本文是学习BindService之后顺便熟悉下AIDL
以前对AIDL有所了解,但是不熟悉BindService,然后就不了了之,
今天有了全新的理解,然后就有了此文
也是对自己的一个笔记
github Demo :https://github.com/cui962256380/AIDL
AIDL定义
AIDL 全称Android Interface Definition Language,即Android接口定义语言。
为了使其他的应用程序也可以访问本应用程序提供的服务,Android系统采用了远程过程调用(Remote Procedure Call,RPC)方式来实现。与很多其他的基于RPC的解决方案一样,Android使用一种接口定义语(Interface Definition Language,IDL)来公开服务的接口。我们知道4个Android应用程序组件中的3(Activity、BroadcastReceiver和ContentProvider)都可以进行跨进程访问,另外一个Android应用程序组件Service同样可以。因此,可以将这种可以跨进程访问的服务称为AIDL(Android Interface Definition Language)服务。
本文将带你做一个简单的Aidl跨进程加法
首先是服务端
废话不多说,上代码
定义IService.aidl
// IService.aidl
package com.example.administrator.aidlservice;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
interface IService {
int sum(int num1,int num2);
}
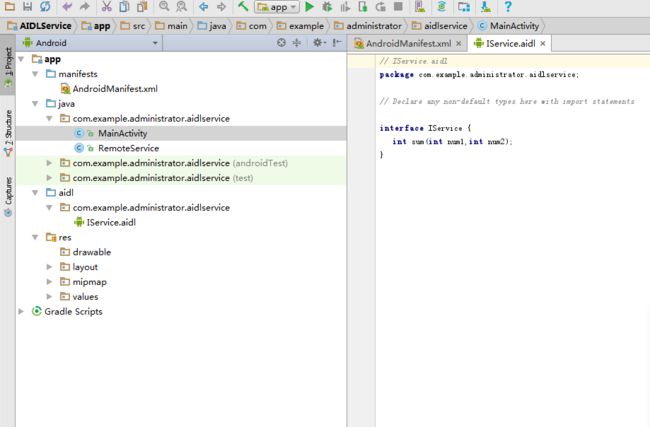
注意和java是同级别的 (看下图)
此处编写完成后Android Studio会自动生成IService.java文件(文件路径看下图)
如果没有自动生成,
手动Build项目即可
生成文件路径(看下图)
定义RemoteService .java
public class RemoteService extends Service {
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new MyBind();
}
class MyBind extends IService.Stub {
@Override
public int sum(int num1, int num2) throws RemoteException {
return num1+num2;
}
}
}
注册服务
android:process=":remote",代表在应用程序里,当需要该service时,会自动创建新的进程。
android:process="remote",没有“:”分号的,则创建全局进程,不同的应用程序共享该进程。
exported="true" 是确定此服务能否很娶她应用程序组件调用或交互
到此,一个服务端已经就写好了
客户端
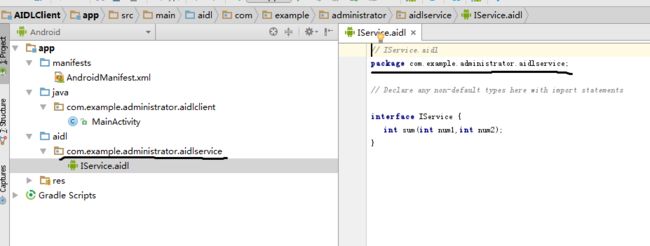
首先客户端结构图
直接将服务段的AIDL文件拷贝过来,注意包名必须和服务段的相同
下面贴代码
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView tv;
private Button add;
private EditText num1,num2;
IService iService;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv= (TextView) findViewById(R.id.sum);
add= (Button) findViewById(R.id.add);
num1= (EditText) findViewById(R.id.num1);
num2= (EditText) findViewById(R.id.num2);
bindService();//绑定服务
add.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int i=0;
try {
i= iService.sum(Integer.parseInt(num1.getText().toString()),Integer.parseInt(num2.getText().toString()));
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
tv.setText(""+i);
}
});
}
private void bindService() {
Intent it=new Intent();
ComponentName cm=new ComponentName("com.example.administrator.aidlservice","com.example.administrator.aidlservice.RemoteService"); //此处通过包名类名匹配。
//也可以使用Action匹配,在服务配置文件添加Action匹配规则即可
it.setComponent(cm);
bindService(it,mySc, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); //进行服务Bind
}
ServiceConnection mySc=new ServiceConnection() { //创建ServiceConnetion对象
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
iService=IService.Stub.asInterface(service);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
iService = null;
}
};
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
unbindService(mySc);
super.onDestroy();
}
XML
到此客户端也就编写完成。
然后分别运行服务端和客户端。
本文就简单讲解完毕