事件分发的重要性我就不多说了,我们先从简到难。
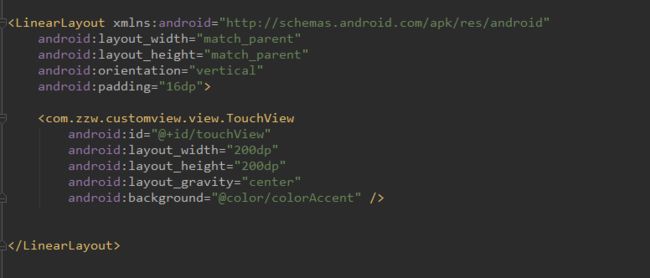
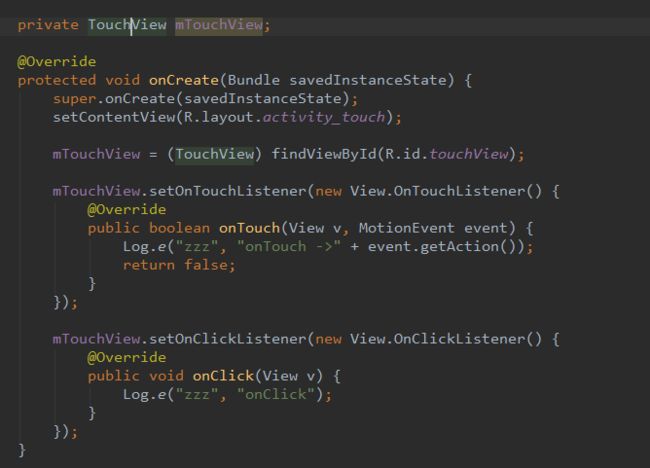
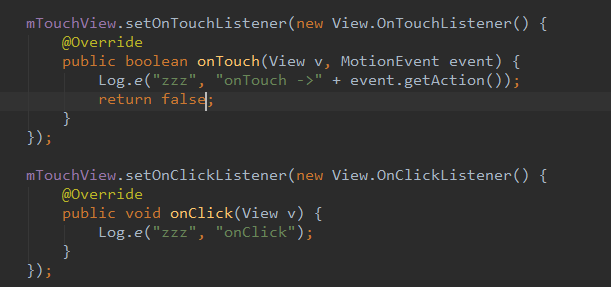
先看View的Touch事件分发,我自定义一个View,重写OnTouchEvent函数,然后分别设置OnTouchListener和OnClick:
ACTION_DOWN = 0 ACTION_UP=1 ACTION_MOVE=2
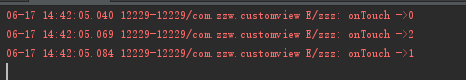
我们我们按下这个View点击一下:
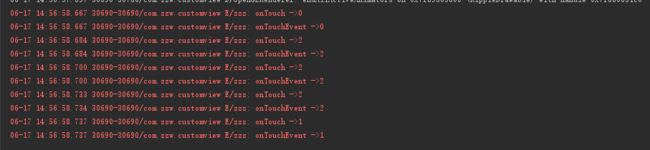
可以发现执行的顺序是:
OnTouchListener.DOWN -> OnTouchEvent.DOWN -> OnTouchListener.MOVE -> OnTouchEvent.MOVE -> OnTouchListener.UP-> OnTouchEvent.UP-> OnClickListener
从这我们就可以猜想执行的优先级为
OnTouchListener > onTouchEvent > onClick
接下来我们验证这个猜想,
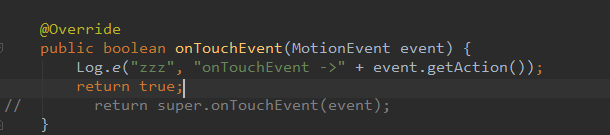
我们把OnTouchListener的onTouch返回值改为true
我在点击一下,这里大胆猜想一下
onTouchEvent和
onClick不会执行了,看看执行的顺序
这时候执行的顺序如下:
OnTouchListener.DOWN ->OnTouchListener.MOVE-> OnTouchListener.UP
这里验证了我的猜想,可以得到如下结论
View的Touch事件分发,OnToucherListener如果返回true的话,就说明把事件从OnToucherListener这里拦截了,后续的onTouchEvent和onClick就收不到事件了。
接下来我们把OnTouchListener的onTouch返回值改为false,让它不拦截事件,把onTouchEvent返回值改为true
我们点击一下,猜想是
OnTouchListener和
onTouchEvent能够接收到事件,
onClick将不会触发
和我们想的一致,这时候执行顺序变为:
OnTouchListener.DOWN ->OnTouchEvent.DOWN-> OnTouchListener.MOVE -> OnTouchEvent.MOVE->OnTouchListener.UP ->OnTouchEvent.UP
这里我们就可能得到结论
View的Touch事件分发,如果OnToucherListener返回false,onTouchEvent返回true,就说明把事件从onTouchEvent这里拦截了,onClick就不会触发。
通过上面两个结论我们验证了我们的优先级猜想
View的Touch事件分发,执行的优先级为OnTouchListener > onTouchEvent > onClick,如果前两个任意一个地方返回true,那么后续将不会收到事件。
接下来我们从源码的角度分析,首先我们需要知道,你点击或者或者触摸任何一个View 都会调用 dispatchTouchEvent()函数,我们就从这里开始分析源码:
/**
* Pass the touch screen motion event down to the target view, or this
* view if it is the target.
*
* @param event The motion event to be dispatched.
* @return True if the event was handled by the view, false otherwise.
*/
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
// If the event should be handled by accessibility focus first.
if (event.isTargetAccessibilityFocus()) {
// We don't have focus or no virtual descendant has it, do not handle the event.
if (!isAccessibilityFocusedViewOrHost()) {
return false;
}
// We have focus and got the event, then use normal event dispatch.
event.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);
}
boolean result = false;
if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onTouchEvent(event, 0);
}
final int actionMasked = event.getActionMasked();
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
// Defensive cleanup for new gesture
stopNestedScroll();
}
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) {
if ((mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED && handleScrollBarDragging(event)) {
result = true;
}
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null
&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
result = true;
}
if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {
result = true;
}
}
if (!result && mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onUnhandledEvent(event, 0);
}
// Clean up after nested scrolls if this is the end of a gesture;
// also cancel it if we tried an ACTION_DOWN but we didn't want the rest
// of the gesture.
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP ||
actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL ||
(actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN && !result)) {
stopNestedScroll();
}
return result;
}
我们先要知道ListenerInfo这个是做什么的?
static class ListenerInfo {
/**
* Listener used to dispatch focus change events.
* This field should be made private, so it is hidden from the SDK.
* {@hide}
*/
protected OnFocusChangeListener mOnFocusChangeListener;
/**
* Listeners for layout change events.
*/
private ArrayList mOnLayoutChangeListeners;
protected OnScrollChangeListener mOnScrollChangeListener;
/**
* Listeners for attach events.
*/
private CopyOnWriteArrayList mOnAttachStateChangeListeners;
/**
* Listener used to dispatch click events.
* This field should be made private, so it is hidden from the SDK.
* {@hide}
*/
public OnClickListener mOnClickListener;
/**
* Listener used to dispatch long click events.
* This field should be made private, so it is hidden from the SDK.
* {@hide}
*/
protected OnLongClickListener mOnLongClickListener;
/**
* Listener used to dispatch context click events. This field should be made private, so it
* is hidden from the SDK.
* {@hide}
*/
protected OnContextClickListener mOnContextClickListener;
/**
* Listener used to build the context menu.
* This field should be made private, so it is hidden from the SDK.
* {@hide}
*/
protected OnCreateContextMenuListener mOnCreateContextMenuListener;
private OnKeyListener mOnKeyListener;
private OnTouchListener mOnTouchListener;
private OnHoverListener mOnHoverListener;
private OnGenericMotionListener mOnGenericMotionListener;
private OnDragListener mOnDragListener;
private OnSystemUiVisibilityChangeListener mOnSystemUiVisibilityChangeListener;
OnApplyWindowInsetsListener mOnApplyWindowInsetsListener;
}
这是一个view所有事件的集合类。接下来进入这段代码,
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null
&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
result = true;
}
if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {
result = true;
}
从这段代码我们就可以知道如果mOnTouchListener !=null并且当前view的是enable=true就会执行li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event),执行li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)返回的false的话就会执行onTouchEvent(event)。
从这我们就可以知道OnTouchListener的优先级大于onTouchEvent。接着我们点击onTouchEvent进入
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
//......代码太长 省略
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
boolean prepressed = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PREPRESSED) != 0;
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0 || prepressed) {
// take focus if we don't have it already and we should in
// touch mode.
boolean focusTaken = false;
if (isFocusable() && isFocusableInTouchMode() && !isFocused()) {
focusTaken = requestFocus();
}
if (prepressed) {
// The button is being released before we actually
// showed it as pressed. Make it show the pressed
// state now (before scheduling the click) to ensure
// the user sees it.
setPressed(true, x, y);
}
if (!mHasPerformedLongPress && !mIgnoreNextUpEvent) {
// This is a tap, so remove the longpress check
removeLongPressCallback();
// Only perform take click actions if we were in the pressed state
if (!focusTaken) {
// Use a Runnable and post this rather than calling
// performClick directly. This lets other visual state
// of the view update before click actions start.
if (mPerformClick == null) {
mPerformClick = new PerformClick();
}
if (!post(mPerformClick)) {
performClick();
}
}
}
if (mUnsetPressedState == null) {
mUnsetPressedState = new UnsetPressedState();
}
if (prepressed) {
postDelayed(mUnsetPressedState,
ViewConfiguration.getPressedStateDuration());
} else if (!post(mUnsetPressedState)) {
// If the post failed, unpress right now
mUnsetPressedState.run();
}
removeTapCallback();
}
mIgnoreNextUpEvent = false;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
mHasPerformedLongPress = false;
if (performButtonActionOnTouchDown(event)) {
break;
}
// Walk up the hierarchy to determine if we're inside a scrolling container.
boolean isInScrollingContainer = isInScrollingContainer();
// For views inside a scrolling container, delay the pressed feedback for
// a short period in case this is a scroll.
if (isInScrollingContainer) {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_PREPRESSED;
if (mPendingCheckForTap == null) {
mPendingCheckForTap = new CheckForTap();
}
mPendingCheckForTap.x = event.getX();
mPendingCheckForTap.y = event.getY();
postDelayed(mPendingCheckForTap, ViewConfiguration.getTapTimeout());
} else {
// Not inside a scrolling container, so show the feedback right away
setPressed(true, x, y);
checkForLongClick(0, x, y);
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:
setPressed(false);
removeTapCallback();
removeLongPressCallback();
mInContextButtonPress = false;
mHasPerformedLongPress = false;
mIgnoreNextUpEvent = false;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
drawableHotspotChanged(x, y);
// Be lenient about moving outside of buttons
if (!pointInView(x, y, mTouchSlop)) {
// Outside button
removeTapCallback();
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0) {
// Remove any future long press/tap checks
removeLongPressCallback();
setPressed(false);
}
}
break;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
可以看到,我们在MotionEvent.ACTION_UP事件里面,经过一系列的判断,然后进入到了performClick()这个函数
/**
* Call this view's OnClickListener, if it is defined. Performs all normal
* actions associated with clicking: reporting accessibility event, playing
* a sound, etc.
*
* @return True there was an assigned OnClickListener that was called, false
* otherwise is returned.
*/
public boolean performClick() {
final boolean result;
final ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnClickListener != null) {
playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants.CLICK);
li.mOnClickListener.onClick(this);
result = true;
} else {
result = false;
}
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED);
return result;
}
这个函数很明显的就知道是执行onClick,从这就可以得到如下结论
onClick事件是在onTouchEvent的MotionEvent.ACTION_UP事件通过performClick()->li.mOnClickListener.onClick(this)触发的。
到这里我们就验证了我们刚才的优先级的结论。当然在onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event源码中,我们在MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN里面可以看到长按事件
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
//...
checkForLongClick(0, x, y);
break;
//检测长按事件
private void checkForLongClick(int delayOffset, float x, float y) {
if ((mViewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE) {
mHasPerformedLongPress = false;
if (mPendingCheckForLongPress == null) {
mPendingCheckForLongPress = new CheckForLongPress();
}
mPendingCheckForLongPress.setAnchor(x, y);
mPendingCheckForLongPress.rememberWindowAttachCount();
postDelayed(mPendingCheckForLongPress,
ViewConfiguration.getLongPressTimeout() - delayOffset);
}
}
private final class CheckForLongPress implements Runnable {
private int mOriginalWindowAttachCount;
private float mX;
private float mY;
@Override
public void run() {
if (isPressed() && (mParent != null)
&& mOriginalWindowAttachCount == mWindowAttachCount) {
//触发长按事件
if (performLongClick(mX, mY)) {
mHasPerformedLongPress = true;
}
}
}
public void setAnchor(float x, float y) {
mX = x;
mY = y;
}
public void rememberWindowAttachCount() {
mOriginalWindowAttachCount = mWindowAttachCount;
}
}
public boolean performLongClick(float x, float y) {
mLongClickX = x;
mLongClickY = y;
final boolean handled = performLongClick();
mLongClickX = Float.NaN;
mLongClickY = Float.NaN;
return handled;
}
public boolean performLongClick() {
return performLongClickInternal(mLongClickX, mLongClickY);
}
private boolean performLongClickInternal(float x, float y) {
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_LONG_CLICKED);
boolean handled = false;
final ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnLongClickListener != null) {
handled = li.mOnLongClickListener.onLongClick(View.this);
}
if (!handled) {
final boolean isAnchored = !Float.isNaN(x) && !Float.isNaN(y);
handled = isAnchored ? showContextMenu(x, y) : showContextMenu();
}
if (handled) {
performHapticFeedback(HapticFeedbackConstants.LONG_PRESS);
}
return handled;
}
从这段代码我们又可以得到如下结论
View的OnLongClickListener是在onTouchEvent的MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN事件通过checkForLongClick() ->performLongClick(mX, mY)->performLongClick() ->performLongClickInternal(mLongClickX, mLongClickY) ->li.mOnLongClickListener.onLongClick(View.this)的执行顺序触发的。
这样View的OnTouch事件分发机制就分析得差不多,具体的判断细节等还是需要自己查看源码。
参考链接:
http://www.jianshu.com/p/98d1895c409d
http://www.jianshu.com/p/e99b5e8bd67b