tomcat 8 源码分析 ,本文主要讲解tomcat拥有哪些组件,容器,又是如何启动的
推荐访问我的个人网站,排版更好看呦: https://chenmingyu.top/tomcat-source-code/
tomcat
简介
Tomcat是Apache 软件基金会(Apache Software Foundation)的Jakarta 项目中的一个核心项目,Tomcat服务器是一个免费的开放源代码的Web 应用服务器,属于轻量级应用服务器。
整体架构
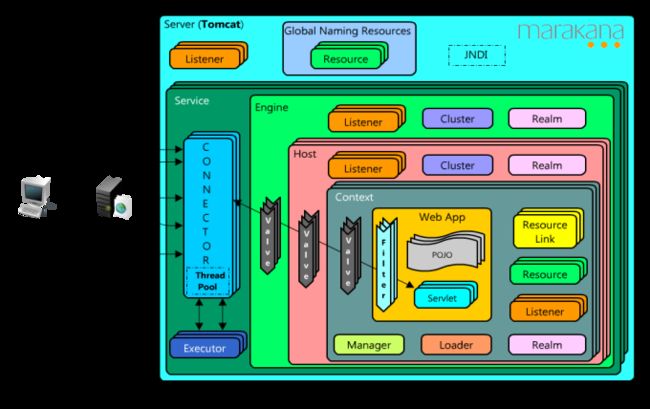
首先我们先看一张图
server:整个servlet容器,一个tomcat对应一个server,一个server包含多个service
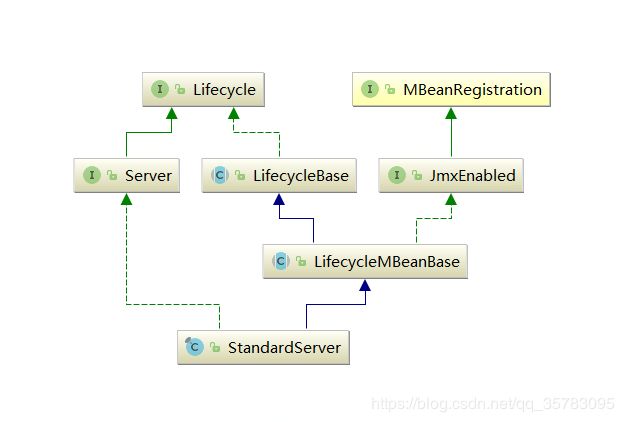
server在tomcat中的实现类是:StandardServer
service: 一个service包含多个connector(接受请求的协议),和一个container(容器)
多个connector共享一个container容器,
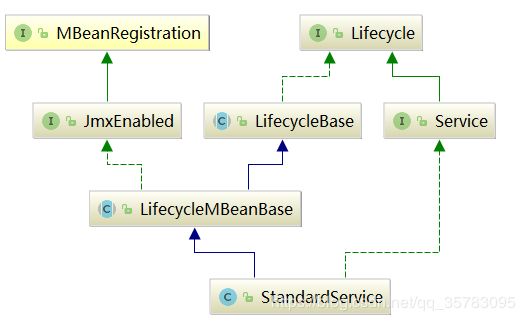
service在tomcat中的实现类是:StandardService
connector:链接器,负责处理客户端请求,解析不同协议及io方式
executor:线程池
container:包含engine,host,context,wrapper等组件
engine:servlet引擎,container容器中顶层的容器对象,一个engine可以包含多个host主机
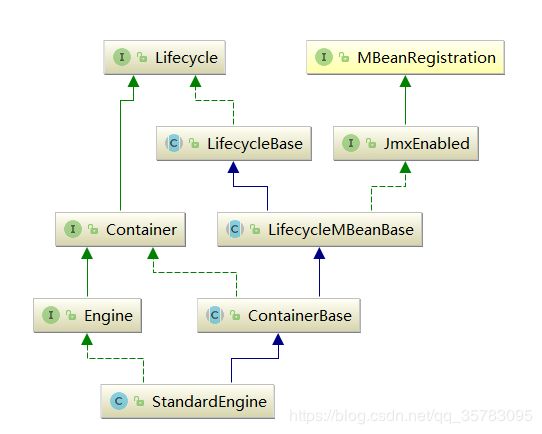
engine在tomcat中的实现类是:StandardEngine
host:engine容器的子容器,一个host对应一个网络域名,一个host包含多个context
host在tomcat中的实现类是:StandardHost
context:host容器的子容器,表示一个web应用
context在tomcat中的实现类是:StandardContext
wrapper:tomcat中最小的容器单元,表示web应用中的servlet
wrapper在tomcat中的实现类是:StandardWrapper
所以tomcat的组件结构大概是这个样子的:
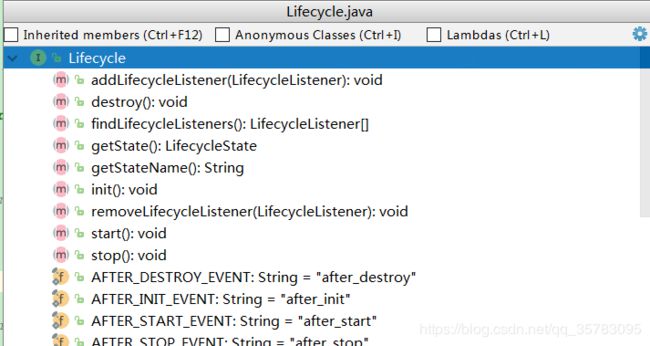
生命周期:Lifecycle
tomcat的启动过程非常规范,使用Lifecycle接口统一管理各组件的生命周期,根据各个组件之间的父子级关系,首先调用init()方法逐级初始化各组件,然后在调用start()的方法进行启动;
Lifecycle接口提供的方法如下,提供了init,start,destory等方法:
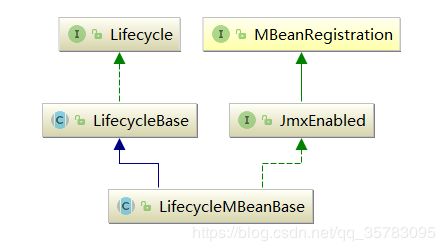
tomcat中的组件基本都继承了LifecycleMBeanBase类,LifecycleMBeanBase集成LifecycleBase,LifecycleBase实现Lifecycle接口:
LifecycleBase重写Lifecycle接口,比如init()方法,在init()方法中调用initInternal()方法,initInternal()方法是抽象方法,具体实现交由各个子类(组件)去实现。如果没有实现initInternal()方法,则调用默认的LifecycleMBeanBase的initInternal方法。
启动过程
接下来从源码看一下tomcat的启动流程:
bootstrap
tomcat的入口类为BootStrap的main方法
Bootstrap中main()方法如下,不重要的代码省略了
/**
* Main method and entry point when starting Tomcat via the provided
* scripts.
*
* @param args Command line arguments to be processed
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
.....
//初始化
bootstrap.init();
.....
if (command.equals("startd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "start";
//实例化各组件 调用Catalina类的load方法
daemon.load(args);
//启动各组件 调用Catalina类的start方法
daemon.start();
}
.....
}bootstrap.init()的工作是初始化Bootstrap类,包含初始化类加载器
/**
* Initialize daemon.
* @throws Exception Fatal initialization error
*/
public void init() throws Exception {
//初始化类加载
initClassLoaders();
......
//实例化Catalina类
Class startupClass = catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");
Object startupInstance = startupClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
......
catalinaDaemon = startupInstance;
}Catalina
接着调用刚初始化的Catalina类的实例catalinaDaemon的load()方法,重要的就两点
/**
* Start a new server instance.
*/
public void load() {
.....
// Digester... 实例化组件
Digester digester = createStartDigester();
.....加载server.xml......
file = configFile();
inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
inputSource = new InputSource(file.toURI().toURL().toString());
......
// 初始化sever
getServer().init();
}Digester
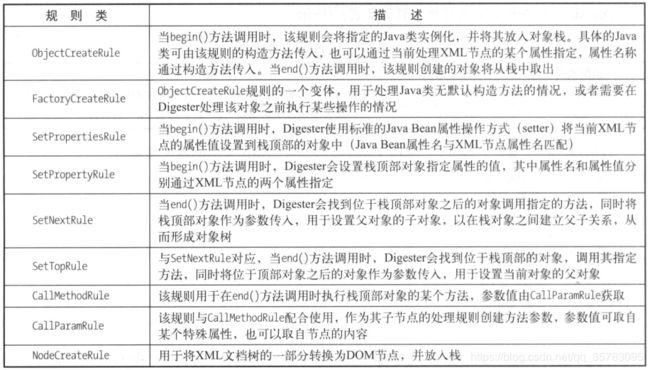
Digester是一种将xml转化为java对象的事件驱动型工具,通过读取xml文件,当识别到特定的节点的时候会执行特定的动作,创建java对象或者执行对象的某个方法
通过Digester去创建了Catania中的大量初始化工作,具体详见源码:
// 创建server实例
digester.addObjectCreate("Server",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer",
"className");
//创建Executor
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Executor",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardThreadExecutor",
"className");
...等等大量初始化工作...接着讲,getServer().init()方法的作用是初始化Sever,调用LifecycleBase的init()方法,在init方法中调用的是StandardServer类initInternal()方法
StandardServer
StandardServer类图如下:
StandardServer类initInternal()方法:
/**
* Invoke a pre-startup initialization. This is used to allow connectors
* to bind to restricted ports under Unix operating environments.
*/
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
...省略很多,但是主要的在下面...
// Initialize our defined Services
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
//调用services的init
services[i].init();
}
}前面的时候讲过一个server初始化多个services;
StandardService
services[i].init();初始化的是StandardService类,类图如下
StandardService的initInternal() 方法的工作是初始化engine组件,初始化线程池,初始化mapperListener,初始化connector
/**
* Invoke a pre-startup initialization. This is used to allow connectors
* to bind to restricted ports under Unix operating environments.
*/
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
//初始化engine
engine.init();
//初始化线程池
// Initialize any Executors
for (Executor executor : findExecutors()) {
if (executor instanceof JmxEnabled) {
((JmxEnabled) executor).setDomain(getDomain());
}
executor.init();
}
//初始化mapperListener
// Initialize mapper listener
mapperListener.init();
//初始化connector
connector.init();
}初始化executor,mapperListener,connector后面再讲其作用,先接初始化engine
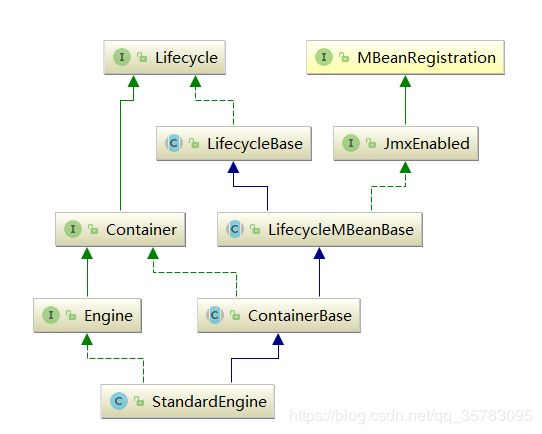
StandardEngine
StandardEngine的类图如下:
在StandardEngine的初始化中并没有直接调用host的初始化,而是调用的父类containerBase的initInternal的方法:
//StandardEngine
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Ensure that a Realm is present before any attempt is made to start
// one. This will create the default NullRealm if necessary.
getRealm();
super.initInternal();
}
//containerBase
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
BlockingQueue startStopQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
startStopExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
getStartStopThreadsInternal(),
getStartStopThreadsInternal(), 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
startStopQueue,
new StartStopThreadFactory(getName() + "-startStop-"));
startStopExecutor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);
super.initInternal();
} host的init是在start阶段去做的,所以后面再说
executor
executor.init();默认调用LifecycleMBeanBase的initInternal方法
mapperListener
mapperListener.init();也默认调用LifecycleMBeanBase的initInternal方法
connector
connector的初始化调用Connector类的initInternal方法,主要是new了一个CoyoteAdapter,初始化protocolHandler
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
// 实例化 CoyoteAdapter 适配器
adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this);
protocolHandler.setAdapter(adapter);
......
try {
//初始化 protocolHandler
protocolHandler.init();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInitializationFailed"), e);
}
}AbstractProtocol是调用endpoint的init方法,这个方法中调用bind()
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
//初始化endpoint
endpoint.init();
}
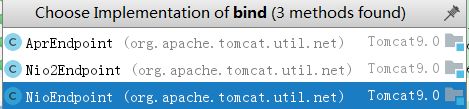
bind()针对不同的io类型提供了三种的默认实现
进入NioEndpoint类的bind()
/**
* Initialize the endpoint.
*/
@Override
public void bind() throws Exception {
//使用nio方式监听端口
if (!getUseInheritedChannel()) {
serverSock = ServerSocketChannel.open();
socketProperties.setProperties(serverSock.socket());
InetSocketAddress addr = (getAddress()!=null?new InetSocketAddress(getAddress(),getPort()):new InetSocketAddress(getPort()));
serverSock.socket().bind(addr,getAcceptCount());
}
//设置非阻塞
serverSock.configureBlocking(true); //mimic APR behavior
......
//开启selectorPool
selectorPool.open();
}start过程
tomcat的start阶段与init阶段相似,都是逐层调用,稍有不同的是在于engine,host,context,wrapper的启动方式;
首先回到Bootstrap的main方法中,继续执行Catalina类的start(),在start()方法中调getServer().start();
调用LifecycleBase类的start()方法,在这个方法中调动StandardServer类实现的startInternal(),在这个类中继续调用service的star()方法,以此类推逐层start调用,直到调用engine的start(),我们看下engine的start()方法,在看下StandardEngine的类图:
StandardEngine的startInternal()调用ContainerBase的startInternal()
/**
* Start this component and implement the requirements
* of {@link org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#startInternal()}.
*
* @exception LifecycleException if this component detects a fatal error
* that prevents this component from being used
*/
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
......
// Start our child containers, if any
Container children[] = findChildren();
List> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(children[i])));
}
......
} findChildren()的方法找到的是engine容器的子容器然后在new StartChild(children[i])中调用子类容器的start();使用这种方式依次启动子容器