SpringBoot系列文章简介
SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇:
Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现
SpringBoot启动流程源码分析:
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(一):SpringApplication类初始化过程
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(二):SpringApplication的run方法
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(三):SpringApplication的run方法之prepareContext()方法
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(四):IoC容器的初始化过程
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(五):SpringBoot自动装配原理实现
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(六):IoC容器依赖注入
笔者注释版Spring Framework与SpringBoot源码git传送门:请不要吝啬小星星
- spring-framework-5.0.8.RELEASE
- SpringBoot-2.0.4.RELEASE
第四步:刷新应用上下文前的准备阶段
一、prepareContext()方法
前面我们介绍了SpringBoot 启动流程run()方法的前三步,本章,我们将用一个章节介绍:第四步:刷新应用上下文前的准备阶段。也就是prepareContext()方法。
首先看prepareContext()方法。
1 private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, 2 ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, 3 ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) { 4 //设置容器环境 5 context.setEnvironment(environment); 6 //执行容器后置处理 7 postProcessApplicationContext(context); 8 //执行容器中的 ApplicationContextInitializer 包括spring.factories和通过三种方式自定义的 9 applyInitializers(context); 10 //向各个监听器发送容器已经准备好的事件 11 listeners.contextPrepared(context); 12 if (this.logStartupInfo) { 13 logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null); 14 logStartupProfileInfo(context); 15 } 16 17 // Add boot specific singleton beans 18 //将main函数中的args参数封装成单例Bean,注册进容器 19 context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", 20 applicationArguments); 21 //将 printedBanner 也封装成单例,注册进容器 22 if (printedBanner != null) { 23 context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner); 24 } 25 26 // Load the sources 27 Set
首先看这行 Set
我们本文重点讲解这行 load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0])); ,其他的方法请参阅注释。
跟进load()方法,看源码
1 protected void load(ApplicationContext context, Object[] sources) { 2 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 3 logger.debug( 4 "Loading source " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(sources)); 5 } 6 //创建 BeanDefinitionLoader 7 BeanDefinitionLoader loader = createBeanDefinitionLoader( 8 getBeanDefinitionRegistry(context), sources); 9 if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) { 10 loader.setBeanNameGenerator(this.beanNameGenerator); 11 } 12 if (this.resourceLoader != null) { 13 loader.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader); 14 } 15 if (this.environment != null) { 16 loader.setEnvironment(this.environment); 17 } 18 loader.load(); 19 }
1.1、getBeanDefinitionRegistry()
继续看getBeanDefinitionRegistry()方法的源码
1 private BeanDefinitionRegistry getBeanDefinitionRegistry(ApplicationContext context) { 2 if (context instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) { 3 return (BeanDefinitionRegistry) context; 4 } 5 ... 6 }
这里将我们前文创建的上下文强转为BeanDefinitionRegistry,是不是很熟悉,前面的文章中咱们也介绍过,他们之间是有继承关系的。BeanDefinitionRegistry定义了很重要的方法registerBeanDefinition(),该方法将BeanDefinition注册进DefaultListableBeanFactory容器的beanDefinitionMap中。
1.2、createBeanDefinitionLoader()
继续看createBeanDefinitionLoader()方法,最终进入了BeanDefinitionLoader类的构造方法,如下
1 BeanDefinitionLoader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object... sources) { 2 Assert.notNull(registry, "Registry must not be null"); 3 Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty"); 4 this.sources = sources; 5 //注解形式的Bean定义读取器 比如:@Configuration @Bean @Component @Controller @Service等等 6 this.annotatedReader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(registry); 7 //XML形式的Bean定义读取器 8 this.xmlReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(registry); 9 if (isGroovyPresent()) { 10 this.groovyReader = new GroovyBeanDefinitionReader(registry); 11 } 12 //类路径扫描器 13 this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(registry); 14 //扫描器添加排除过滤器 15 this.scanner.addExcludeFilter(new ClassExcludeFilter(sources)); 16 }
先记住上面的三个属性,具体有什么用,先看看注释。前面的文章,我们说过,IoC容器的初始化分为三个步骤,上面三个属性在,BeanDefinition的Resource定位,和BeanDefinition的注册中起到了很重要的作用。
1.3、loader.load();
跟进load()方法
1 private int load(Object source) { 2 Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null"); 3 // 从Class加载 4 if (source instanceof Class) { 5 return load((Class) source); 6 } 7 // 从Resource加载 8 if (source instanceof Resource) { 9 return load((Resource) source); 10 } 11 // 从Package加载 12 if (source instanceof Package) { 13 return load((Package) source); 14 } 15 // 从 CharSequence 加载 ??? 16 if (source instanceof CharSequence) { 17 return load((CharSequence) source); 18 } 19 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid source type " + source.getClass()); 20 }
当前我们的主类会按Class加载。
继续跟进load()方法。
1 private int load(Class source) { 2 if (isGroovyPresent() 3 && GroovyBeanDefinitionSource.class.isAssignableFrom(source)) { 4 // Any GroovyLoaders added in beans{} DSL can contribute beans here 5 GroovyBeanDefinitionSource loader = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(source, 6 GroovyBeanDefinitionSource.class); 7 load(loader); 8 } 9 if (isComponent(source)) { 10 //将 启动类的 BeanDefinition注册进 beanDefinitionMap 11 this.annotatedReader.register(source); 12 return 1; 13 } 14 return 0; 15 }
isComponent(source)判断主类是不是存在@Component注解,主类@SpringBootApplication是一个组合注解(后面讲解自动装配会讲解
this.annotatedReader.register(source);跟进register()方法,最终进到AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader类的doRegisterBean()方法。
1void doRegisterBean(Class annotatedClass, @Nullable Supplier instanceSupplier, @Nullable String name, 2 @Nullable Classextends Annotation>[] qualifiers, BeanDefinitionCustomizer... definitionCustomizers) { 3 4 //将指定的类 封装为AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition 5 AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(annotatedClass); 6 if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) { 7 return; 8 } 9 10 abd.setInstanceSupplier(instanceSupplier); 11 // 获取该类的 scope 属性 12 ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd); 13 abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName()); 14 String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry)); 15 16 AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd); 17 if (qualifiers != null) { 18 for (Classextends Annotation> qualifier : qualifiers) { 19 if (Primary.class == qualifier) { 20 abd.setPrimary(true); 21 } 22 else if (Lazy.class == qualifier) { 23 abd.setLazyInit(true); 24 } 25 else { 26 abd.addQualifier(new AutowireCandidateQualifier(qualifier)); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 for (BeanDefinitionCustomizer customizer : definitionCustomizers) { 31 customizer.customize(abd); 32 } 33 34 BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName); 35 definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry); 36 // 将该BeanDefinition注册到IoC容器的beanDefinitionMap中 37 BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry); 38 }
在该方法中将主类封装成AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);方法将BeanDefinition注册进beanDefinitionMap
1 public static void registerBeanDefinition( 2 BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) 3 throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 4 // Register bean definition under primary name. 5 // primary name 其实就是id吧 6 String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName(); 7 registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition()); 8 // Register aliases for bean name, if any. 9 // 然后就是注册别名 10 String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases(); 11 if (aliases != null) { 12 for (String alias : aliases) { 13 registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias); 14 } 15 } 16 }
继续跟进registerBeanDefinition()方法。
1 @Override 2 public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) 3 throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 4 5 Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty"); 6 Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null"); 7 8 if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) { 9 try { 10 // 最后一次校验了 11 // 对bean的Overrides进行校验,还不知道会在哪处理这些overrides 12 ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate(); 13 } catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { 14 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName, 15 "Validation of bean definition failed", ex); 16 } 17 } 18 // 判断是否存在重复名字的bean,之后看允不允许override 19 // 以前使用synchronized实现互斥访问,现在采用ConcurrentHashMap 20 BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName); 21 if (existingDefinition != null) { 22 //如果该类不允许 Overriding 直接抛出异常 23 if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) { 24 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName, 25 "Cannot register bean definition [" + beanDefinition + "] for bean '" + beanName + 26 "': There is already [" + existingDefinition + "] bound."); 27 } else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) { 28 // e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE 29 if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { 30 logger.warn("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName + 31 "' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" + 32 existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]"); 33 } 34 } else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) { 35 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 36 logger.info("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName + 37 "' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition + 38 "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]"); 39 } 40 } else { 41 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 42 logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName + 43 "' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition + 44 "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]"); 45 } 46 } 47 //注册进beanDefinitionMap 48 this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition); 49 } else { 50 if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) { 51 // Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration) 52 synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) { 53 this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition); 54 ListupdatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1); 55 updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames); 56 updatedDefinitions.add(beanName); 57 this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions; 58 if (this.manualSingletonNames.contains(beanName)) { 59 Set updatedSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.manualSingletonNames); 60 updatedSingletons.remove(beanName); 61 this.manualSingletonNames = updatedSingletons; 62 } 63 } 64 } else { 65 // Still in startup registration phase 66 //如果仍处于启动注册阶段,注册进beanDefinitionMap 67 this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition); 68 this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName); 69 this.manualSingletonNames.remove(beanName); 70 } 71 this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null; 72 } 73 74 if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) { 75 resetBeanDefinition(beanName); 76 } 77 }
最终来到DefaultListableBeanFactory类的registerBeanDefinition()方法,DefaultListableBeanFactory类还熟悉吗?相信大家一定非常熟悉这个类了。DefaultListableBeanFactory是IoC容器的具体产品。
仔细看这个方法registerBeanDefinition(),首先会检查是否已经存在,如果存在并且不允许被覆盖则直接抛出异常。不存在的话就直接注册进beanDefinitionMap中。
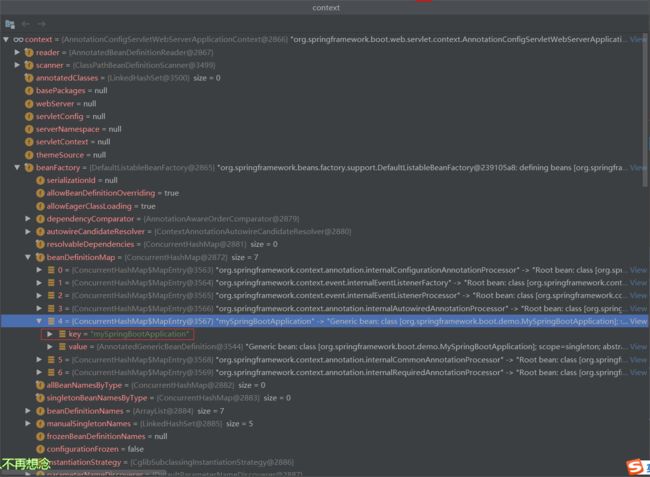
debug跳过prepareContext()方法,可以看到,启动类的BeanDefinition已经注册进来了。
OK,到这里启动流程的第五步就算讲完了,其实在这没必要讲这么细,因为启动类BeanDefinition的注册流程和后面我们自定义的BeanDefinition的注册流程是一样的。这先介绍一遍这个流程,后面熟悉了这个流程就好理解了。后面马上就到最最最重要的refresh()方法了。
原创不易,转载请注明出处。
如有错误的地方还请留言指正。