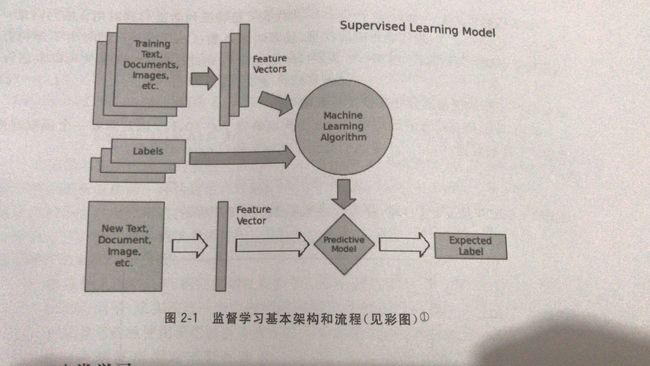
2.1监督学习经典模型
监督学习:
2.1.1分类学习
二分类:从两个类别中选择一个作为预测结果。
多类分类:多于两个类别中选择一个。
多标签分类:一个样本是否同时属于多个不同类别。
2.1.1.1线性分类器(linear classifier)
模型介绍:是一种假设特征与分类结果存在线性关系的模型。这个模型通过累加计算每个维度的特征与各自权重的乘积来帮助类别决策。
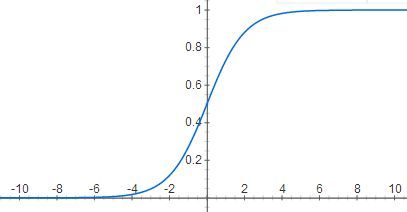
我们所要处理的最简单的二分类问题数据f属于{0,1};因此需要一个函数把原先的f属于R映射到{0,1}。于是我们想到了逻辑斯蒂函数。
我们可以观察到该模型如何处理一个待分类的特征向量:如果z=0,那么g=0.5;若z<0则g<0.5,这个特征向量被判别为一类;反之,若z>0,则g>0.5,其被归为另外一类。
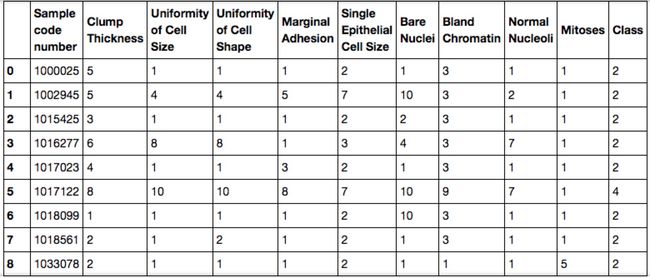
数据描述
Sample code number:样本编号
Clump Thickness:细胞厚度
Uniformity of Cell Size:细胞大小的均匀度
Uniformity of Cell Shape:细胞形状的均匀度
Marginal Adhesion:细胞边缘的黏着度
Single Epithelial Cell Size:单一的上皮细胞的大小
Bare Nuclei:裸露细胞核
Bland Chromatin:染色质
Normal Nucleoli:正常细胞核
Mitoses:有丝分裂
Class:类型。2-良性,4-恶性
数据:共699条,良性肿瘤458条(65.5%),恶性肿瘤241条(34.5%),16条缺失值(?标出)。
数据预处理
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
#创建特征列表
column_names=['Sample code number','Clump Thickness','Uniformity of Cell Size','Uniformity of Cell Shape','Marginal Adhesion','Single Epithelial Cell Size','Bare Nuclei','Bland Chromatin','Normal Nucleoli','Mitoses','Class']
#使用pandas.read_csv函数从互联网读取指定函数
data=pd.read_csv('https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/breast-cancer-wisconsin/breast-cancer-wisconsin.data',names=column_names)
#将?替换为标准缺失值表示
data=data.replace(to_replace='?',value=np.nan)
#丢弃带有缺失值的数据(只要有一个维度有缺失)
data=data.dropna(how='any')
#输出data的数据量和维度
data.shape
(683, 11)
训练、测试数据
#使用sklearn.cross_valiation里的train_test_split模块用于分割数据
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
#随机采样25%的数据用于测试,剩下的75%用于构建训练集合,设置 random_state 可以让每次划分训练集和验证集的时候都是完全一样的
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(data[column_names[1:10]],data[column_names[10]],test_size=0.25,random_state=33)
#查验训练样本的数量和类别分布
y_train.value_counts()
2 344
4 168
Name: Class, dtype: int64
#查验测试样本的数量和类别分布,683*0.25=171
y_test.value_counts()
2 100
4 71
Name: Class, dtype: int64
预测任务
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
#标准化数据,保证每个维度的特征数据方差为1,均值为0.使得预测结果不会被某些维度过大的特征值而主导
ss=StandardScaler()
X_train=ss.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test=ss.transform(X_test)
LogisticRegression预测任务
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
#初始化LogisticRregression
lr=LogisticRegression()
#调用LogisticRegression中的fit函数/模块用来训练模型参数
lr.fit(X_train,y_train)
#使用训练好的模型lr对X_test进行预测,结果储存在变量lr_y_predict中。
lr_y_predict=lr.predict(X_test)
SGDClassifier预测任务
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
#初始化SGDClassifier
sgdc=SGDClassifier()
#调用SGDClassifier中的fit函数/模块用来训练模型参数
sgdc.fit(X_train,y_train)
#使用训练好的模型lr对X_test进行预测,结果储存在变量sgdc_y_predict中。
sgdc_y_predict=sgdc.predict(X_test)
性能测评
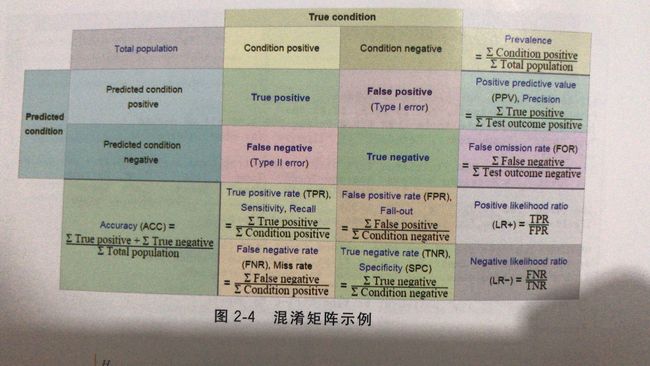
定义:
恶性肿瘤为阳性positive
良性肿瘤为阴性negative
真阳性true positive
假阳性false positive
真阴性true negative
假阴性false negative
评价指标:
精确性,对于给定的测试数据集,分类器正确分类的样本数与总样本数之比。
accuracy = (TP + TN) / (TP + FP + TN + FN)
精确率,所有"正确被检索的item(TP)"占所有"实际被检索到的(TP+FP)"的比例。
precision = TP / (TP + FP)
召回率,所有"正确被检索的item(TP)"占所有"应该检索到的item(TP+FN)"的比例。
recall = TP / (TP + FN)
F1指标,精确值和召回率的调和均值
F1 Score = 2P*R/(P+R),其中P和R分别为 precision 和 recall
预测任务的性能分析
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
使用逻辑斯蒂回归模型自带的评分函数score获得模型在测试集上的准确性结果
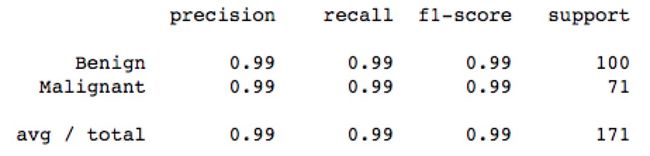
print('Accuracy of LR Classifier:',lr.score(X_test,y_test))
Accuracy of LR Classifier: 0.988304093567
#利用classification_report模块获得LogisticRegression其他三个指标的结果
print(classification_report(y_test,lr_y_predict,target_names=['Benign','Malignant']))
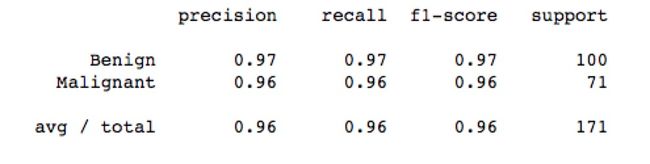
#使用随机梯度下降模型自带的评分函数score获得模型在测试集上的准确性结果
print('Accuracy of LR Classifier:',sgdc.score(X_test,y_test))
Accuracy of LR Classifier: 0.964912280702
#利用classification_report模块获得SGDClassifier其他三个指标的结果
print(classification_report(y_test,sgdc_y_predict,target_names=['Benign','Malignant']))
question:最后两步的结果每次都不一样???
特点分析
线性分类器可以说是最基本和最常用的机器学习模型。尽管受限于数据特征与分类目标之间的线性假设,我们仍然可以在科学研究与工程实践中把线性分类器的表现性能作为基准。
LogisticRegression:对参数的计算采用精确解析的方式,计算时间长但是模型性能高。
SGDClassifier:采用随机梯度上升算法估计模型参数,计算时间短但是产出的模型性能低。适用于对于训练数据规模在10万量级以上的数据,考虑到时间的耗用,笔者更加推荐使用随机梯度算法对模型参数进行估计。
参考资料https://wenku.baidu.com/view/fe7e334d482fb4daa58d4b97.html