GreenDao 八大特性
- 1.对象/关系映射(ORM---Object relation mapping)
GreenDAO的本质是为存储在关系数据库SQLite中的数据提供面向对象的界面。使用过程中,我们只需定义数据模型,而GreenDAO将创建Java数据对象(实体)和DAO(数据访问对象)
- 2.性能
GreenDao官方说过一句话:GreenDAO does not make any compromises regarding performance.
GreenDAO对性能不做任何妥协!!!
在目前所知道的ORM中,GreenDao是最快的,非常适合存储大量数据。所以这也是为什么我已经了解LitePal了还要再学习GreenDao的原因!!!
举一个简单的例子,使用了GreenDao,大多数实体可以以每秒几千个实体的速率进行插入,更新和加载。
这是官方测试图例:
性能实在是太高了!!!!为什么不学呢!!!!! - 3.加密支持
GreenDao支持加密数据库来保护敏感数据 - 4.微小的依赖库
GreenDao关键依赖库大小不超过100kb因此也不会出现因为引入GreenDao而出现65k问题. - 5.活动实体
如果需要,实体可以被“激活”.而活动实体可以透明地解析关系(我们要做的只是调用getter即可),并且有更新、删除和刷新方法,以便方便地访问持久性功能. - 6.协议缓冲区支持
GreenDAO允许将协议缓冲区(protobuf)对象直接保存到数据库中.如果用户通过protobuf通话到用户的服务器,则不需要另一个映射。常规实体的所有持久性操作都可用于protobuf对象。因此,相信这是GreenDAO的独特之处. - 7.自动生成代码
使用GreenDao,我们无需关注实体类以及Dao.体贴的GreenDao已为我们自动生成. - 8.开源
可以查看源码,深入了解机制.
GreenDao 优势
- 1.目前来说性能最高,内存消耗最小,支持数据库加密;
- 2.依赖库小于
100kb,且使用人数众多,维护者也一直在更新; - 3.完善的
api,并且对Android进行了高度优化,个人觉得很不错
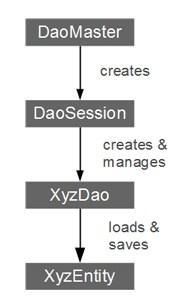
GreenDao核心类简介
- 1.
DaoMaster:
使用GreenDao的切入点(开始)。
DaoMaster保存数据库对象(SQLiteDatabase)并管理特定模式的Dao类(而不是对象)。它具有静态方法来创建表或将它们删除。其内部类OpenHelper和DevOpenHelper是在SQLite数据库中创建模式的SQLiteOpenHelper实现。 - 2.
DaoSession:
管理特定模式的所有可用Dao对象,可以使用其中一个getter方法获取。DaoSession还为实体提供了一些通用的持久性方法,如插入,加载,更新,刷新和删除。最后,DaoSession对象也跟踪一个身份范围。有关更多详细信息,请点击查看会话文档。 - 3.
Dao层:
全称Data access Objects.数据访问对象(Dao)持续存在并查询实体。对于每个实体,GreenDao生成一个Dao,它比DaoSession有更多的持久化方法,例如:count,loadAll和insertInTx。 - 4.实体:
持久对象---通常实体是使用标准Java属性(如POJO或JavaBean)来表示数据库行的对象.
配置GreenDao
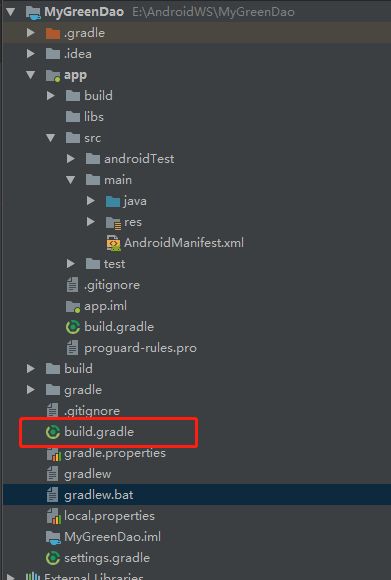
工程目录下build.gradle下配置
apply plugin: 'org.greenrobot.greendao' // apply plugin
.....
dependencies {
compile 'org.greenrobot:greendao:3.2.2' // add library
}
在module的build.gradle文件中配置如下
buildscript {
repositories {
mavenCentral() // add repository
}
dependencies {
classpath 'org.greenrobot:greendao-gradle-plugin:3.2.2' // add plugin
}
在上面两个build.gradlel面对greenDao进行配置完之后。配置之后就搭建好了greenDao的环境,可以自动生成相关的类。
当然你还可以配置greenDao的数据库版本号以及自动生成的包名的路径,当然路径可选择性的配置。
android{
...
}
greendao{
schemaVersion 2 // 数据库版本号
daoPackage 'com.doris.sample.greendao'//greenDao 自动生成的代码保存的包名
targetGenDir 'src/main/java' //自动生成的代码存储的路径,默认是 build/generated/source/greendao.
generateTests false //true的时候自动生成测试单元
}
用户自定义entity
接下来你定义自己的entity并且make project就可以开始对数据库进行操作了.
greenDAO3用注释去schemas 和实体类entities
@Entity注释
@Entity:将一个Java类转变成一个实体类。greenDao会根据这个生成对应的代码。PS: 必须是java类,kotlin不支持。
在Entity中我们可以配置许多信息,比如nameInDb是声明了该表数据库中的表名。
indexes用于建立索引,索引的应用场景可用于,当你的表有多个主键的时候,来标志一条数据的唯一性,配合unique。
当然上面两个只是我们常用的属性,还有几个其他属性,目前我还没有用到:
schema = "myschema",当你有多个schema,用这个属性来告诉数据库当前entity属于哪个schema。
active = true,用于标志某个entity是否是active的,active的实体类有删改的方法。默认是false,为true的时候会自动生成下面的代码在entity里面:
@Entity(
// 如果你有一个以上的模式,你可以告诉greendao实体属于哪个模式(选择任何字符串作为名称)。
schema = "myschema",
// 标志允许实体类可有更新,删除,刷新方法
active = true,
// 指定数据库中表的名称。默认情况下,该名称基于实体类名。(重要)
nameInDb = "AWESOME_USERS",
// 在这里定义多个列的索引(重要)
indexes = {
@Index(value = "name DESC", unique = true)
},
// 如果DAO创建数据库表(默认为true),则设置标记去标识。如果有多个实体映射到一个表,或者在greenDAO之外创建表创建,将此设置为false。(重要)
createInDb = false,
// 是否应该生成所有的属性构造函数。一个无args构造函数总是需要的
generateConstructors = true,
// 是否生成属性的getter和setter
generateGettersSetters = true
)
@Id注解
标志主键
选择long / Long(多使用Long)属性作为实体ID。在数据库方面,它是主要的关键参数autoincrement 是使ID值不断增加的标志(不重复使用旧值),也就是我们经常说的自增长。
@Property
如果定义了这个属性,那么nameInDb的值就是该列在数据表里面,该列的名称。
比如下面的代码中StudentName就是该类stuName(原列)在数据表里面,该列的名称.
@Property(nameInDb = "StudentName")
private String stuName;
允许用户定义属性映射到的非默认列名称。如果缺少,greenDAO将以SQL-ish方式使用字段名称(大写字母,下划线而不是驼峰命名法,例如customName将成为CUSTOM_NAME)。注意:当前只能使用内联常量来指定列名。
@NotNull
标志这个字段不能是null
该属性在数据库端成为“NOT NULL”列。通常使用@NotNull标记原始类型(long,int,short,byte)是有意义的,而具有包装类(Long,Integer,Short,Byte))的可空值。
@Transient
表示不存储在数据库中
@Index
为相应的数据库列创建数据库索引
名称:如果不喜欢greenDAO为索引生成的默认名称,则可以在此处指定。
唯一:向索引添加UNIQUE约束,强制所有值都是唯一的。
entity必须有一个long/Long的属性作为主键,但是有时候我们的主键不一定是long/Long型的可能是string或者其它,这个时候我们就可以定义索引属性并且注明其独一无二
@Index(name = "keyword", unique = true)
private String key;
@Unique
向数据库列添加了一个UNIQUE约束。请注意,SQLite还会隐式地为其创建索引
编写自己的entity---Student类
//告诉GreenDao该对象为实体,只有被@Entity注释的Bean类才能被dao类操作
//在Entity中我们可以配置许多信息,比如nameInDb是声明了该表数据库中的表名。
//indexes 用于建立索引,索引的应用场景可用于,当你的表有多个主键的时候,来标志一条数据的唯一性,配合unique。
@Entity
public class Student {
// id自增长
//(autoincrement = true)表示主键会自增,如果false就会使用旧值
@Id(autoincrement = true)
//学员id,注意这里的stuId只能是Long类型
private Long stuId;
// 学员编号---这里的意思是学员编号stuNo具有唯一性即数据库中不能有两个一样的stuNo
//如果数据库中有两个相同的stuNo会报错违反unique规则
//注意这里的@Index(unique =true)只是针对stuNo的,和下面的stuName stuSex stuScore没有什么关系
@Index(unique =true)
private String stuNo;
// 学员姓名
//@Property:在数据库中,会对应生成一个字段,nameInDb:StudentName(字段名称)
//@NotNull 标志这个字段不能是null
//@Property 如果定义了这个属性,那么nameInDb的值就是该列在数据表里面,该列的名称。
// 下面的例子,stuName的值存储在数据表里面的StudentName那一列。
//@Transient 表示不存储在数据库中
@Property(nameInDb = "StudentName") @NotNull
private String stuName;
// 学员性别
private String stuSex;
// 学员成绩
private String stuScore;
}
// 学员姓名
//@Property:在数据库中,会对应生成一个字段,nameInDb:StudentName(字段名称)
//@NotNull 标志这个字段不能是null
//@Property 如果定义了这个属性,那么nameInDb的值就是该列在数据表里面,该列的名称。
// 下面的例子,stuName的值存储在数据表里面的StudentName那一列。
//@Transient 表示不存储在数据库中
@Property(nameInDb = "StudentName") @NotNull
private String stuName;
用图片来说明:
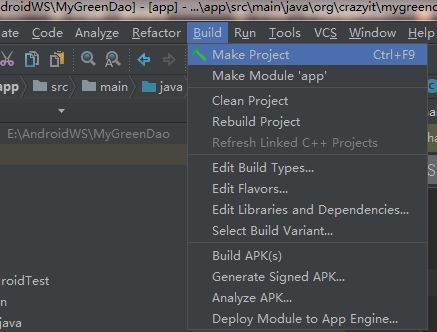
点击Build-> make project就可以自动生成相关的代码了。
项目目录结构中多出了如下文件夹,(因为我们改了默认的目录结构,详情见下行代码我们之前设置的,所以才会出现项目目录中多出了如下文件夹)
greendao{
......
targetGenDir 'src/main/java' //自动生成的代码存储的路径,默认是 build/generated/source/greendao.
}
然后我们编写的
student类中也多出来了如下代码:
//@Generated:编译后自动生成的构造函数、方法等的注释,提示构造函数、方法等不能被修改
@Generated(hash = 315497705)
public Student(Long stuId, String stuNo, String stuName, String stuSex,
String stuScore) {
this.stuId = stuId;
this.stuNo = stuNo;
this.stuName = stuName;
this.stuSex = stuSex;
this.stuScore = stuScore;
}
@Generated(hash = 1556870573)
public Student() {
}
public Long getStuId() {
return this.stuId;
}
public void setStuId(Long stuId) {
this.stuId = stuId;
}
public String getStuNo() {
return this.stuNo;
}
public void setStuNo(String stuNo) {
this.stuNo = stuNo;
}
public String getStuName() {
return this.stuName;
}
public void setStuName(String stuName) {
this.stuName = stuName;
}
public String getStuSex() {
return this.stuSex;
}
public void setStuSex(String stuSex) {
this.stuSex = stuSex;
}
public String getStuScore() {
return this.stuScore;
}
public void setStuScore(String stuScore) {
this.stuScore = stuScore;
}
获取StudentDao
初始化Dao
//创建数据库名字为xdl.db
DaoMaster.DevOpenHelper devOpenHelper=new DaoMaster.DevOpenHelper(this,"xdl.db",null);
SQLiteDatabase db=devOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
DaoMaster daoMaster=new DaoMaster(db);
DaoSession daoSession=daoMaster.newSession();
//获取StudentDao,通过StudentDao来CURD数据
StudentDao studentDao=daoSession.getStudentDao();
Dao的CURD方法
1.1新增一条数据
/**
* Insert an entity into the table associated with a concrete DAO.
*
* @return row ID of newly inserted entity
*/
/**
*将一个实体插入与具体DAO关联的表中。
*
* @新插入的实体的返回行ID
*/
public long insert(T entity) {
return executeInsert(entity, statements.getInsertStatement(), true);
}
studentDao.insert(new Student(null,"002","张针","男孩","0"));
1.2.新增List集合数据
/**
* Inserts the given entities in the database using a transaction.
*
* @param entities The entities to insert.
*/
/**
*使用事务将给定的实体插入到数据库中。
*
* @参数实体要插入的实体。
*/
public void insertInTx(Iterable entities) {
insertInTx(entities, isEntityUpdateable());
}
case R.id.id_insert_list:
List list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Student(null, "006", "贺利权", "大爷儿们", "35"));
list.add(new Student(null, "007", "贺利权", "老爷儿们", "99"));
list.add(new Student(null, "008", "贺利权", "老少爷儿们", "88"));
list.add(new Student(null, "009", "贺利权", "小爷儿们", "43"));
//新增集合数据
studentDao.insertInTx(list);
break;
2.删除指定信息
case R.id.id_delete:
studentDao.queryBuilder().where(StudentDao.Properties.StuName.eq("申学超")).buildDelete().executeDeleteWithoutDetachingEntities();
Toast.makeText(this,"删除成功",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
3.更新指定信息
case R.id.id_update:
Student student=studentDao.queryBuilder().where(StudentDao.Properties.StuName.eq("张针")).build().unique();
if (student!=null){
student.setStuName("屎壳郎");
studentDao.update(student);
}
Toast.makeText(this,"更新成功",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
4.1查询所有
case R.id.id_search_all:
List stulist= studentDao.queryBuilder().list();
if (stulist!=null){
String searchAllInfo=" ";
for (int i=0;i 4.2.查询指定数据 查询姓名为"徐冬磊"的信息
case R.id.id_search_assign:
String searchAssignInfo = "";
List stuList = studentDao.queryBuilder().where(StudentDao.Properties.StuName.eq("徐冬磊")).list();
for (int i = 0; i < stuList.size(); i++) {
Student student = stuList.get(i);
searchAssignInfo += "id:" + student.getStuId() + "编号:" + student.getStuNo() + "姓名:" + student.getStuName() + "性别:" + student.getStuSex() + "成绩:" + student.getStuScore() + "\n";
}
mTvInsertAssing.setText(searchAssignInfo);
break;
4.3.查询指定数据 查询姓名为"贺利权"的信息并按照成绩排序-降序
case R.id.id_search_assign_order_desc:
String searchAssignorderdesc = "";
List stuList1 = studentDao.queryBuilder().where(StudentDao.Properties.StuName.eq("贺利权")).orderDesc(StudentDao.Properties.StuScore).list();
for (int i = 0; i < stuList1.size(); i++) {
Student student = stuList1.get(i);
searchAssignorderdesc += "id:" + student.getStuId() + "编号:" + student.getStuNo() + "姓名:" + student.getStuName() + "性别:" + student.getStuSex() + "成绩:" + student.getStuScore() + "\n";
}
mTvsearchdesc.setText(searchAssignorderdesc);
break;
4.4.查询指定数据 查询姓名为"贺利权"的信息并按照成绩排序-升序
case R.id.id_search_assign_order_asc:
String searchassignorderasc=" ";
List stuList2=studentDao.queryBuilder().where(StudentDao.Properties.StuName.eq("贺利权")).orderAsc(StudentDao.Properties.StuScore).list();
for (int i=0;i 4.5.组合查询数据 查询姓名为"贺利权" 并且成绩小于等于60
case R.id.id_search_combination:
String search_combination=" ";
List stuList3=studentDao.queryBuilder().where(StudentDao.Properties.StuName.eq("贺利权"),StudentDao.Properties.StuScore.le(60)).list();
for (int i=0;i 4.6.查询所有返回数据 但只返回前三条数据
case R.id.id_search_limit:
List stuList4=studentDao.queryBuilder().limit(3).list();
if (stuList4!=null){
String searchlimit=" ";
for (int i=0;i 4.7.查询所有返回数据 但只返回前三条数据 并且跳过第一条数据
case R.id.id_search_limit_offset:
List stuList5=studentDao.queryBuilder().limit(3).offset(1).list();
if (stuList5!=null){
String searchlimit=" ";
for (int i=0;i 4.8.查询所有信息总条数
case R.id.id_search_count:
int stucount=studentDao.queryBuilder().list().size();
//stucount是一个整型数据而setText需要传入的是一个CharSequence型数据所以如果只传入stucount会报错
mTvSearchCountInfo.setText(stucount+" ");
break;
程序源码
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private DaoMaster.DevOpenHelper devOpenHelper;
private SQLiteDatabase db;
private DaoMaster daoMaster;
private DaoSession daoSession;
private StudentDao studentDao;
private Button mBtnInsert;
private Button mBtnInsetList;
private Button mBtnInsertall;
private TextView mTvSearchAllInfo;
private Button mBtnInsertassign;
private TextView mTvInsertAssing;
private Button mBtnSearchdesc;
private TextView mTvsearchdesc;
private Button mBtnSearchasc;
private TextView mTvsearchasc;
private Button mBtnSearchCombine;
private TextView mTvSearchCombine;
private Button mBtnSearchLimit;
private TextView mTvSearchLimitInfo;
private Button mBtnSearchLimitOffset;
private TextView mTvSearchLimitOffsetInfo;
private Button mBtnSearchCount;
private TextView mTvSearchCountInfo;
private Button mBtnDelete;
private Button mBtnUpdate;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
devOpenHelper =new DaoMaster.DevOpenHelper(this,"xdl.db",null);
db=devOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
daoMaster=new DaoMaster(db);
daoSession=daoMaster.newSession();
studentDao=daoSession.getStudentDao();
mBtnInsert=findViewById(R.id.id_insert);
mBtnInsert.setOnClickListener(this);
mBtnInsetList=findViewById(R.id.id_insert_list);
mBtnInsetList.setOnClickListener(this);
mBtnInsertall=findViewById(R.id.id_search_all);
mBtnInsertall.setOnClickListener(this);
mTvSearchAllInfo=findViewById(R.id.id_search_all_info);
mBtnInsertassign=findViewById(R.id.id_search_assign);
mBtnInsertassign.setOnClickListener(this);
mTvInsertAssing=findViewById(R.id.id_search_assign_info);
mBtnSearchdesc=findViewById(R.id.id_search_assign_order_desc);
mBtnSearchdesc.setOnClickListener(this);
mTvsearchdesc=findViewById(R.id.id_search_assign_order_desc_info);
mBtnSearchasc=findViewById(R.id.id_search_assign_order_asc);
mTvsearchasc=findViewById(R.id.id_search_assign_order_asc_info);
mBtnSearchasc.setOnClickListener(this);
mBtnSearchCombine=findViewById(R.id.id_search_combination);
mTvSearchCombine=findViewById(R.id.id_search_combination_info);
mBtnSearchCombine.setOnClickListener(this);
mBtnSearchLimit=findViewById(R.id.id_search_limit);
mTvSearchLimitInfo=findViewById(R.id.id_search_limit_info);
mBtnSearchLimit.setOnClickListener(this);
mBtnSearchLimitOffset=findViewById(R.id.id_search_limit_offset);
mBtnSearchLimitOffset.setOnClickListener(this);
mTvSearchLimitOffsetInfo=findViewById(R.id.id_search_limit_offset_info);
mBtnSearchCount=findViewById(R.id.id_search_count);
mBtnSearchCount.setOnClickListener(this);
mTvSearchCountInfo=findViewById(R.id.id_search_count_info);
mBtnDelete=findViewById(R.id.id_delete);
mBtnDelete.setOnClickListener(this);
mBtnUpdate=findViewById(R.id.id_update);
mBtnUpdate.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.id_insert:
Student stu = new Student(null,"001", "徐冬磊", "男孩", "50");
long end=studentDao.insert(stu);
if (end>0){
Toast.makeText(this,"001新增成功",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}else
{
Toast.makeText(this,"001新增失败",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
studentDao.insert(new Student(null,"002","张针","男孩","0"));
studentDao.insert(new Student(null,"003","申学超","男孩","60"));
studentDao.insert(new Student(null,"004","李东","男孩","40"));
studentDao.insert(new Student(null,"005","黄伟健","男孩","80"));
Toast.makeText(this, "002 003 004新增成功~", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case R.id.id_insert_list:
List list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Student(null, "006", "贺利权", "大爷儿们", "35"));
list.add(new Student(null, "007", "贺利权", "老爷儿们", "99"));
list.add(new Student(null, "008", "贺利权", "老少爷儿们", "88"));
list.add(new Student(null, "009", "贺利权", "小爷儿们", "43"));
//新增集合数据
studentDao.insertInTx(list);
break;
case R.id.id_search_all:
List stulist= studentDao.queryBuilder().list();
if (stulist!=null){
String searchAllInfo=" ";
for (int i=0;i stuList = studentDao.queryBuilder().where(StudentDao.Properties.StuName.eq("徐冬磊")).list();
for (int i = 0; i < stuList.size(); i++) {
Student student = stuList.get(i);
searchAssignInfo += "id:" + student.getStuId() + "编号:" + student.getStuNo() + "姓名:" + student.getStuName() + "性别:" + student.getStuSex() + "成绩:" + student.getStuScore() + "\n";
}
mTvInsertAssing.setText(searchAssignInfo);
break;
case R.id.id_search_assign_order_desc:
String searchAssignorderdesc = "";
List stuList1 = studentDao.queryBuilder().where(StudentDao.Properties.StuName.eq("贺利权")).orderDesc(StudentDao.Properties.StuScore).list();
for (int i = 0; i < stuList1.size(); i++) {
Student student = stuList1.get(i);
searchAssignorderdesc += "id:" + student.getStuId() + "编号:" + student.getStuNo() + "姓名:" + student.getStuName() + "性别:" + student.getStuSex() + "成绩:" + student.getStuScore() + "\n";
}
mTvsearchdesc.setText(searchAssignorderdesc);
break;
case R.id.id_search_assign_order_asc:
String searchassignorderasc=" ";
List stuList2=studentDao.queryBuilder().where(StudentDao.Properties.StuName.eq("贺利权")).orderAsc(StudentDao.Properties.StuScore).list();
for (int i=0;i stuList3=studentDao.queryBuilder().where(StudentDao.Properties.StuName.eq("贺利权"),StudentDao.Properties.StuScore.le(60)).list();
for (int i=0;i stuList4=studentDao.queryBuilder().limit(3).list();
if (stuList4!=null){
String searchlimit=" ";
for (int i=0;i stuList5=studentDao.queryBuilder().limit(3).offset(1).list();
if (stuList5!=null){
String searchlimit=" ";
for (int i=0;i /**
* Created by Administrator on 2018/4/21.
*/
//告诉GreenDao该对象为实体,只有被@Entity注释的Bean类才能被dao类操作
//在Entity中我们可以配置许多信息,比如nameInDb是声明了该表数据库中的表名。
//indexes 用于建立索引,索引的应用场景可用于,当你的表有多个主键的时候,来标志一条数据的唯一性,配合unique。
@Entity
public class Student {
// id自增长
//(autoincrement = true)表示主键会自增,如果false就会使用旧值
@Id(autoincrement = true)
//学员id,注意这里的stuId只能是Long类型
private Long stuId;
// 学员编号---这里的意思是学员编号stuNo具有唯一性即数据库中不能有两个一样的stuNo
//如果数据库中有两个相同的stuNo会报错违反unique规则
//注意这里的@Index(unique =true)只是针对stuNo的,和下面的stuName stuSex stuScore没有什么关系
@Index(unique =true)
private String stuNo;
// 学员姓名
//@Property:在数据库中,会对应生成一个字段,nameInDb:StudentName(字段名称)
//@NotNull 标志这个字段不能是null
//@Property 如果定义了这个属性,那么nameInDb的值就是该列在数据表里面,该列的名称。
// 下面的例子,stuName的值存储在数据表里面的StudentName那一列。
//@Transient 表示不存储在数据库中
@Property(nameInDb = "StudentName") @NotNull
private String stuName;
// 学员性别
private String stuSex;
// 学员成绩
private String stuScore;
//@Generated:编译后自动生成的构造函数、方法等的注释,提示构造函数、方法等不能被修改
@Generated(hash = 315497705)
public Student(Long stuId, String stuNo, String stuName, String stuSex,
String stuScore) {
this.stuId = stuId;
this.stuNo = stuNo;
this.stuName = stuName;
this.stuSex = stuSex;
this.stuScore = stuScore;
}
@Generated(hash = 1556870573)
public Student() {
}
public Long getStuId() {
return this.stuId;
}
public void setStuId(Long stuId) {
this.stuId = stuId;
}
public String getStuNo() {
return this.stuNo;
}
public void setStuNo(String stuNo) {
this.stuNo = stuNo;
}
public String getStuName() {
return this.stuName;
}
public void setStuName(String stuName) {
this.stuName = stuName;
}
public String getStuSex() {
return this.stuSex;
}
public void setStuSex(String stuSex) {
this.stuSex = stuSex;
}
public String getStuScore() {
return this.stuScore;
}
public void setStuScore(String stuScore) {
this.stuScore = stuScore;
}
}
结束语
当然CRUD方法还不是很全可以再看看官方文档:
GreenDao 官网:http://greenrobot.org/greendao/
GreenDao 特征介绍:http://greenrobot.org/greendao/features/
GreenDao 学习文档:http://greenrobot.org/greendao/documentation/
GreenDao 更新日志:http://greenrobot.org/greendao/changelog/
GreenDao GitHub地址:https://github.com/greenrobot/greenDAO