Masonry 是一个轻量级的用于自动布局(AutoLayout)的第三方框架,以其简洁的使用方式,受到广大开发者的青睐。本篇文章将带你一步步的去了解其实现原理,知其所以然!
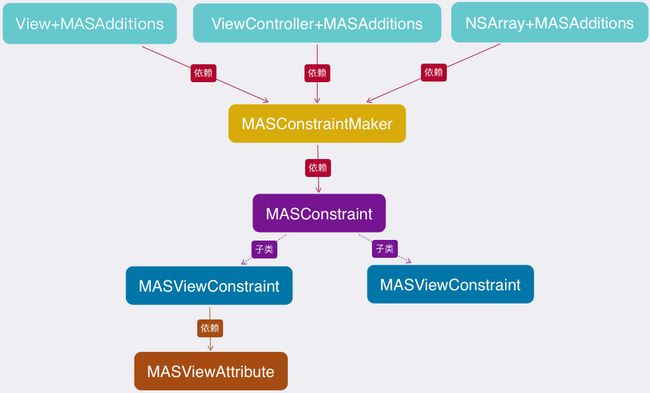
结构概览
-
最上面的几个
category,包含了我们常用的一些方法及属性,例如:- (NSArray *)mas_makeConstraints:(void(NS_NOESCAPE ^)(MASConstraintMaker *make))block; 中间的是一个继承自
NSObject的工厂类,主要负责创建MASConstraint对象以及把约束添加到视图上。-
最下面
MASConstraint是个抽象类,其中有很多的方法都必须在子类中重写。MASViewConstraint和MASCompositeConstraint是它的两个子类,介绍这两个之前我们先说下MASViewAttribute:我们都知道系统创建一条约束的方法:
+(instancetype)constraintWithItem:(id)view1 attribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)attr1 relatedBy:(NSLayoutRelation)relation toItem:(nullable id)view2 attribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)attr2 multiplier:(CGFloat)multiplier constant:(CGFloat)c;MASViewAttribute就是对attribute和Item这两个属性的封装;MASViewConstraint就是对MASViewAttribute的封装,可以理解为一条约束对象;MASCompositeConstraint则就是约束的集合,它里面有个私有的数组用来存放多个MASViewAttribute对象。
源码分析
View+MASAdditions
我们绘制一个居于父视图(self)上、左为 20.0f ,右为 -20.0f并且高度一半的 view 的约束大概是这样的:
[view mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.height.equalTo(self).multipliedBy(0.5);
make.top.equalTo(self).offset(20.0f);
make.left.equalTo(@20.0f);
make.right.offset(-20.0f);
}];
我们点进 View+MASAdditions.m 里面可以看到内部:
- (NSArray *)mas_makeConstraints:(void(^)(MASConstraintMaker *))block {
self.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = NO;
MASConstraintMaker *constraintMaker = [[MASConstraintMaker alloc] initWithView:self];
block(constraintMaker);
return [constraintMaker install];
}
- 首先这里已经帮我们把
translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints属性设置为NO了,这样我们在外面可以省去这一步。 - 然后初始化
MASConstraintMaker工厂实例对象并保存了当前视图self.view。 - 接着把初始化好的
MASConstraintMaker对象传入block,回调给外面配置约束属性。 - 最后调用
install方法,把配置好的约束添加到视图上去。
以上就是添加约束的大概流程,我们再看看更新和重新构建约束的方法,也就是:
- (NSArray *)mas_updateConstraints:(void(^)(MASConstraintMaker *))block {
self.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = NO;
MASConstraintMaker *constraintMaker = [[MASConstraintMaker alloc] initWithView:self];
constraintMaker.updateExisting = YES;
block(constraintMaker);
return [constraintMaker install];
}
- (NSArray *)mas_remakeConstraints:(void(^)(MASConstraintMaker *make))block {
self.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = NO;
MASConstraintMaker *constraintMaker = [[MASConstraintMaker alloc] initWithView:self];
constraintMaker.removeExisting = YES;
block(constraintMaker);
return [constraintMaker install];
}
我们可以发现它们和 mas_makeConstraints 唯一的区别在于多传了 updateExisting 以及 removeExisting 这两个 BOOL属性值:
-
mas_updateConstraints:找到需要更新的NSLayoutConstraint,替换成新约束。 -
mas_remakeConstraints:清除所有NSLayoutConstraint,再添加新约束。
MASConstraintMaker
知道了这三个方法的大概作用和关系,我们来详细看看 MASConstraintMaker 这个工厂类是如何配置约束的:
make.height
调用链如下:
- (MASConstraint *)height {
return [self addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:NSLayoutAttributeHeight];
}
- (MASConstraint *)addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
return [self constraint:nil addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
}
- (MASConstraint *)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
MASViewAttribute *viewAttribute = [[MASViewAttribute alloc] initWithView:self.view layoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
MASViewConstraint *newConstraint = [[MASViewConstraint alloc] initWithFirstViewAttribute:viewAttribute];
if ([constraint isKindOfClass:MASViewConstraint.class]) { ··· }
if (!constraint) {
newConstraint.delegate = self;
[self.constraints addObject:newConstraint];
}
return newConstraint;
}
由于 constraint 传的是 nil,所以我们先忽略中间一段代码:
- 这里先是初始化了
MASViewAttribute对象并保存了view、item以及NSLayoutAttribute三个属性。
- (id)initWithView:(MAS_VIEW *)view layoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
self = [self initWithView:view item:view layoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
return self;
}
- (id)initWithView:(MAS_VIEW *)view item:(id)item layoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
self = [super init];
if (!self) return nil;
_view = view;
_item = item;
_layoutAttribute = layoutAttribute;
return self;
}
- 然后又初始化了
MASViewConstraint对象,内部配置了些默认参数并保存了第一个约束参数MASViewAttribute。
- (id)initWithFirstViewAttribute:(MASViewAttribute *)firstViewAttribute {
self = [super init];
if (!self) return nil;
_firstViewAttribute = firstViewAttribute;
self.layoutPriority = MASLayoutPriorityRequired;
self.layoutMultiplier = 1;
return self;
}
- 最后设置
MASViewConstraint对象代理并添加到一开始准备好的self.constraints数组中,返回。
这些工作就是在输入 make.height 进行的全部工作,它会返回一个 MASViewConstraint 对象,用于之后的继续配置。
MASViewConstraint
make.height.equalTo(self)
在 make.height 返回 MASViewConstraint 对象后,会继续在这个链式的语法中调用下一个方法来指定约束的关系。
- (MASConstraint * (^)(id attr))equalTo;
- (MASConstraint * (^)(id attr))greaterThanOrEqualTo;
- (MASConstraint * (^)(id attr))lessThanOrEqualTo;
文章开头说过,MASConstraint 是个抽象类,具体实现都在它的两个子类中,equalTo(self) 的调用链如下:
//MASConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint * (^)(id))equalTo {
return ^id(id attribute) {
return self.equalToWithRelation(attribute, NSLayoutRelationEqual);
};
}
//MASViewConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint * (^)(id, NSLayoutRelation))equalToWithRelation {
return ^id(id attribute, NSLayoutRelation relation) {
if ([attribute isKindOfClass:NSArray.class]) {
.....
} else {
.....
self.layoutRelation = relation;
self.secondViewAttribute = attribute;
return self;
}
};
}
这里同样先省略部分代码,方便我们阅读:
- 首先是
self.layoutRelation保存了约束关系且重写了set方法,在里面用self.hasLayoutRelation这个BOOL标识已经有约束关系。
- (void)setLayoutRelation:(NSLayoutRelation)layoutRelation {
_layoutRelation = layoutRelation;
self.hasLayoutRelation = YES;
}
- 然后同样是重写了
self.secondViewAttribute的set方法,这里会根据不同的情况做不同的操作。
- (void)setSecondViewAttribute:(id)secondViewAttribute {
if ([secondViewAttribute isKindOfClass:NSValue.class]) {
[self setLayoutConstantWithValue:secondViewAttribute];
} else if ([secondViewAttribute isKindOfClass:MAS_VIEW.class]) {
_secondViewAttribute = [[MASViewAttribute alloc] initWithView:secondViewAttribute layoutAttribute:self.firstViewAttribute.layoutAttribute];
} else if ([secondViewAttribute isKindOfClass:MASViewAttribute.class]) {
_secondViewAttribute = secondViewAttribute;
} else {
NSAssert(NO, @"attempting to add unsupported attribute: %@", secondViewAttribute);
}
}
第一种情况对应的是:
make.height.equalTo(@20.0f)
调用链如下:
//MASViewConstraint.m
if ([secondViewAttribute isKindOfClass:NSValue.class]) {
[self setLayoutConstantWithValue:secondViewAttribute];
}
//MASConstraint.m
- (void)setLayoutConstantWithValue:(NSValue *)value {
if ([value isKindOfClass:NSNumber.class]) {
self.offset = [(NSNumber *)value doubleValue];
} else if (strcmp(value.objCType, @encode(CGPoint)) == 0) {
CGPoint point;
[value getValue:&point];
self.centerOffset = point;
} else if (strcmp(value.objCType, @encode(CGSize)) == 0) {
CGSize size;
[value getValue:&size];
self.sizeOffset = size;
} else if (strcmp(value.objCType, @encode(MASEdgeInsets)) == 0) {
MASEdgeInsets insets;
[value getValue:&insets];
self.insets = insets;
} else {
NSAssert(NO, @"attempting to set layout constant with unsupported value: %@", value);
}
}
//MASViewConstraint.m
- (void)setOffset:(CGFloat)offset {
self.layoutConstant = offset;
}
//MASViewConstraint.m
- (void)setLayoutConstant:(CGFloat)layoutConstant {
_layoutConstant = layoutConstant;
#if TARGET_OS_MAC && !(TARGET_OS_IPHONE || TARGET_OS_TV)
if (self.useAnimator) {
[self.layoutConstraint.animator setConstant:layoutConstant];
} else {
self.layoutConstraint.constant = layoutConstant;
}
#else
self.layoutConstraint.constant = layoutConstant;
#endif
}
上面到最后会有个 CGFloat 类型的 layoutConstant 属性来保存值,并且在最后调用 install 方法的时候作为 constant 参数传入。
这里只看了下传入的 NSValue 为offset 的情况,还有 centerOffset、sizeOffset 和 insets,也都大同小异,就不熬述了。
其实这里有一点我没明白:
直到最后调用 install 方法前,self.layoutConstraint 这个 MASLayoutConstraint 类型的属性都是 nil,那么:
self.layoutConstraint.constant = layoutConstant;
这里的赋值又有什么意义呢?
第二种情况一般是直接传入一个视图:
make.height.equalTo(self)
这时,就会初始化一个 layoutAttribute 属性与 firstViewArribute (第一个约束参数对象)相同的 MASViewAttribute 对象,也就是第二个约束参数对象,上面代码意思就是使视图与 self 高度相等。
第三种情况会传入一个视图的 MASViewAttribute:
make.height.equalTo(self.height)
//或者
make.height.equalTo(self.mas_height)
这两种写法其实效果是一样的,都是创建并返回一个 MASViewAttribute 对象。View+MASShorthandAdditions.h 这个 category 只有个 .h,定义了我们常用的属性和方法,但是具体实现还是调用的 View+MASAdditions 里面的方法,可以理解为去掉 mas_ 命名前缀。
这里还有许多属性可以设置,比如 multipliedBy、priority等等,就不一一熬述了。
链式语法特性的重要一环
make.height.width.equalTo(@20);
这种同时设置多个约束属性的方式相信大家一定不陌生,认真看的人可能已经猜到了:那就是通过 delegate 的方式。
上面已经提到过,在 make.height 设置第一个约束属性时,
- (MASConstraint *)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute
方法中,会设置 MASViewConstraint 对象代理,其作用就是为了能够同时设置多个约束属性!我们来看看 make.height.width 中 .width的调用链:
//MASConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint *)width {
return [self addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:NSLayoutAttributeWidth];
}
//MASViewConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint *)addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
NSAssert(!self.hasLayoutRelation, @"Attributes should be chained before defining the constraint relation");
return [self.delegate constraint:self addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
}
//MASConstraintMaker.m
- (MASConstraint *)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
MASViewAttribute *viewAttribute = [[MASViewAttribute alloc] initWithView:self.view layoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
MASViewConstraint *newConstraint = [[MASViewConstraint alloc] initWithFirstViewAttribute:viewAttribute];
if ([constraint isKindOfClass:MASViewConstraint.class]) {
//replace with composite constraint
NSArray *children = @[constraint, newConstraint];
MASCompositeConstraint *compositeConstraint = [[MASCompositeConstraint alloc] initWithChildren:children];
compositeConstraint.delegate = self;
[self constraint:constraint shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:compositeConstraint];
return compositeConstraint;
}
....
}
通过上面的调用链我们可以发现,最终就是通过 delegate 的方式,调用 MASConstraintMaker 工厂类中的 constraint:addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute: 方法,这也是链式语法能链起来的原因。
我们还可以发现因为 constraint 不为 nil,所以这次初始化并返回的不是 MASViewConstraint 对象,而是 MASCompositeConstraint 这个对象了,下面我们来看看这个类。
MASCompositeConstraint
我们先来回顾下开头是怎么介绍 MASCompositeConstraint 这个类的:“MASCompositeConstraint 是约束的集合,它里面有个私有的数组用来存放多个 MASViewAttribute 对象”。
我们接着上面的例子看:
make.height.width.equalTo(@20)
当走到 .width时:
- (MASConstraint *)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
MASViewAttribute *viewAttribute = [[MASViewAttribute alloc] initWithView:self.view layoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
MASViewConstraint *newConstraint = [[MASViewConstraint alloc] initWithFirstViewAttribute:viewAttribute];
if ([constraint isKindOfClass:MASViewConstraint.class]) {
//replace with composite constraint
NSArray *children = @[constraint, newConstraint];
MASCompositeConstraint *compositeConstraint = [[MASCompositeConstraint alloc] initWithChildren:children];
compositeConstraint.delegate = self;
[self constraint:constraint shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:compositeConstraint];
return compositeConstraint;
}
....
}
成功的走进 if 判读里面,将 .height.wight 两条约束 MASViewConstraint 对象塞到数组里,创建 MASCompositeConstraint 对象,并且同样设置了 delegate,最后还把 self.constraints 里面事先添加好的约束 MASViewConstraint 对象替换成了 MASCompositeConstraint 对象。
- (void)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:(MASConstraint *)replacementConstraint {
NSUInteger index = [self.constraints indexOfObject:constraint];
NSAssert(index != NSNotFound, @"Could not find constraint %@", constraint);
[self.constraints replaceObjectAtIndex:index withObject:replacementConstraint];
}
我们可以点击 MASCompositeConstraint 初始化方法里看看,它内部会通过 for 循环,把数组里面的所有 MASViewConstraint 对象同样设置了 delegate。
- (id)initWithChildren:(NSArray *)children {
self = [super init];
if (!self) return nil;
_childConstraints = [children mutableCopy];
for (MASConstraint *constraint in _childConstraints) {
constraint.delegate = self;
}
return self;
}
这么做的目的同时是为了能够继续链式调用,比如我们再加个 .left:
make.height.width.left.equalTo(@20);
这时候的调用链如下:
//MASConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint *)left {
return [self addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:NSLayoutAttributeLeft];
}
//MASCompositeConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint *)addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
[self constraint:self addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
return self;
}
- (MASConstraint *)constraint:(MASConstraint __unused *)constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
id strongDelegate = self.delegate;
MASConstraint *newConstraint = [strongDelegate constraint:self addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
newConstraint.delegate = self;
[self.childConstraints addObject:newConstraint];
return newConstraint;
}
可以发现,这里又是通过 delegate 方式,调用 MASConstraintMaker 工厂类中的:
- (MASConstraint *)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
MASViewAttribute *viewAttribute = [[MASViewAttribute alloc] initWithView:self.view layoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
MASViewConstraint *newConstraint = [[MASViewConstraint alloc] initWithFirstViewAttribute:viewAttribute];
....
return newConstraint;
}
不过这次仅仅是初始化了个 MASViewConstraint 对象就直接返回了,然后回到上个方法中添加到 MASCompositeConstraint 的私有数组 self.childConstraints 中返回备用。
equalTo(@20)
因为到.left 时,返回的是 MASCompositeConstraint 对象,到这一步的时候会有点变化,调用链如下:
//MASConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint * (^)(id))equalTo {
return ^id(id attribute) {
return self.equalToWithRelation(attribute, NSLayoutRelationEqual);
};
}
//MASCompositeConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint * (^)(id, NSLayoutRelation))equalToWithRelation {
return ^id(id attr, NSLayoutRelation relation) {
for (MASConstraint *constraint in self.childConstraints.copy) {
constraint.equalToWithRelation(attr, relation);
}
return self;
};
}
可以发现,这里会循环之前准备好的私有数组 self.childConstraints,调用 MASViewConstraint.m 的 equalToWithRelation 方法,和上面讲的一样了。
make.edges.equalTo(view)
我们再来看看这种写法,调用链如下:
//MASConstraintMaker.m
- (MASConstraint *)edges {
return [self addConstraintWithAttributes:MASAttributeTop | MASAttributeLeft | MASAttributeRight | MASAttributeBottom];
}
- (MASConstraint *)addConstraintWithAttributes:(MASAttribute)attrs {
__unused MASAttribute anyAttribute = (MASAttributeLeft | MASAttributeRight | MASAttributeTop | MASAttributeBottom | MASAttributeLeading
| MASAttributeTrailing | MASAttributeWidth | MASAttributeHeight | MASAttributeCenterX
| MASAttributeCenterY |
......
NSMutableArray *attributes = [NSMutableArray array];
if (attrs & MASAttributeLeft) [attributes addObject:self.view.mas_left];
if (attrs & MASAttributeRight) [attributes addObject:self.view.mas_right];
if (attrs & MASAttributeTop) [attributes addObject:self.view.mas_top];
......
NSMutableArray *children = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:attributes.count];
for (MASViewAttribute *a in attributes) {
[children addObject:[[MASViewConstraint alloc] initWithFirstViewAttribute:a]];
}
MASCompositeConstraint *constraint = [[MASCompositeConstraint alloc] initWithChildren:children];
constraint.delegate = self;
[self.constraints addObject:constraint];
return constraint;
}
代码太多省略了一部分,可以发现这段代码作用就是返回一个包含多条约束的 MASCompositeConstraint 对象,接着后面的操作也都是一样的了。
上面这种写法还可以这样:
make.edges.equalTo(UIEdgeInsetsMake(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
这里的 equalTo 需要注意下,它是一个宏,定义在 MASConstraint.h 中:
#define mas_equalTo(...) equalTo(MASBoxValue((__VA_ARGS__)))
#define mas_greaterThanOrEqualTo(...) greaterThanOrEqualTo(MASBoxValue((__VA_ARGS__)))
#define mas_lessThanOrEqualTo(...) lessThanOrEqualTo(MASBoxValue((__VA_ARGS__)))
#define mas_offset(...) valueOffset(MASBoxValue((__VA_ARGS__)))
#ifdef MAS_SHORTHAND_GLOBALS
#define equalTo(...) mas_equalTo(__VA_ARGS__)
#define greaterThanOrEqualTo(...) mas_greaterThanOrEqualTo(__VA_ARGS__)
#define lessThanOrEqualTo(...) mas_lessThanOrEqualTo(__VA_ARGS__)
#define offset(...) mas_offset(__VA_ARGS__)
我们来修改下代码:
make.edges.equalTo(MASBoxValue(UIEdgeInsetsMake(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)));
可以发现,其实里面调用的是 MASBoxValue 这个宏,它将 C 和 Objective-C 语言中的一些基本数据结构比如说 double CGPoint CGSize 这些值用 NSValue 进行包装。
这里还支持直接调用 size、center 等,具体实现都差不多,就不熬述了:
make.center.equalTo(CGPointMake(0, 50));
make.size.equalTo(CGSizeMake(200, 100));
make.height.equalTo(@[redView, blueView])
我再来看看这种传数组的,在走到 .equalTo 时,最终会调用 MASViewConstraint.m 里面的 equalToWithRelation 方法:
- (MASConstraint * (^)(id, NSLayoutRelation))equalToWithRelation {
return ^id(id attribute, NSLayoutRelation relation) {
if ([attribute isKindOfClass:NSArray.class]) {
NSAssert(!self.hasLayoutRelation, @"Redefinition of constraint relation");
NSMutableArray *children = NSMutableArray.new;
for (id attr in attribute) {
MASViewConstraint *viewConstraint = [self copy];
viewConstraint.layoutRelation = relation;
viewConstraint.secondViewAttribute = attr;
[children addObject:viewConstraint];
}
MASCompositeConstraint *compositeConstraint = [[MASCompositeConstraint alloc] initWithChildren:children];
compositeConstraint.delegate = self.delegate;
[self.delegate constraint:self shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:compositeConstraint];
return compositeConstraint;
} else { .... }
};
}
这边还是遍历数组,并且 MASViewConstraint 实现 NSCopying 协议,调用 [self copy] 会创建 MASViewConstraint 对象:
- (id)copyWithZone:(NSZone __unused *)zone {
MASViewConstraint *constraint = [[MASViewConstraint alloc] initWithFirstViewAttribute:self.firstViewAttribute];
constraint.layoutConstant = self.layoutConstant;
constraint.layoutRelation = self.layoutRelation;
constraint.layoutPriority = self.layoutPriority;
constraint.layoutMultiplier = self.layoutMultiplier;
constraint.delegate = self.delegate;
return constraint;
}
然后会根据传的数组里面的 Value 类型来做不同的操作,前面讲过就不熬述了:
- (void)setSecondViewAttribute:(id)secondViewAttribute {
if ([secondViewAttribute isKindOfClass:NSValue.class]) {
[self setLayoutConstantWithValue:secondViewAttribute];
} else if ([secondViewAttribute isKindOfClass:MAS_VIEW.class]) {
_secondViewAttribute = [[MASViewAttribute alloc] initWithView:secondViewAttribute layoutAttribute:self.firstViewAttribute.layoutAttribute];
} else if ([secondViewAttribute isKindOfClass:MASViewAttribute.class]) {
_secondViewAttribute = secondViewAttribute;
} else {
NSAssert(NO, @"attempting to add unsupported attribute: %@", secondViewAttribute);
}
}
最后便是生成 MASCompositeConstraint 对象,并通过 delegate 方式,调用 MASConstraintMaker 的方法,替换 self.constraints 数组里的约束:
- (void)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:(MASConstraint *)replacementConstraint {
NSUInteger index = [self.constraints indexOfObject:constraint];
NSAssert(index != NSNotFound, @"Could not find constraint %@", constraint);
[self.constraints replaceObjectAtIndex:index withObject:replacementConstraint];
}
添加约束到视图
mas_makeConstraints 方法的最后会调用 [constraintMaker install] 方法来添加所有存储在 self.constraints 数组中的所有约束。
// MASConstraintMaker.m
- (NSArray *)install {
if (self.removeExisting) {
NSArray *installedConstraints = [MASViewConstraint installedConstraintsForView:self.view];
for (MASConstraint *constraint in installedConstraints) {
[constraint uninstall];
}
}
NSArray *constraints = self.constraints.copy;
for (MASConstraint *constraint in constraints) {
constraint.updateExisting = self.updateExisting;
[constraint install];
}
[self.constraints removeAllObjects];
return constraints;
}
如果需要重新构建约束,也就是 调用 mas_remakeConstraints: 方法,会先取出视图的所有约束,然后通过一个 for 循环,调用 uninstall 来清空所有约束:
- (void)uninstall {
if ([self supportsActiveProperty]) {
self.layoutConstraint.active = NO;
[self.firstViewAttribute.view.mas_installedConstraints removeObject:self];
return;
}
[self.installedView removeConstraint:self.layoutConstraint];
self.layoutConstraint = nil;
self.installedView = nil;
[self.firstViewAttribute.view.mas_installedConstraints removeObject:self];
}
如果不需要重新构建约束,会取出 self.constraints 数组中准备好的约束,通过 for 循环,调用 install 来把约束添加到视图上:
if (self.hasBeenInstalled) {
return;
}
如果约束以及存在并是 active 会直接返回。
if ([self supportsActiveProperty] && self.layoutConstraint) {
self.layoutConstraint.active = YES;
[self.firstViewAttribute.view.mas_installedConstraints addObject:self];
return;
}
如果 self.layoutConstraint 响应了 isActive 方法并且不为空,会激活这条约束并添加到 mas_installedConstraints 数组中,最后返回。
MAS_VIEW *firstLayoutItem = self.firstViewAttribute.item;
NSLayoutAttribute firstLayoutAttribute = self.firstViewAttribute.layoutAttribute;
MAS_VIEW *secondLayoutItem = self.secondViewAttribute.item;
NSLayoutAttribute secondLayoutAttribute = self.secondViewAttribute.layoutAttribute;
这边是获取即将用于初始化 NSLayoutConstraint 的子类 MASLayoutConstraint 的几个属性。
if (!self.firstViewAttribute.isSizeAttribute && !self.secondViewAttribute) {
secondLayoutItem = self.firstViewAttribute.view.superview;
secondLayoutAttribute = firstLayoutAttribute;
}
这边是判断当前即将添加的约束是否是 size 类型的并且 self.secondViewAttribute 也就是约束的第二个参数是 nil,(eg make.left.equalTo(@10))会自动将约束添加到约束的第一个参数视图的 superview 上。
MASLayoutConstraint *layoutConstraint = [MASLayoutConstraint
constraintWithItem:firstLayoutItem
attribute:firstLayoutAttribute
relatedBy:self.layoutRelation
toItem:secondLayoutItem
attribute:secondLayoutAttribute
multiplier:self.layoutMultiplier
constant:self.layoutConstant];
layoutConstraint.priority = self.layoutPriority;
layoutConstraint.mas_key = self.mas_key;
然后就会初始化 NSLayoutConstraint 的子类 MASLayoutConstraint。
if (self.secondViewAttribute.view) {
MAS_VIEW *closestCommonSuperview = [self.firstViewAttribute.view mas_closestCommonSuperview:self.secondViewAttribute.view];
NSAssert(closestCommonSuperview,
@"couldn't find a common superview for %@ and %@",
self.firstViewAttribute.view, self.secondViewAttribute.view);
self.installedView = closestCommonSuperview;
} else if (self.firstViewAttribute.isSizeAttribute) {
self.installedView = self.firstViewAttribute.view;
} else {
self.installedView = self.firstViewAttribute.view.superview;
}
这段代码会先判断是否有约束第二个参数的视图,有的话会寻找约束第一个和第二参数视图的公共 Superview,相当于求两个数的最小公倍数;如果不满足第一个条件,会判断约束第一个参数是否是 size 类型的,是的话直接取到它的视图;最后都不满足会直接取到约束第一个参数视图父视图。
MASLayoutConstraint *existingConstraint = nil;
if (self.updateExisting) {
existingConstraint = [self layoutConstraintSimilarTo:layoutConstraint];
}
if (existingConstraint) {
// just update the constant
existingConstraint.constant = layoutConstraint.constant;
self.layoutConstraint = existingConstraint;
} else {
[self.installedView addConstraint:layoutConstraint];
self.layoutConstraint = layoutConstraint;
[firstLayoutItem.mas_installedConstraints addObject:self];
}
如果需要升级当前的约束就会获取原有的约束,并替换为新的约束,这样就不需要再次为 view 安装约束。如果原来的 view 中不存在可以升级的约束,那么就会在上一步寻找到的 installedView 上面添加约束。
结束语
阅读懂源码真是一件很爽的事情,如果有什么理解的不到位的地方大家多多指正。也希望大家能够耐心的看下去,一定会有所收获的。
参考链接
http://www.cnblogs.com/ludashi/p/5591572.html
https://github.com/Draveness/iOS-Source-Code-Analyze/blob/master/contents/Masonry/iOS%20%E6%BA%90%E4%BB%A3%E7%A0%81%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90%20---%20Masonry.md