1、upperBound(Type t)方法
/**
* The "rvalue conversion".
* The upper bound of most types is the type itself. Wildcards, on the other hand have upper and lower bounds.
* @param t a type
* @return the upper bound of the given type
*/
public Type upperBound(Type t) {
return upperBound.visit(t);
}
// where
private final MapVisitor upperBound = new MapVisitor() {
@Override
public Type visitWildcardType(WildcardType t, Void ignored) {
if (t.isSuperBound())
return t.bound == null ? syms.objectType : t.bound.bound;
else
return visit(t.type);
}
@Override
public Type visitCapturedType(CapturedType t, Void ignored) {
return visit(t.bound);
}
};
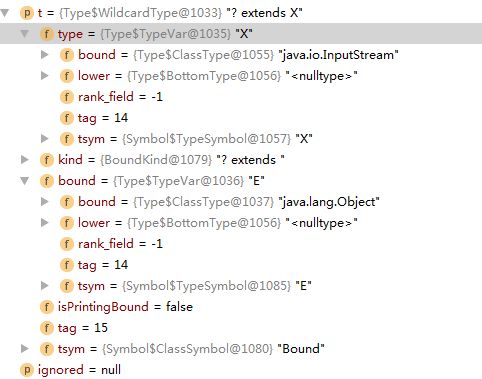
举个例子,如List或者List时,这个WildcardType的isSuperBound()返回都为true,如果为List,那么上界为Object类型,否则就是类声明的上界。查看List的实现,如下:
public interface Listextends Collection { // ... }
那么bound类型为E,bound.bound为Object。如果为List时,如下:
public class Test{ public void test() { List x; } }
那么bound类型为TypeVar,则TypeVar的bound为X的bound
如果为List或List时会调用visit(t.type),而这个type类型就是InputStream(ClassType类型)或者X(TypeVar类型)来继续查找上界。举个例子如下:
public class Test{ public void test(){ List x = new ArrayList(); x.add(null); } }
这时候传入方法的t参数如下:
调用visit(t.type)后会返回TypeVar类型,如果为CapturedType,那么就访问upperBound实例中的visitCapturedType(CapturedType t,Void ignored)方法,然后继续visit(t.bound)进行上界的查找。
2、lowerBound(Type t)方法
/**
* The "lvalue conversion".
* The lower bound of most types is the type itself. Wildcards, on the other hand have upper and lower bounds.
* @param t a type
* @return the lower bound of the given type
*/
public Type lowerBound(Type t) {
return lowerBound.visit(t);
}
// where
private final MapVisitor lowerBound = new MapVisitor() {
@Override
public Type visitWildcardType(WildcardType t, Void ignored) {
return t.isExtendsBound() ? syms.botType : visit(t.type);
}
@Override
public Type visitCapturedType(CapturedType t, Void ignored) {
return visit(t.getLowerBound());
}
};
如果如List或者List或者List时,下界为null,否则就是List或者List时调用visit(t.type)查找下界,如果t.type为非CapturedType,那么下界就是t.type,如果为CapturedType类型时,则继续查找
t.getLowerBound()类型的下界。
3、isUnbounded(Type t)方法
/**
* Checks that all the arguments to a class are unbounded wildcards or something else that doesn't make any restrictions
* on the arguments. If a class isUnbounded, a raw super- or subclass can be cast to it without a warning.
* @param t a type
* @return true iff the given type is unbounded or raw
*/
public boolean isUnbounded(Type t) {
return isUnbounded.visit(t);
}
// where
private final UnaryVisitor isUnbounded = new UnaryVisitor() {
public Boolean visitType(Type t, Void ignored) {
return true;
}
@Override
public Boolean visitClassType(ClassType t, Void ignored) {
List parms = t.tsym.type.allparams();
List args = t.allparams();
while (parms.nonEmpty()) {
// public WildcardType(Type type, BoundKind kind, TypeSymbol tsym, TypeVar bound)
WildcardType unb = new WildcardType(syms.objectType,
BoundKind.UNBOUND,
syms.boundClass,
(TypeVar)parms.head);
if (!containsType(args.head, unb)) {
return false;
}
parms = parms.tail;
args = args.tail;
}
return true;
}
};
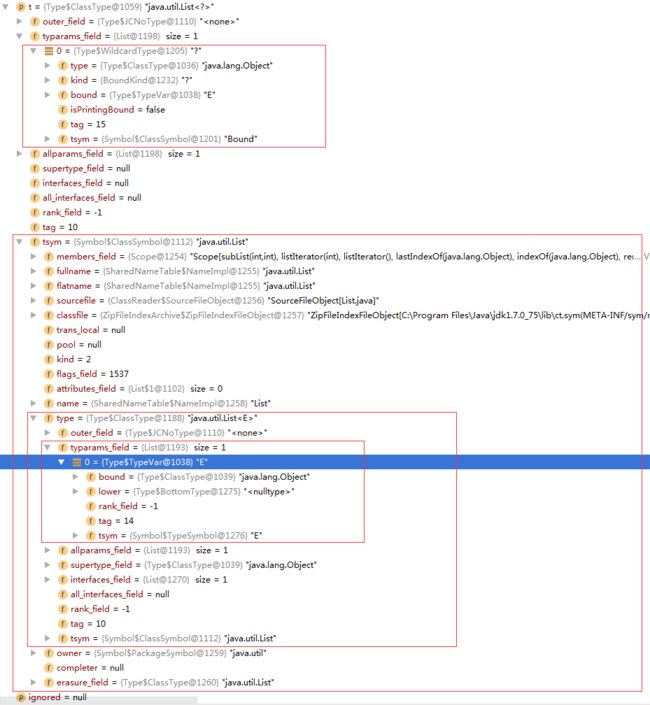
举个例子,如下:
List x = new ArrayList(); Object y = (List)x;
传入的ClassType的t参数如下截图:
实际的类型参数是否包含形式类型参数来决定是否对实际的类型参数产生约束。
3、containsType() 方法
这个方法的注释如下:
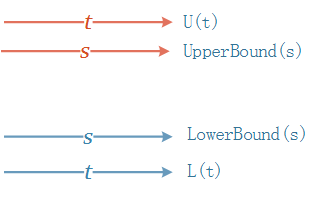
Check if t contains s.
T contains S if:
L(T) <: L(S) && U(S) <: U(T)
This relation is only used by ClassType.isSubtype(), that is,
C <: C
Because of F-bounds, this relation can lead to infinite recursion. Thus we must somehow break that recursion. Notice that containsType() is only called from ClassType.isSubtype(). Since the arguments have already been checked against their bounds, we know:
U(S) <: U(T) if T is "super" bound (U(T) *is* the bound)
L(T) <: L(S) if T is "extends" bound (L(T) is bottom)
通过如下方法就可知道代码是如何来判断两者之间的关系的,如下:
void debugContainsType(WildcardType t, Type s) {
System.err.println();
System.err.format(" does %s contain %s?%n", t, s);
System.err.format(" %s U(%s) <: U(%s) %s = %s%n",
upperBound(s), s, t, U(t),
t.isSuperBound() ||
isSubtypeNoCapture(upperBound(s), U(t)));
System.err.format(" %s L(%s) <: L(%s) %s = %s%n",
L(t), t, s, lowerBound(s),
t.isExtendsBound() ||
isSubtypeNoCapture(L(t), lowerBound(s)));
System.err.println();
}
在TypeRelation匿名类中,有两个私有方法,代码如下:
private Type U(Type t) {
while (t.tag == WILDCARD) {
WildcardType w = (WildcardType)t;
if (w.isSuperBound())
return w.bound == null ? syms.objectType : w.bound.bound;
else
t = w.type;
}
return t;
}
private Type L(Type t) {
while (t.tag == WILDCARD) {
WildcardType w = (WildcardType)t;
if (w.isExtendsBound())
return syms.botType;
else
t = w.type;
}
return t;
}
主要的逻辑就是求通配符的上界和下界。剩下就是处理特定几个类型了,如下:
@Override
public Boolean visitWildcardType(WildcardType t, Type s) {
if (s.tag >= firstPartialTag)
return containedBy(s, t);
else {
debugContainsType(t, s);
if(isSameWildcard(t, s)){
return true;
}
if(isCaptureOf(s, t)){
return true;
}
boolean a = t.isExtendsBound() || isSubtypeNoCapture(L(t), lowerBound(s));
boolean b = t.isSuperBound() || isSubtypeNoCapture(upperBound(s), U(t));
return a && b;
}
}
可以看到主要还是处理WildcardType与UndeterminedVariable类型。
(1)visitWildcardType(WildcardType t,Type s)判断t是否包含了s类型,如果s.tag>=firstPartialTag,那么调用containedBy(s,t)方法来判断两者之间的关系。也就是
/** The tag of an unknown type
*/
public static final int UNKNOWN = ERROR+1;
/** The tag of all instantiatable type variables.
*/
public static final int UNDETVAR = UNKNOWN+1;
/** The number of type tags.
*/
public static final int TypeTagCount = UNDETVAR+1;
当s为UNKNOWN或者UNDETVAR类型时调用containedBy()方法。
当s与t是两个相同的WildcardType时,返回true,如何判断两个WildcardType类型相同呢?
public boolean isSameWildcard(WildcardType t, Type s) {
if (s.tag != WILDCARD)
return false;
WildcardType w = (WildcardType)s;
return w.kind == t.kind && w.type == t.type;
}
kind相同同时type也相同,kind是一个枚举类型,如下:
public enum BoundKind {
EXTENDS("? extends "),
SUPER("? super "),
UNBOUND("?");
private final String name;
BoundKind(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String toString() { return name; }
}
接下来调用isCaptureOf()方法进行判断,代码如下:
public boolean isCaptureOf(Type s, WildcardType t) {
if (s.tag != TYPEVAR || !((TypeVar)s).isCaptured())
return false;
return isSameWildcard(t, ((CapturedType)s).wildcard);
}
看一下CaptureType类型的实现代码,如下:
/** A captured type variable comes from wildcards which can have
* both upper and lower bound. CapturedType extends TypeVar with a lower bound.
*/
public static class CapturedType extends TypeVar {
public WildcardType wildcard;
public CapturedType(Name name,
Symbol owner,
Type upper,
Type lower,
WildcardType wildcard) {
super(name, owner, lower);
this.lower = Assert.checkNonNull(lower);
this.bound = upper;
this.wildcard = wildcard;
}
@Override
public R accept(Type.Visitor v, S s) {
return v.visitCapturedType(this, s);
}
@Override
public boolean isCaptured() {
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "capture#"
+ (hashCode() & 0xFFFFFFFFL) % Printer.PRIME
+ " of "
+ wildcard;
}
}
这个CaptureType继承了TypeVar类型,也就和TypeVar有相同的tag值。所以如果s.tag!=TYPEVAR,那就一定不是CaptureType类型。然后继续调用TypeVar类型的isCaptured()方法进行了判断。只有CapturedType类型的isCaptured()方法返回true,TypeVar及其它类型返回为false。
也就可以断定,如果走到了if判断语句的下面,那么s类型肯定为CaputuredType。
接下来有两个判断,如下:
boolean a = t.isExtendsBound() || isSubtypeNoCapture(L(t), lowerBound(s)); // L(t)是否为LowerBound(s)的子类型 boolean b = t.isSuperBound() || isSubtypeNoCapture(upperBound(s), U(t)); // upperBound(s)是否为U(t)的子类型
关于isExtendsBond()与isSuperBound()方法定义在WildcardType类型中,代码如下:
public boolean isSuperBound() {
return kind == SUPER || kind == UNBOUND;
}
public boolean isExtendsBound() {
return kind == EXTENDS || kind == UNBOUND;
}
public boolean isUnbound() {
return kind == UNBOUND;
}
关于a与b的判断条件如下:
当t要包含s类型时,t的上界要大于s的上界,t的下界要小于s的下界。
当t为UndetVar类型时,判断逻辑代码如下:
@Override
public Boolean visitUndetVar(UndetVar t, Type s) {
if (s.tag != WILDCARD)
return isSameType(t, s);
else
return false;
}
当s不为通配符类型时判断是否为同一个类型,否则就没有包含的关系。
@Override
public Boolean visitType(Type t, Type s) {
if (s.tag >= firstPartialTag)
return containedBy(s, t);
else
return isSameType(t, s);
}
@Override
public Boolean visitErrorType(ErrorType t, Type s) {
return true;
}
也就是如果t是非ErrorType,CapturedType与UndetVar类型时,会调用visitType()方法来判断包含关系。
当t为ErrorType时为什么会返回true?