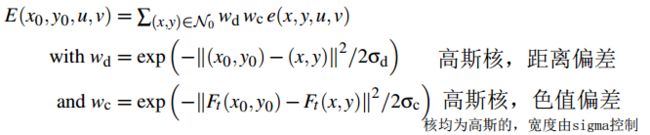阅读时间v1:20190728.
这篇算作本人第一篇电子读书笔记,所以希望定一个标准:笔记内容将包括,Abstract Duplication,Approach,Contributions/Goodness and Weakness.
- Abstract Duplication
optical flow is a critical component of video editing applications, e.g. for tasks such as object tracking, segmentation, and selection. In this paper, we propose an optical flow algorithm called simpleflow whose running times increase sublinearly in the number of pixels. Central to our approach is a probabilistic representation of the motion flow that is computed using only local evidence and without resorting to global optimization. To estimate the flow in image regions where the motion is smooth, we use a sparse set of samples only, thereby avoiding the expensive computation inherent in traditional dense algorithms. We show that our results can be used as is for a variety of video editing tasks. For applications where accuracy is paramount, we use our result to bootstrap a global optimization. This significantly reduces the running times of such methods without sacrificing accuracy. We also demonstrate that the simpleflow algorithm can process hd and 4k footage in reasonable times.
中心思想:提出了一种运行时间为亚线性复杂度的快速配准算法—Simple Flow。在金字塔模型架构下,从 (l+1) 层到 (l) 层的上采样过程中,根据patch内局部运动流的跨度情况,确定该patch下像素的运动性,若为dense flow,在 (l) 层,将对patch内每一像素点的运动流进行精准计算;若为smooth flow,在 (l) 层,将首先计算patch的角上的光流,然后使用插值办法得到其它位置的光流,仅使用了smooth flow的稀疏样本。该方法在存在smooth and slow 的region,由于插值运算快于计算每个像素optical flow的速度,所以是亚线性的计算复杂度,当场景是dense flow 顶多也是线性的,可以接受。
- Approcah
Notation: we consider two successive frames ft and ft+1. we use (x, y) for pixel positions and (u, v) for flow vectors, that is, we seek to estimate u and v at each pixel such that the scene point at (x, y) in ft is visible at (x + u, y + v) in ft+1. although strictly speaking, u and v depend on (x, y); for the sake of clarity, we will use the notation (u, v) instead of (u(x, y),v(x, y)) when possible. we use ft(x, y) to denote the rgb color of the (x, y) pixel in ft.
作者同样假设constant-color 和flow is locally smooth的assumption。公式1用来表示前后两帧的能量差:
式2用来计算(x0,y0)处最佳光流(u0, v0)使得能量损最小:
![]() (2)
(2)
上式中,Σ项相当于盒式滤波,即各像素值相加,不利于区分边界信息,故引入cross- or joint-bilateral filtering:
- Multiscale Flow Estimation
作者对Pyramid的讲述很清晰,直接引用:“We construct an image pyramid for each image frame in which each level is twice coarser than the previous one,at the coarsest level of the pyramid, we estimate the flow using the scheme described[ in section 2论文中的]. we now explain how to compute the flow at level l assuming the flow at l +1 is known.”
剩下的详细部分看论文,很清晰!特别是对于稀疏性判定的部分:
“for each layer, we estimate a flow irregularity map where the flow is smooth and where it varies more. at each pixel (x0;y0), we compute the irregularity value as:
![]()
during upscaling, if this value is above a threshold t, we run the full pipeline on the corresponding upscaled pixels. otherwise, we compute the flow at the corners of the patch, and find the flows at other pixel using bilinear interpolation.but when more accuracy is desirable, one could trade-off estimating the flow at more points and fitting a higher-order function to them.”
- Contributions/Goodness:
1、对运动缓慢的区域使用线性插值减少时间,速度贼快,对运动快速的区域使用配准算法计算,还可以实现亚像素估计哦
2、若希望准确度高,该论文算法可以作为其它算法的引导步骤,具体见caption of Figure 8
"we presented a simple method for optical flow with running times that grow sublinearly with video resolution. a key property of our approach is that we do not resort to global optimization to propagate local information across the image. instead, we average local probability distributions computed from standard color differences.The local aspect of our scheme is also the key component that enables sublinear computation "
End!
第一次写读书笔记,目的是为了以后复习阅后的论文有方便之处,但是感觉写起来比较慢,在未来的写作过程中,将仍以摘抄作者的英文原文为基础,加上自己的理解,这样可以减少时间,也能正确的表达作者的意思,有时候翻译成中文再看已经不是那样了。
与君共勉!