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('graphs/', sess.graph)
# 2、Close summary writer
writer.close()
# 3、Visualize the graph in tensorboard
tensorboard --logdir graphs [--port 8888 --host 192.168.1.144] # 括号为可选参数,当在服务器上使用时可能会需要这些参数
2. TensorFlow 的运行模型------会话(Session)
a、Session 的简介
- 图必须通过
创建一个 Session 对象来执行计算任务,会话将图的 op分发到诸如 CPU 或 GPU 之类的设备上, 同时提供执行 op 的方法。 - 这些方法执行后,将产生
numpy.ndarray类型的数据返回。# 通过 Python 的上下文管理器来管理这个会话,不需要再调用Session.close()函数来关闭会话 with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(...)
b、Session 的初始化参数
- target:specifies the
execution engineto use. - graph:specifies the
Graph objectthat will be launched in the Session. If no,the default graphwill be launched - config:allows users to specify options to configure the session, such as
limiting the number of CPUs or GPUsto use,setting optimization parametersfor graphs, andloggingoptions.
c、Session 对象的 run 方法
- Runs operations and evaluates tensors in fetches
必选参数(fetches):A single graph element, a list of graph elements, or a dictionary whose values are graph elements or lists of graph elements可选参数(feed_dict):A dictionary that maps graph elements to values,用于为数据流图喂数据或者覆盖数据流图中的 Tensor 对象值
3. Operation 操作符
a、Operation 简介
- An Operation is a
nodein a TensorFlow Graph that takeszero or more Tensor objectsas input, and produceszero or more Tensor objectsas output. - 每个 op 构造方法都可接收一个
name 参数:give an identifier to the nodes we create
b、Operation 节点之间的依赖关系
- how do we make sure our computer only computes the necessary nodes without having to tell it by hand?
The answer:use our dependencies to ensure each node has alist of the nodesit directly (not indirectly) depends on
- The main thing to look out for is to keep track of nodes that were already calculated and to
store their value in memory- that way wedon’t calculate the same node over and over again
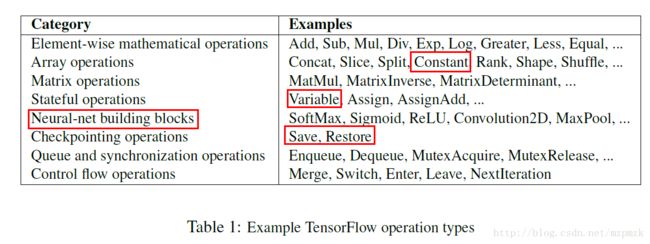
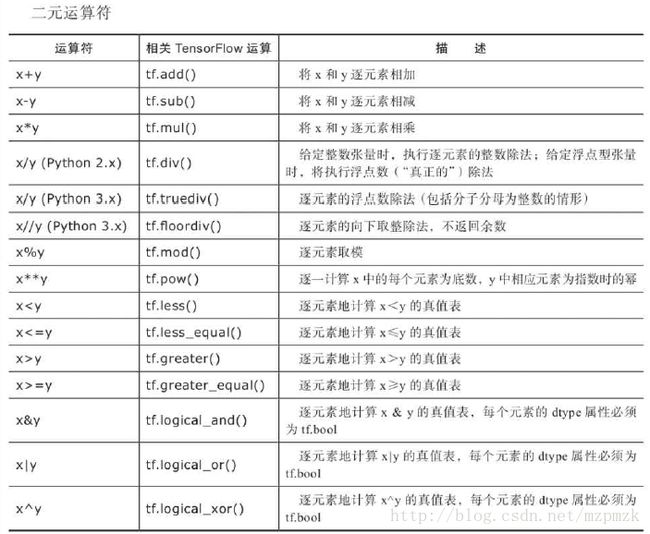
c、常用 op 操作的类型:
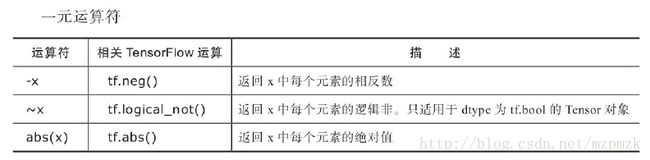
d、op 操作符的重载
Using these overloaded operators can be great when quickly putting together code, but you will not be able to give name values to each of these Operations
- 判断操作符(==):
judge_bool = tf.equal(x, y, name=None)- 赋值操作符:
update = tf.assign(old_value, new_value)
4. TensorFlow 的数据模型------张量(Tensor)
三、参考资料
1、https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/graphs&sessions
2、https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Graph
3、https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/GraphKeys
4、通过 g.as_graph_def().node 获取模型全部节点的名称