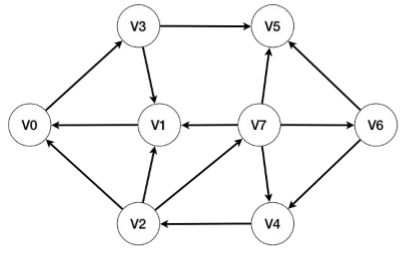
(以下图为例子)采用邻接矩阵的方法定义图的数据结构,并实现图的深度优先周游算法。
1.首先先定义并实现图的边Edge类,Edge类中的成员变量有:from->起点 to->终点 weight->权值(权值初始化为0)
Edge.h
1 class Edge
2 {
3 public:
4 int from, to, weight;
5 public:
6 Edge() {
7 from = -1;
8 to = -1;
9 weight = 0;
10 }
11
12 Edge(int f, int t, int w){
13 from = f;
14 to = t;
15 weight = w;
16 }
17 ~Edge() {}
18 };
2.定义图的基类,便于邻接矩阵的继承
Graph.h
1 #include "Edge.h"
2 class Graph
3 {
4 protected:
5 const int UNVISITED;
6 const int VISITED;
7 public:
8 int numVertex; //图中顶点的总个数
9 int numEdge; //边数
10 int *Mark; //标记
11 //int *Indegree; //存放图中顶点的入度
12 public:
13 bool IsEdge(Edge oneEdge); //判断是否为边
14 Graph(int numVertex);
15 ~Graph();
16 };
Graph.cpp
1 #include "Graph.h"
2
3 Graph::Graph(int numVertex):UNVISITED(0),VISITED(1){
4 this->numVertex = numVertex;
5 this->numEdge = 0; //初始化顶点数为0
6 this->Mark = new int [numVertex]; //为标记数组动态分配空间
7 //this->Indegree = new int [numVertex];
8
9 for (int i = 0; i < numVertex; i++)
10 {
11 Mark[i] = UNVISITED; //将全部点初始化为未访问
12 //Indegree[i] = 0;
13 }
14 }
15
16 Graph::~Graph(){
17 delete []Mark;
18 //delete []Indegree;
19 }
20
21 bool Graph::IsEdge(Edge oneEdge){
22 if (oneEdge.weight > 0 && oneEdge.to >= 0)
23 {
24 return true;
25 }
26 else return false;
27 }
3.定义Graph类的子类,将图转换为邻接矩阵
tips: Initialize函数形参中的*pWArray2D传进的是一个二维数组。
Graphm.h
1 #include "Graph.cpp"
2
3 class Graphm:public Graph
4 {
5 private:
6 int **matrix; //指向邻接矩阵的指针
7 public:
8 Edge FirstEdge(int oneVertex); //返回以oneVertex为顶点的第一条Edge
9 Edge NextEdge(Edge preEdge); //返回与preEdge有相同顶点的下一条边
10 void setEdge(int from,int to,int weigth); //设置边
11 void delEdge(int from,int to); //删除边
12 void Initialize(Graphm *Graphm,int *pWArray2D ); //初始化图
13 void Visited(Graphm &M,int v); //输出访问过的点
14 void DFS(Graphm &M,int v); //深度优先周游
15 int ToVertex(Edge oneEdge); //返回边的终点
16 void Travel(Graphm &G,int startVertex); //周游全图
17 Graphm(int numVertex);
18 ~Graphm();
19 };
Graphm.cpp
1 #include "Graphm.h"
2 #include
3 using namespace std;
4
5 //构造函数
6 Graphm::Graphm(int numVertex):Graph(numVertex){
7 int i,j;
8 matrix = (int **)new int *[numVertex]; //申请matrix数组行向量数组
9
10 for (i = 0; i < numVertex; i++){
11 matrix[i] = new int[numVertex]; //申请行的存储空间(列向量)
12 }
13
14 for (i = 0; i < numVertex; i++){
15 for (j = 0; j < numVertex; j++){
16 matrix[i][j] = 0;
17 }
18 }
19 cout << "构造函数执行!" << endl;
20 }
21 //析构函数释放二维数组的动态分配的空间
22 Graphm::~Graphm(){
23 for (int i = 0; i < numVertex; i++)
24 {
25 delete [] matrix[i];
26 }
27 delete [] matrix;
28 cout << "释放空间成功!" << endl;
29 }
30 //初始化图
31 void Graphm::Initialize(Graphm *Graphm,int *pWArray2D){
32 cout << "开始初始化!" << endl;
33 int N = numVertex;
34 int array_i_j = 0;
35 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
36 {
37 for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
38 {
39 array_i_j = *(pWArray2D + i*N + j); //获得二维数组中每一个元素的值
40 //cout << array_i_j << endl;
41 if (array_i_j > 0) //当元素的值大于0时,证明有从i指向j的边
42 {
43 Graphm->setEdge(i,j,array_i_j); //设置边
44 }
45 }
46 }
47 cout << "初始化成功!" << endl;
48 /*for (int i = 0; i < numVertex; i++)
49 {
50 for (int j = 0; j < numVertex; j++)
51 {
52 cout << matrix[i][j] << " ";
53 }
54 cout << endl;
55
56 }*/
57 }
58 //返回以oneVertex为顶点的第一条Edge
59 Edge Graphm::FirstEdge(int oneVertex){
60 Edge myEdge;
61 myEdge.from = oneVertex;
62
63 for (int i = 0; i < numVertex; i++)
64 {
65 if (matrix[oneVertex][i] != 0)
66 {
67 myEdge.to = i;
68 myEdge.weight = matrix[oneVertex][i];
69 break;
70 }
71 }
72 return myEdge;
73 }
74 //返回与preEdge有相同顶点的下一条Edge
75 Edge Graphm::NextEdge(Edge preEdge){
76 Edge myEdge;
77 myEdge.from = preEdge.from;
78 if (preEdge.to+1 < numVertex)
79 {
80 for (int i = preEdge.to+1; i < numVertex; i++)
81 {
82 if (matrix[preEdge.from][i] != 0)
83 {
84 myEdge.to = i;
85 myEdge.weight = matrix[preEdge.from][i];
86 break;
87 }
88 }
89 }
90 return myEdge;
91 }
92 //为图设置边
93 void Graphm::setEdge(int from,int to,int weigth){
94 if (matrix[from][to] <= 0)
95 {
96 numEdge++; //边的个数加1
97 //Indegree[to]++;
98 }
99 matrix[from][to] = weigth;
100 }
101 //删除边
102 void Graphm::delEdge(int from,int to){
103 if (matrix[from][to] > 0)
104 {
105 numEdge--; //边的个数减1
106 //Indegree[to]--;
107 }
108 matrix[from][to] = 0;
109 }
110 //输出访问过的点
111 void Graphm::Visited(Graphm &M,int v){
112 cout << "v" << v << " ";
113 }
114 //返回边的终点
115 int Graphm::ToVertex(Edge oneEdge){
116 return oneEdge.to;
117 }
118 //深度优先周游
119 void Graphm::DFS(Graphm &M,int v){
120 M.Mark[v] = VISITED;
121 Visited(M,v);
122 for (Edge e = M.FirstEdge(v); M.IsEdge(e); e = M.NextEdge(e))
123 {
124 if (M.Mark[M.ToVertex(e)] == UNVISITED)
125 {
126 //cout << M.ToVertex(e) << endl;
127 DFS(M,M.ToVertex(e));
128 }
129 }
130 }
131 //周游完整的图
132 void Graphm::Travel(Graphm &G,int startVertex){
133 DFS(G,startVertex); //不一定能周游每一个顶点
134 //更换顶点周游
135 for (int i = 0; i < numVertex; i++)
136 {
137 if (G.Mark[i] == UNVISITED)
138 {
139 DFS(G,i);
140 }
141 }
142 }
4.主函数的实现
tips: 先根据图画出邻接矩阵,再将邻接矩阵作为实参进行传递
Main.cpp
1 #include "Graphm.cpp"
2 #define N 8
3 int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
4 {
5
6 //int N = 8;
7 int M[N][N] = {
8 0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,
9 1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
10 1,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,
11 0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,
12 0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,
13 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
14 0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,
15 0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0
16 };
17 Graphm G(N);
18 G.Initialize(&G,(int*)M);
19 cout << "全部深度周游:";
20
21 G.Travel(G,3);
22 cout << endl;
23
24 return 0;
25 }
注:以下总结仅代表个人观点(如有错误,欢迎指出)
总结:1.将图写为基类在此处体现出来的意义其实并不大(在此题中完全可以将Graph类与Graphm类合并起来),但是也是为了养成良好的习惯。
2.主函数中二维数组的传递值得一记,传递的过程将其当成一位数组进行传递。
3.周游的过程中需要考虑到当图为不连通图时,以某个顶点为起点时可能周游出来的结果不完整(以上的Travvel函数则能周游出全部的点。
4.熟练掌握根据图画出对应的邻接矩阵。
5.无权图的权值可设为1。
6.动态分配的空间记得手动释放,最好的做法是写在析构函数中。