HBase 中 HMaster、HRegionServer 和 Client 之间的通信使用了两个技术,Google Protobuf RPC 和 Java NIO。
主要代码位置:
.
|—— hbase-client
| |—— org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc
| |—— org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client
|—— hbase-server
| |—— org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc
| |—— org.apache.hadoop.hbase.master
| |—— org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver
|—— hbase-protocal
| |—— org.apache.hadoop.hbase.protobuf.generated
...
HBase RPC
什么是 PRC
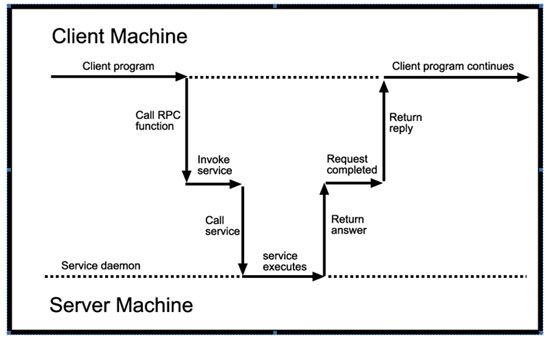
RPC(Remote Procedure Call)即远程过程调用。对于本地调用,定义好一个函数以后,程序的其他部分通过调用该函数,就可以返回想要的结果。RPC 的区别就是函数定义和函数调用位于不同的机器(大部分情况),因为涉及到不同的机器,所以 RPC 相比较本地函数调用多了通信部分。主要涉及到两个角色:调用方(client)和函数定义实现(server),RPC 调用的流程如下面图所示:
HBase Server 端主要类关系:
[图片上传失败...(image-6f67b9-1560062040880)]
HMaster 继承 HRegionServer,rpcService 提供 RPC Server 端实现(HRegionServier 中由 RSRpcService 实现,HMaster 中由 MasterRpcService 实现),rpcServer 是具体的 RPC Server 实现(实现 RpcServerInterface 接口),Listener 线程负责监听请求,Resonder 线程负责发送请求结果。
HBase Client 端主要类关系:
HBase Client 访问 HBase 需要先创建 HConnection,Connection 中的 rpcClient(RpcClient 接口,RpcClientImpl 是实现类)表示 Rpc Client 端实现,由 RpcClientFactory 创建。
RPC 初始化
在 HRegionServer 启动类的源码中,有以下代码,分别初始化 RpcServer 和 RpcClient:
public HRegionServer(Configuration conf, CoordinatedStateManager csm)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// ...
rpcServices = createRpcServices();
// ...
}
private void initializeThreads() {
// ...
rpcClient = RpcClientFactory.createClient(conf, clusterId, new InetSocketAddress(
rpcServices.isa.getAddress(), 0), clusterConnection.getConnectionMetrics());
// ...
}
RPC Server
先来看以下 RPC Server 端的一些实现,从一些重要类的初始化开始
初始化
createRpcServices()
createRpcServices() 方法是初始化 RPC Server 端实现的入口:
class HRegionServer {
protected RSRpcServices createRpcServices() throws IOException {
return new RSRpcServices(this);
}
}
class HMaseter implements HRegionServer {
@Override
protected RSRpcServices createRpcServices() throws IOException {
return new MasterRpcServices(this);
}
}
RSRpcServices#Constructor
MasterRpcServices 的构造方法调用父类 RSRpcServices 的构造方法:
public MasterRpcServices(HMaster m) throws IOException {
super(m);
// set HMaster
master = m;
}
public RSRpcServices(HRegionServer rs) throws IOException {
// set HRegionServer
regionServer = rs;
// 初始化 RpcSchedulerFactory
// 反射 hbase.region.server.rpc.scheduler.factory.class 指定的类
// 默认使用 SimpleRpcSchedulerFactory
RpcSchedulerFactory rpcSchedulerFactory = ...
// ...
// 优先级函数(调度请求时使用)
priority = createPriority();
// 设置访问时的重试次数
ConnectionUtils.setServerSideHConnectionRetriesConfig(rs.conf, name, LOG);
// 初始化 RpcServer
try {
rpcServer = new RpcServer(rs, name, getServices(),
bindAddress,
rs.conf,
rpcSchedulerFactory.create(rs.conf, this, rs));
} catch (BindException be) {
// throw Execption
}
// 初始化配置信息
// hbase.client.scanner.timeout.period # Client 端 Scan Timeout
// hbase.server.scanner.max.result.size Scan # Scan 获取的最大条目数
// hbase.rpc.timeout # RPC 处理请求 Timeout 时间
// hbase.region.server.rpc.minimum.scan.time.limit.delta #
scannerLeaseTimeoutPeriod = rs.conf.getInt(...);
maxScannerResultSize = rs.conf.getLong(...);
rpcTimeout = rs.conf.getInt(...);
minimumScanTimeLimitDelta = rs.conf.getLong(...);
}
RpcServer#Constructor
RpcServer 实现了 RpcServerInterface 接口,构造函数:
public RpcServer(final Server server, final String name,
final List services,
final InetSocketAddress bindAddress, Configuration conf,
RpcScheduler scheduler)
throws IOException {
// 初始化属性 ...
// 设置 Listener
listener = new Listener(name);
// 设置 Responder
responder = new Responder();
// 设置 Scheduler(调用方通过 RpcSchedulerFactory 创建)
this.scheduler = scheduler;
this.scheduler.init(new RpcSchedulerContext(this));
}
主要处理角色
Rpc Server 监控、读取、请求基于 Reactor 模式,主要流程如下图:
Listener
Listener 负责监听请求,对于获取到的请求,交由 Reader 负责读取:
private class Listener extends Thread {
private ServerSocketChannel acceptChannel = null;
private Selector selector = null;
private Reader[] readers = null;
private ExecutorService readPool;
public Listener(final String name) throws IOException {
// ...
// 创建非阻塞的 ServerSocketChannel
acceptChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
acceptChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 绑定 Socket 到 RpcServer#bingAddress
bind(acceptChannel.socket(), bindAddress, backlogLength);
// 创建 selector
selector = Selector.open();
// 初始化 Reader ThreadPool
readers = new Reader[readThreads];
readPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(readThreads,
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat(...)
.setDaemon(true)
.build());
for (int i = 0; i < readThreads; ++i) {
Reader reader = new Reader();
readers[i] = reader;
readPool.execute(reader);
}
// 注册 selector
acceptChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}
}
Reader
处理请求的逻辑在 Reader 中,生成 Call 对象交由 RpcSchedule 进行分发
private class Reader implements Runnable {
private final Selector readSelector;
@Override
public void run() {
try {
doRunLoop();
} finally {
// close readSelector
}
}
private synchronized void doRunLoop() {
while (running) {
try {
// 线程阻塞,知道有请求到来
readSelector.select();
Iterator iter = readSelector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
iter.remove();
if (key.isValid()) {
if (key.isReadable()) {
// 请求有效,进行处理
doRead(key);
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// ...
}
}
}
}
doRead() 方法在 Listener 中,由 Connection 对象处理,生成 Call,并包装为 CallRunner 交给 Scheduler
class Listener {
void doRead(SelectionKey key) throws InterruptedException {
Connection c = (Connection) key.attachment();
try {
count = c.readAndProcess();
} catch (Exception e) {
// ...
}
}
}
class Connection {
protected void processRequest(byte[] buf) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// ...
// Dispatches an RPC request asynchronously
if (!scheduler.dispatch(new CallRunner(RpcServer.this, call))) {
// ...
responder.doRespond(call);
}
}
}
Scheduler
Scheduler 是一个生产者消费者模型,内部有一个队列缓存请求,另外有一些线程负责从队列中拉取消息进行分发
Scheduler 默认实现为 SimpleRpcScheduler(HBase 提供的另一种实现为 FifoRpcScheduler),包含三个 RpcExecutor(callExecutor、priorityExecutor、replicationExecutor)
public class SimpleRpcScheduler extends RpcScheduler {
/**
* callExecutor = RWQueueRpcExecutor or BalancedQueueRpcExecutor
* priorityExecutor = BalancedQueueRpcExecutor or NULL
* replicationExecutor = BalancedQueueRpcExecutor or NULL
**/
private final RpcExecutor callExecutor;
private final RpcExecutor priorityExecutor;
private final RpcExecutor replicationExecutor;
// 分发请求
@Override
public boolean dispatch(CallRunner callTask) throws InterruptedException {
// 选择不同的 Executor 处理
// 大部分基于的请求都是通过 callExecutor 来执行
if (priorityExecutor != null && level > highPriorityLevel) {
return priorityExecutor.dispatch(callTask);
} else if (replicationExecutor != null && level == HConstants.REPLICATION_QOS) {
return replicationExecutor.dispatch(callTask);
} else {
return callExecutor.dispatch(callTask);
}
}
}
RpcExecutor
阻塞队列
RpcExecutor 的实现类 RWQueueRpcExecutor 使用阻塞队列缓存消息(BalancedQueueRpcExecutor 实现类似):
class RWQueueRpcExecutor extends RpcExecutor {
private final List> queues;
@Override
public boolean dispatch(final CallRunner callTask) throws InterruptedException {
// 进入队列
return queues.get(queueIndex).offer(callTask);
}
}
消费线程
RpcExecutor 处理的具体逻辑在 consumerLoop() 方法中,从阻塞队列中取出 CallRunner 对象,并执行:
public abstract class RpcExecutor {
// 启动多线程处理
protected void startHandlers(final String nameSuffix, final int numHandlers,
final List> callQueues,
final int qindex, final int qsize, final int port) {
for (int i = 0; i < numHandlers; i++) {
final int index = qindex + (i % qsize);
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
consumerLoop(callQueues.get(index));
}
});
t.start();
}
}
// 核心处理逻辑(省略部分代码)
protected void consumerLoop(final BlockingQueue myQueue) {
try {
while (running) {
try {
// 如果 BlockingQueue 中没有数据,会在此阻塞
CallRunner task = myQueue.take();
try {
// 执行请求
task.run();
} catch (Throwable e) {
// throw or abort
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
interrupted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (interrupted) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
}
CallRunner & Call
CallRunner 和 Call 关键代码如下:
class CallRunner {
private Call call;
public void run() {
// ...
Pair resultPair = null;
try {
// make the call
resultPair = this.rpcServer.call(call.service, call.md, call.param, call.cellScanner,
call.timestamp, this.status);
} catch (Throwable e) {
// ...
}
// Call to respond
call.sendResponseIfReady();
}
}
class Call {
public synchronized void sendResponseIfReady() throws IOException {
// 结果返回给 Client
this.responder.doRespond(this);
}
}
调用执行方法在 RpcServer#call() 方法中:
class RpcServer {
@Override
public Pair call(BlockingService service, MethodDescriptor md,
Message param, CellScanner cellScanner, long receiveTime, MonitoredRPCHandler status)
throws IOException {
try {
// call method
// com.google.protobuf#BlockingService
Message result = service.callBlockingMethod(md, controller, param);
if (tooSlow || tooLarge) {
// logging
}
return new Pair(result, controller.cellScanner());
} catch (Throwable e) {
// ...
}
}
}
Responder
Resonder 负责发送 RPC 请求结果给 Client,Scheduler 调度请求后,执行结果通过 doRespond() 加入到返回结果的相应队列里面
class Responder extends Thread {
void doRespond(Call call) throws IOException {
boolean added = false;
// 如果已经有一个正在进行的写入,不会等待。
// 这允许立即释放处理程序以执行其他任务。
if (call.connection.responseQueue.isEmpty() &&
call.connection.responseWriteLock.tryLock()) {
try {
if (call.connection.responseQueue.isEmpty()) {
// 这里如果完成写操作,直接返回
if (processResponse(call)) {
return; // we're done.
}
call.connection.responseQueue.addFirst(call);
added = true;
}
} finally {
call.connection.responseWriteLock.unlock();
}
}
if (!added) {
call.connection.responseQueue.addLast(call);
}
// Add a connection to the list that want to write,
call.responder.registerForWrite(call.connection);
}
}
如果在 doRespond() 中没有完成写操作,通过将 Call 对象的 connection 注册到 selector,由 Responder 中的线程进行后续的操作。
protected class Responder extends Thread {
private final Selector writeSelector;
public void registerForWrite(Connection c) {
if (writingCons.add(c)) {
writeSelector.wakeup();
}
}
private void doRunLoop() {
while (running) {
try {
// 获取要写入的连接列表,并在 selector 中注册
registerWrites();
// ...
Set keys = writeSelector.selectedKeys();
Iterator iter = keys.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
iter.remove();
if (key.isValid() && key.isWritable()) {
// 异步写
doAsyncWrite(key);
}
}
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
// return or sleep
}
}
}
private void doAsyncWrite(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
Connection connection = (Connection) key.attachment();
if (processAllResponses(connection)) {
// ...
}
}
private boolean processAllResponses(final Connection connection) throws IOException {
// Only one writer on the channel for a connection at a time.
connection.responseWriteLock.lock();
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
Call call = connection.responseQueue.pollFirst();
if (!processResponse(call)) {
connection.responseQueue.addFirst(call);
return false;
}
}
} finally {
connection.responseWriteLock.unlock();
}
return connection.responseQueue.isEmpty();
}
}