Composite 模式
一、描述
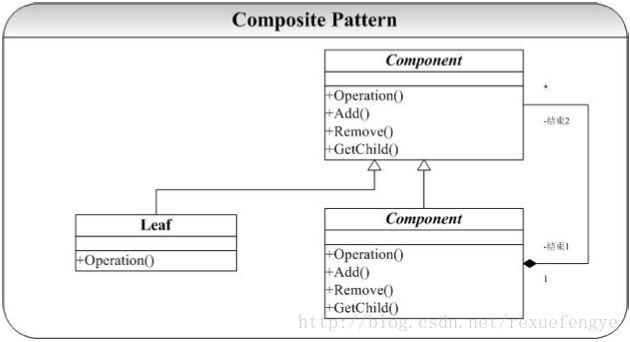
概念:将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分-整体”的层次结构。 Composite使得用户对单个对象和组合的使用具有一致性。
Composite 模式的典型结构图为:
二、实例:
大家在上学的时候应该都学过“数据结构”这门课程吧,还记得其中有一节叫“二叉树”吧,我们上学那会儿这一章节是必考内容,左子树,右子树,什么先序遍历后序遍历什么,重点就是二叉树的的遍历, 我还记得当时老师就说,考试的时候一定有二叉树的构建和遍历,现在想起来还是觉的老师是正确的,树状结果在实际项目应用的非常广泛。
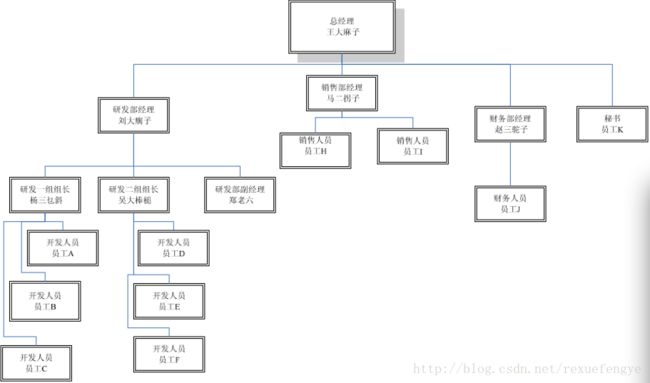
咱就先说个最常见的例子,公司的人事管理就是一个典型的树状结构,你想想你公司的结构是不是这样:
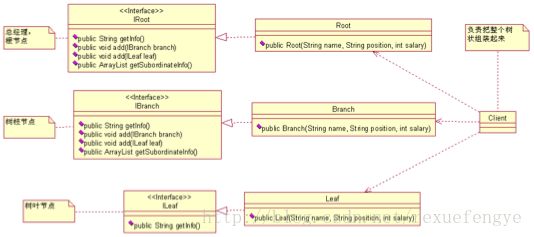
老大,往下一层一层的管理,最后到我们这层小兵,很典型的树状结构(说明一下,这不是二叉树,有关二叉树的定义可以翻翻以前的教科书),我们今天的任务就是要把这个树状结构实现出来,并且还要把它遍历一遍, 你要确认你建立的树是否有问题呀。 从这个树状结构上分析,有两种节点:有分支的节点(如研发部经理)和无分支的节点(如员工 A、员工 D 等),我们增加一点学术术语上去,总经理叫做根节点(是不是想到 XML 中的那个根节点 root,那就对了), 类似研发部经理有分支的节点叫做树枝节点,类似员工 A 的无分支的节点叫做树叶节点,都很形象,三个类型的的节点,那是不是定义三个类就可以?好,我们按照这个思路走下去,先看我们自己设计的类图:
这个类图是初学者最容易想到的类图(这个类图有缺陷了),你有没有发觉有问题?getInfo 每个接口都有为什么不能抽象出来? Root 类和 Branch 类有什么差别?为什么要定义成两个接口两个类?如果我要加一个任职期限,你是不是每个类都需要修改?如果我要后序遍历(从员工找到他的上级领导)能做吗?——彻底晕菜了!
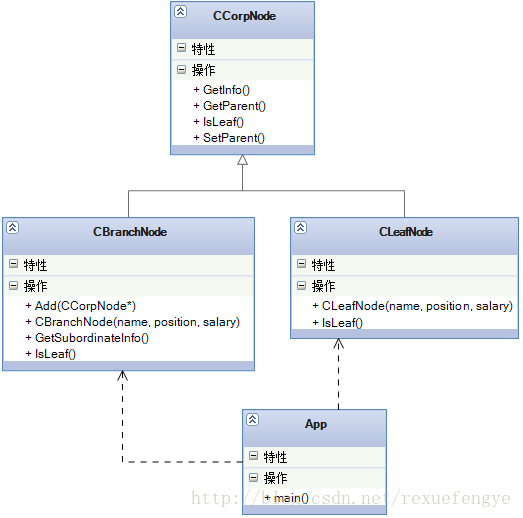
问题很多,我们一个一个解决,先说抽象的问题,确实可以吧 IBranch 和 IRoot 合并成一个接口,这个我们先肯定下来,这是个比较大的改动,我们先画个类图(类名稍微做下变化):
注释:
main(),客户
CCorpNode,抽象基类,实现基本信息
CBranchNode,树枝节点,实现Addordinate() 函数和GetSubordinate()函数
CLeafNode,叶子节点,IsLeaf属性总是“true”
说明:组合模式主要是实现在CBranchNode对象里增加对其它对象的数组,如vector,数组里可以存放CBranchNode和CLeafNode对象。 这样方便进行遍历操作。
注意:组合模式有透明组合模式和安全组合模式。 透明组合模式是将Addordinate和GetSubordinate这两个函数也抽象到CCorpNode基类里,这增加了操作叶子节点的难度,更易出现逻辑问题。 所以尽量使用安全模式。
这个简单了,可以想像一下TreeView和TreeNode基本上是这个意思了,将很多数据组织在一块。
代码:
抽象基类,实现基本信息:CorpNode类
CorpNode.h
#ifndef __Composite__CorpNode__
#define __Composite__CorpNode__
#include
using std::string;
class CCorpNode {
public:
CCorpNode(void);
CCorpNode(string _name,string _pos,string _salary);
virtual ~CCorpNode(void);
virtual string GetInfo();
void SetParent(CCorpNode *_pParent);
CCorpNode *GetParent();
virtual bool IsLeaf() = 0;
private:
string m_name;
string m_position;
string m_salary;
protected:
bool m_isLeaf;
CCorpNode *m_pParent;
};
CorpNode.cpp
#include "CorpNode.h"
CCorpNode::CCorpNode(void)
{
m_name = "";
m_position = "";
m_salary = "0";
}
CCorpNode::CCorpNode(string _name,string _pos,string _salary):m_name(_name), m_position(_pos), m_salary(_salary)
{
}
CCorpNode::~CCorpNode(void)
{
}
string CCorpNode::GetInfo()
{
string info = "";
info.append("姓名: ");
info.append(this->m_name);
info.append("\t职位:");
info.append(this->m_position);
info.append("\t薪水:");
info.append(this->m_salary);
return info;
}
void CCorpNode::SetParent(CCorpNode *_pParent)
{
this->m_pParent = _pParent;
}
CCorpNode * CCorpNode::GetParent()
{
return this->m_pParent;
}
树枝节点:BranchNode类
BranchNode.h
#ifndef __Composite__BranchNode__
#define __Composite__BranchNode__
#include
#include "CorpNode.h"
#include
using std::vector;
using std::string;
class CBranchNode:public CCorpNode
{
public:
CBranchNode(void);
CBranchNode(string name,string pos,string salary);
~CBranchNode(void);
void Add(CCorpNode* pcorpNode);
vector GetSubordinateInfo();
bool IsLeaf();
private:
vector m_subordinateList;
};
BranchNode.cpp
#include "BranchNode.h"
CBranchNode::CBranchNode(void)
{
m_isLeaf = false;
}
CBranchNode::CBranchNode(string name ,string pos,string salary):CCorpNode(name,pos,salary)
{
m_isLeaf = false;
}
CBranchNode::~CBranchNode(void)
{
}
void CBranchNode::Add(CCorpNode *pcorpNode)
{
pcorpNode->SetParent(this);
m_subordinateList.push_back(pcorpNode);
}
vector CBranchNode::GetSubordinateInfo()
{
return this->m_subordinateList;
}
bool CBranchNode::IsLeaf()
{
return m_isLeaf;
}
叶子节点:LeafNode类
LeafNode.h
#ifndef __Composite__LeafNode__
#define __Composite__LeafNode__
#include
#include "CorpNode.h"
class CLeafNode:public CCorpNode
{
public:
CLeafNode(void);
CLeafNode(string name,string pos,string salary);
~CLeafNode(void);
bool IsLeaf();
};
LeafNode.cpp
#include "LeafNode.h"
CLeafNode::CLeafNode(void)
{
m_isLeaf = true;
}
CLeafNode::CLeafNode(string name ,string pos,string salary):CCorpNode(name,pos,salary)
{
m_isLeaf = true;
}
CLeafNode::~CLeafNode(void)
{
}
bool CLeafNode::IsLeaf()
{
return m_isLeaf;
}
客户:main主程序
main.cpp
#include
#include "CorpNode.h"
#include "BranchNode.h"
#include "LeafNode.h"
#include "CConvert.h"
using std::cout;
string getTreeInfo(CBranchNode *root)
{
vector subordinateList = root->GetSubordinateInfo();
string info = "";
for (vector::iterator it = subordinateList.begin();it != subordinateList.end();it++)
{
if ((*it)->IsLeaf())
{
info = info.append(" "+(*it)->GetInfo()+"\n");
}
else
{
info = info.append((*it)->GetInfo()+"\n"+getTreeInfo((CBranchNode*)(*it)));
}
}
return info;
}
CBranchNode *compositeCorpTree()
{
//首先产生总经理CEO
CBranchNode *root = new CBranchNode("王大麻子","总经理","100000");
//把三个部门经理产生出来
CBranchNode *developDep = new CBranchNode("刘大瘸子","研发部门经理","10000");
CBranchNode *salesDep = new CBranchNode("马二拐子","销售部门经理","20000");
CBranchNode *financeDep = new CBranchNode("赵三驼子","财务部经理","10000");
//再把三个小组长产生出来
CBranchNode *firstDevGroup = new CBranchNode("杨三乜斜","开发一组组长","5000");
CBranchNode *secondDevGroup = new CBranchNode("吴大棒槌","开发二组组长","6000");
//把所有的小兵都产生出来
CLeafNode *a = new CLeafNode("a","开发人员","2000");
CLeafNode *b = new CLeafNode("b","开发人员","2000");
CLeafNode *c = new CLeafNode("c","开发人员","2000");
CLeafNode *d = new CLeafNode("d","开发人员","2000");
CLeafNode *e = new CLeafNode("e","开发人员","2000");
CLeafNode *f = new CLeafNode("f","开发人员","2000");
CLeafNode *g = new CLeafNode("g","开发人员","2000");
CLeafNode *h = new CLeafNode("h","销售人员","2000");
CLeafNode *i = new CLeafNode("i","销售人员","2000");
CLeafNode *j = new CLeafNode("i","财务人员","2000");
CLeafNode *k = new CLeafNode("k","CEO秘书","2000");
CLeafNode *zhengLaoLiu = new CLeafNode("郑老六","研发部副经理","2000");
//开始组装
//CEO下有三个部门经理和一个秘书
root->Add(developDep);
root->Add(salesDep);
root->Add(financeDep);
root->Add(k);
//研发部经理
developDep->Add(zhengLaoLiu);
developDep->Add(firstDevGroup);
developDep->Add(secondDevGroup);
//看看开发两个开发小组下有什么
firstDevGroup->Add(a);
firstDevGroup->Add(b);
firstDevGroup->Add(c);
secondDevGroup->Add(d);
secondDevGroup->Add(e);
secondDevGroup->Add(f);
//再看销售部下的人员情况
salesDep->Add(h);
salesDep->Add(i);
//最后一个财务
firstDevGroup->Add(j);
return root;
delete zhengLaoLiu,k,j,i,h,g,f,e,d,c,b,a,secondDevGroup,firstDevGroup,financeDep,salesDep,developDep,root;
}
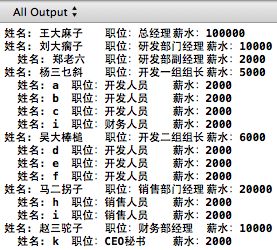
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
CBranchNode *CEO = compositeCorpTree();
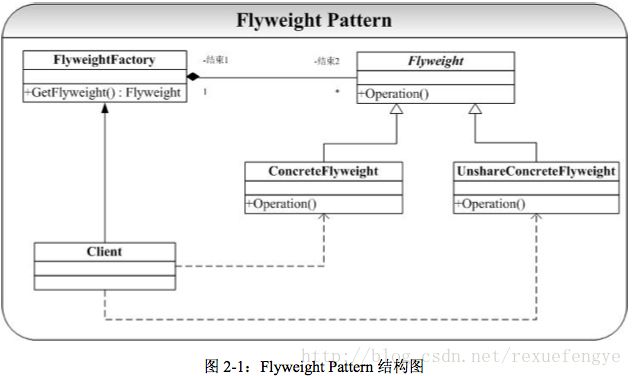
cout cout<< getTreeInfo(CEO); // insert code here... //printf("Hello, World!\n"); return 0; } 结果如下: 享元模式 一、描述 设计模式中的享元模式,避免大量拥有相同内容的小类的开销(如耗费内存),使大家共享一个类(元类). 在面向对象系统的设计何实现中,创建对象是最为常见的操作。 这里面就有一个问题:如果一个应用程序使用了太多的对象,就会造成很大的存储开销。 特别是对于大量轻量级(细粒度)的对象,比如在文档编辑器的设计过程中,我们如果为没有字母创建一个对象的话,系统可能会因为大量的对象而造成存储开销的浪费。 例如一个字母“a”在文档中出现了100000 次,而实际上我们可以让这一万个字母“a”共享一个对象,当然因为在不同的位置可能字母“a”有不同的显示效果(例如字体和大小等设置不同),在这种情况我们可以为将对象的状态分为“ 外部状态”和“内部状态”,将可以被共享(不会变化)的状态作为内部状态存储在对象中,而外部对象(例如上面提到的字体、大小等)我们可以在适当的时候将外部对象最为参数传递给对象(例如在显示的时候,将字体、大小等信息传递给对象)。 其典型的结构图为: 可以从图 2-1 中看出,Flyweight 模式中有一个类似 Factory 模式的对象构造工厂 FlyweightFactory,当客户程序员(Client)需要一个对象时候就会向 FlyweightFactory 发出请求对象的消息 GetFlyweight()消息,FlyweightFactory 拥有一个管理、 存储对象的“仓库”(或者叫对象池,vector 实现),GetFlyweight()消息会遍历对象池中的对象,如果已经存在则直接返回给 Client,否则创建一个新的对象返回给 Client。 当然可能也有不想被共享的对象(例如结构图中的 UnshareConcreteFlyweight),但不在本模式的讲解范围,故在实现中不给出。 二、实例 如上所描述的信息,创建类图: 注释: main:客户程序员(Client) FlyweightFactory:“仓库”(对象池), Flyweight:对象池中的对象 ConcreteFlyweight:被共享的对象 代码: 仓库”(对象池):FlyweightFactory类 FlyweightFactory.h #ifndef __Flyweight__FlyweightFactory__ #define __Flyweight__FlyweightFactory__ #include #include "Flyweight.h" #include #include #include "ConcreteFlyweight.h" using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::string; using std::vector; class FlyweightFactory { public: FlyweightFactory(); ~FlyweightFactory(); Flyweight* GetFlyweight(const string &key); private: vector _fly; }; FlyweightFactory.cpp #include "FlyweightFactory.h" FlyweightFactory::FlyweightFactory() { } FlyweightFactory::~FlyweightFactory() { } Flyweight* FlyweightFactory::GetFlyweight(const string &key) { vector::iterator it = _fly.begin(); for (; it != _fly.end(); it++) { if ((*it)->GetIntrinsicState() == key) { cout<<"already created by users...."< return *it; } } Flyweight *fn = new ConcreteFlyweight(key); _fly.push_back(fn); return fn; } 对象池中的对象:Flyweight类 Flyweight.h #ifndef __Flyweight__Flyweight__ #define __Flyweight__Flyweight__ #include #include using std::string; class Flyweight { public: Flyweight(void); virtual ~Flyweight(void); virtual void Operation(const string& extrinsicState); string GetIntrinsicState(); protected: Flyweight(string intrinsicState); private: string _intrinsicState; }; Flyweight.cpp #include "Flyweight.h" Flyweight::Flyweight(void) { } Flyweight::Flyweight(string intrinsicState) { this->_intrinsicState = intrinsicState; } Flyweight::~Flyweight() { } void Flyweight::Operation(const string &extrinsicState) { } string Flyweight::GetIntrinsicState() { return this->_intrinsicState; } 被共享的对象:ConcreteFlyweight ConcreteFlyweight.h #ifndef __Flyweight__ConcreteFlyweight__ #define __Flyweight__ConcreteFlyweight__ #include #include "Flyweight.h" class ConcreteFlyweight:public Flyweight { public: ConcreteFlyweight(void); ConcreteFlyweight(string intrinsicState); ~ConcreteFlyweight(); void Operation(const string& extrinsicState); }; ConcreteFlyweight.cpp #include "ConcreteFlyweight.h" using std::cout; using std::endl; ConcreteFlyweight::ConcreteFlyweight(void) { } ConcreteFlyweight::ConcreteFlyweight(string intrinsicState) { cout<<"ConcreteFlyweight Build....."< } ConcreteFlyweight::~ConcreteFlyweight() { } void ConcreteFlyweight::Operation(const string &extrinsicState) { cout<<"ConcreteFlyweight:内蕴[" } 客户程序员(Client) main.cpp #include #include "Flyweight.h" #include "ConcreteFlyweight.h" #include "FlyweightFactory.h" using namespace std; int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { FlyweightFactory *fc = new FlyweightFactory(); Flyweight* fw1 = fc->GetFlyweight("hello"); Flyweight* fw2 = fc->GetFlyweight("world!"); Flyweight* fw3 = fc->GetFlyweight("hello2"); // insert code here... std::cout << "Hello, World!\n"; return 0; } 结果如下: