用户可以以触摸屏幕或摇动设备等多种方式操作他们的iOS设备。 iOS系统会对用户操作设备的时动作做出解释并把该信息传递给应用程序。应用程序对用户各种自然的动作都能处理越全面,用户体验也就越好。
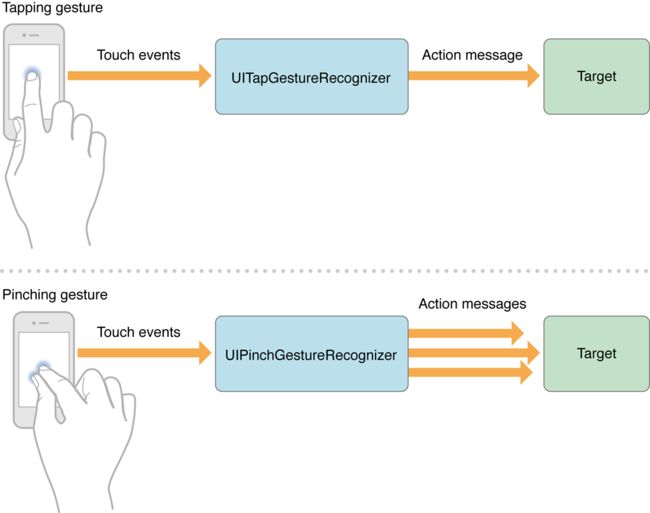
iOS系统通过事件(Event)将用户的操作传递给app,事件分为多种形式:多触摸事件,运动事件以及控制多媒体(通过外部硬件控制)的事件。程序中可以通过内置在UIKit里的常用手势和一些定制化手势来响应用户的各种操作手势。如果可能的话,最好是使用这些内置的手势,可以缩减了代码总量。内置在UIKit里标准控件的手势例如 UIButton 和 UISlider, 分别可以对点击和拖动手势响应。如果想应用程序识别一个独特的手势,比如一个漩涡状运动,可以创建自定义手势。 手势识别器为复杂的事件处理逻辑提供了一个高层次的抽象,应用程序中实现触摸事件处理(touch-event handling)应该考虑使用。
UIKit 内置的手势及对应class包括:
点击Tapping (any number of taps)::UITapGestureRecognizer
向内/外捏Pinching in and out (for zooming a view)::UIPinchGestureRecognizer
滑动/拖动Panning or dragging::UIPanGestureRecognizer
快速滑动Swiping (in any direction)::UISwipeGestureRecognizer
旋转Rotating (fingers moving in opposite directions)::UIRotationGestureRecognizer
长按Long press (also known as “touch and hold”)::UILongPressGestureRecognizer
手势可以分为离散手势和连续手势。 一个离散手势,如一次tap或一次swipe,只发生一次。一个连续手势,如捏合,发生时持续一段时间。 对于离散手势,手势识别就给目标发送一个操作消息。对于连续手势,手势识别则一直发送操作消息给目标直到操作结束。
你需要做三件事来添加一个内建手势识别到应用程序:
创建并配置一个手势识别实例。该步骤包括分配一个响应手势的目标,操作,以及手势指定的各种属性(比如 numberOfTapsRequired).
把手势识别连接到一个视图。
实现响应手势的操作方法。
对于离散型手势:
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
// Create and initialize a tap gesture
UITapGestureRecognizer *tapRecognizer = [[UITapGestureRecognizer alloc]
initWithTarget:self action:@selector(respondToTapGesture:)];
// Specify that the gesture must be a single tap
tapRecognizer.numberOfTapsRequired = 1;
// Add the tap gesture recognizer to the view
[self.view addGestureRecognizer:tapRecognizer];
}
// 手势的响应方法
- (IBAction)showGestureForTapRecognizer:(UITapGestureRecognizer *)recognizer
{
// Get the location of the gesture
CGPoint location = [recognizer locationInView:self.view];
// Display an image view at that location
[self drawImageForGestureRecognizer:recognizer atPoint:location];
// Animate the image view so that it fades out
[UIView animateWithDuration:0.5 animations:^{
self.imageView.alpha = 0.0;
}];
}```
###对于连续型手势:
// Respond to a rotation gesture
-
(IBAction)showGestureForRotationRecognizer:(UIRotationGestureRecognizer *)recognizer
{
CGPoint location = [recognizer locationInView:self.view];// 随着手势旋转图片 CGAffineTransform transform = CGAffineTransformMakeRotation([recognizer rotation]); self.imageView.transform = transform; [self drawImageForGestureRecognizer:recognizer atPoint:location]; // 通过手势状态决定最终形式 if (([recognizer state] == UIGestureRecognizerStateEnded) || ([recognizer state] == UIGestureRecognizerStateCancelled)) { [UIView animateWithDuration:0.5 animations:^{ self.imageView.alpha = 0.0; self.imageView.transform = CGAffineTransformIdentity; }]; }
}
###手势状态
手势识别在有限状态机中的各种预定的状态之间切换。所有的手势识别起点都是“可能的状态UIGestureRecognizerStatePossible”
* 对于离散型手势,手势可能识别失败UIGestureRecognizerStateFailed或被识别UIGestureRecognizerStateRecognized,从而结束识别过程;

* 对于连续性手势,每次手势识别改变状态时,除非过渡到失败或取消状态,都给它的响应目标发送消息。当手势第一次被识别时,从可能状态UIGestureRecognizerStatePossible转到开始状态UIGestureRecognizerStateBegan,然后过渡到改变状态UIGestureRecognizerStateChanged, 当手势发生时又从改变状态变为改变状态。 当用户的最后一个手指从视图上抬起时,手势识别过渡到结束状态UIGestureRecognizerStateEnded, 识别完成(结束状态是识别完成状态的一个别名)。如果一个连续手势不再符合某个手势预期的模式时,识别将过渡到取消状态UIGestureRecognizerStateCancelled。

###多个手势的竞争处理
使用UIGestureRecognizer类方法,委托方法,以及其子类重写的方法可以处理如两个手势谁先响应、是否同时、哪个手势禁止响应某个动作等竞争问题。最常见的容易冲突的swipe和pan手势,swipe手势会首先被识别为pan手势,但是如何打破这个顺序,让swipe首先被识别,如果确定不是swipe再识别pan?
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
[self.panRecognizer requireGestureRecognizerToFail:self.swipeRecognizer];
}
requireGestureRecognizerToFail: 使pan手势在等待swipe手势识别过渡到Failed状态期间,始终处于Possible状态。如果swipe手势识别失败了,pan手势分析事件并变为下个状态。如果swipe手势识别过渡到Recognized 或者 Began状态,pan手势就变为Failed 状态。 关于状态过渡的信息参考[“Gesture Recognizers Operate in a Finite State Machine.”](https://developer.apple.com/library/ios/documentation/EventHandling/Conceptual/EventHandlingiPhoneOS/GestureRecognizer_basics/GestureRecognizer_basics.html#//apple_ref/doc/uid/TP40009541-CH2-SW22)
UIGestureRecognizerDelegate协议提供了方法来阻止手势识别分析触摸。 可以使用协议中的
gestureRecognizer:shouldReceiveTouch:方法 或 gestureRecognizerShouldBegin: (如果视图或视图控制器不能成为手势识别的代理,可以使用)
-(BOOL)gestureRecognizer:(UIGestureRecognizer *)gestureRecognizer shouldReceiveTouch:(UITouch *)touch
{
if ([touch view] == self.customSubview)
{
// If it is, prevent all of the delegate's gesture recognizers from receiving the touch
return NO;
}
return YES;
}
两个手势识别不能同时识别它们的不同手势,通过代理方法可以让两个手势识别同时识别一个手势gestureRecognizer:shouldRecognizeSimultaneouslyWithGestureRecognizer:
如果你想要控制两个识别的交互为一个单向关系,你可以重写canPreventGestureRecognizer:方法并返回NO(默认为YES)。 比如,如果你想用一个旋转手势阻止一个捏合手势,但是又不想捏合手势阻止一个旋转手势,可以用 rotationGestureRecognizer canPreventGestureRecognizer:pinchGestureRecognizer;
在iOS 6.0 以后版本中,默认控件操作方法阻止重复手势识别的行为。如一个按钮的默认操作是一个单击。如果你有一个单击手势识别绑定到一个按钮的父视图上,然后用户点击该按钮,最后按钮的操作方法接收触摸事件而不是定制添加的手势识别。 还有:
* 单个手势在 UISlider上的快速滑动,轻扫方向跟slider平行;
* 单个手指的在 UISwitch 控件上的慢速拖动手势,方向跟switch平行。
###触摸UITouch 和 事件UIEvent
一个触摸UITouch 是一个手指在屏幕上的存在或运动。 一个手势有一个或多个触摸。
一个事件UIEvent包含一个多点触摸序列的所有触摸,包含了应用程序决定如何响应该事件的事件信息。 一个多点触摸序列以一个手指触摸屏幕开始,以最后一个手指离开屏幕结束。 当一个手指移动时,iOS给事件UIEvent发送多个触摸对象UITouch。
每个触摸对象只跟踪一个手指,并且只在触摸序列期间跟踪。 在序列期间,UIKit跟踪手指并更新触摸对象的各种属性。 这些属性包括触摸阶段,它在视图中的位置,前一个位置,以及时间戳。
触摸阶段表明一个触摸何时开始,它是移动的还是静止的,以及它何时结束---当手指不再触摸屏幕的时间。应用程序在任何触摸的每个阶段之间接收事件对象。

各个阶段对应代理方法:
touchesBegan:withEvent: 当一个或多个手指触摸屏幕时调用
touchesMoved:withEvent:当一个或多个手势移动时调用
touchesEnded:withEvent:当一个或多个手指离开屏幕时调用
touchesCancelled:withEvent:当触摸序列被系统事件取消时调用,比如有一个来电。
注意: 这些方法跟手势识别状态没有关联
当一个触摸发生时,触摸对象从UIApplication对象传递到UIWindow对象。 然后,窗口首先把触摸发送给触摸发生的视图上关联的手势识别器,如果识别出响应手势将响应者变为视图所在vc,而不再发给视图。如果没有识别出手势,才会发送给视图对象自身。即下图123的顺序:

我们可以通过属性delaysTouchesBegan等延迟将事件传递给视图,而让手势识别先进行完。
当你通过子类化实现一个定制的手势识别器时,最重要的事情是正确地使用手势识别器的state,在各个状态下获取手势的情况来识别。
- (void)reset; // 在Recognized/Ended, Canceled, 或者Failed状态时复位
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event;
- (void)touchesMoved:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event;// 离散手势无此状态
- (void)touchesEnded:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event;
- (void)touchesCancelled:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event;
###响应链
当iOS系统识别到一个事件,它把事件传递给看起来最有可能处理的初始对象,如果初始对象不能处理该事件,iOS继续把它传递给更多的对象,直到找到能够处理该事件的对象。这些有顺序的对象构成一个响应链(responder chain) 。

响应链与事件的传递链是互逆的:
事件传递过程:
iOS设备的硬件检测到用户的触摸事件 -> 产生UIEvent -> UIApplication -> UIWindow -> ......

iOS系统通过hittest寻找响应者的过程就是一个遍历树的子节点的过程,需要遍历所有相关的vc和vc上面的所有view及其子view,直到最叶子节点的view响应,如果没有子view能响应,就找到最叶的vc;如果没有叶子vc可以响应,就找到UIWindow;否则找到UIApplication。