马上周末了,好开心!
今天手头事情不多,撸一个自定义的viewgroup吧,简单实现瀑布流效果的热门搜索条目:
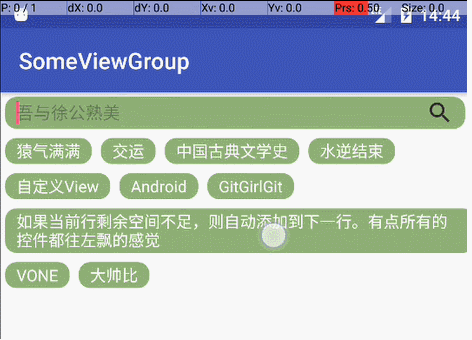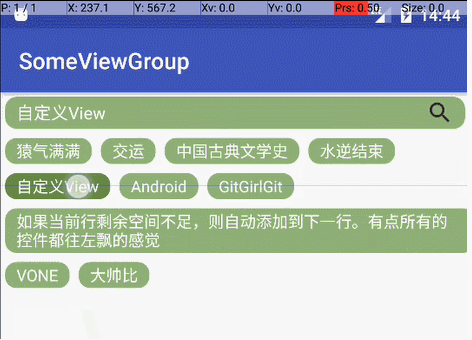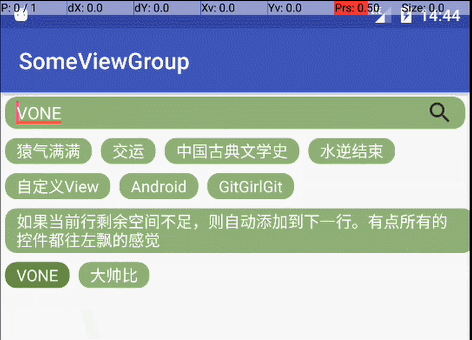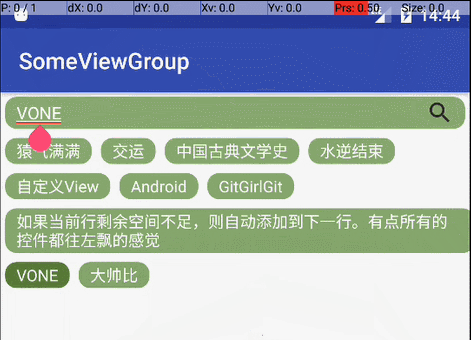
最终效果如下:
如果对自定义viewgroup的一些基本概念不是很熟,可以先看看大神的文章,写的很细致:
自定义viewgroup入门——Hongyang大神
下面就是我们这个viewgroup的实现步骤了:
-
首先,写一个ViewGroup的子类,重写generateLayoutParams(),这一步是为我们的ViewGroup指定一个LayoutParams:
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);//直接使用系统的MarginLayoutParams
}
-
接下来,爸爸要根据儿子们的需求买地了。就是onMeasure(),需要量测viewgroup的尺寸了
计算原理:
- 把每一个child的尺寸的width累加,累加之前先计算,如果加上这个
child的width会超过系统量测的最大width,就换行;
- 每一行的行高是取这一行的所有儿子中最高的;
- 最后的viewgroup的宽取所有行宽最大的,高是所有的行高累加起来;
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int width = 0;//如果设置width为wrap_content时的width
int height = 0;//同理
int lineWidth = 0;//记录每一行的宽度, width最后取最大的值
int lineHeight = 0;//记录每一行的高度,height不断累加
//遍历每一个view,计算容器的总尺寸
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
measureChild(childView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
MarginLayoutParams childParams = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
int childWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth() + childParams.leftMargin + childParams.rightMargin;
int childHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight() + childParams.topMargin + childParams.bottomMargin;
if (lineWidth + childWidth > widthSize) {//如果当前控件和当前这一行的宽度之和大于widthSize,换行
width = Math.max(lineWidth, childWidth);
lineWidth = childWidth;//重新记录lineWidth,初始为childWidth
height += childHeight;
lineHeight = childHeight;
} else {//不需要换行时
lineWidth += childWidth;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
}
if (i == getChildCount() - 1) {
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth);
height += lineHeight;
}
}
//如果是wrap_content,就用计算的值,否则就用系统量测的值,至于另外的UNSPECIFIED先不考虑,毕竟用的少
setMeasuredDimension((MeasureSpec.EXACTLY == widthMode) ? widthSize : width,
(MeasureSpec.EXACTLY == heightMode) ? heightSize : height);
}
-
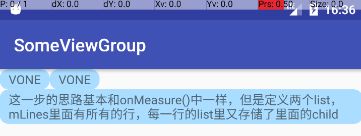
onLayout(),为每一个儿子划好地产,就是分配它们的绘制区域
- 这一步的思路基本和onMeasure()中一样,但是定义两个list,mLines里面有所有的行,每一行的list里又存储了里面的child
private ArrayList> mLines = new ArrayList<>();//二级List,里面有所有的view
private ArrayList mLineHeight = new ArrayList<>();//记录每一行的行高
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
MarginLayoutParams childParams = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//先处理需要换行的情况
if (lineWidth + childWidth + childParams.leftMargin + childParams.rightMargin > width) {
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
mLines.add(lineViews);
lineWidth = 0;
lineViews = new ArrayList<>();
}
//不用换行时,累加
lineWidth = childWidth + childParams.leftMargin + childParams.rightMargin + lineWidth;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childParams.topMargin + childParams.bottomMargin + childHeight);
lineViews.add(child);
}
//记录最后一行
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
mLines.add(lineViews);
- 再根据mLines进行两次for循环,为每一个child定位
int left = 0, top = 0;
//根据行数和每行的view个数遍历所有view
for (int i = 0; i < mLines.size(); i++) {
lineViews = mLines.get(i);
lineHeight = mLineHeight.get(i);
//遍历当前行所有的view
for (int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j++) {
View childView = lineViews.get(j);
if (childView.getVisibility() == GONE) continue;
MarginLayoutParams childParams = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
int childLeft = left + childParams.leftMargin;
int childTop = top + childParams.topMargin;
int childBottom = childTop + childView.getMeasuredHeight();
int childRight = childLeft + childView.getMeasuredWidth();
childView.layout(childLeft, childTop, childRight, childBottom);
left += childView.getMeasuredWidth() + childParams.leftMargin + childParams.rightMargin;
}
left = 0;
top += lineHeight;
}
-
viewgroup的子类的基本方法实现完成,先在xml中引用一下
跑一下效果如下,基本可以实现了(为了方便观察效果,textview中加了点shape属性)
-
那么接下来就比较简单了,实现类似RadioGroup的功能,将childView上的文字加到edittext上就行了
- 先定义一个接口:
public interface OnChildSelectedListener{
void onChildSelected(String content,View child);
}
- 在我们自定义的子类中,得到这个接口的实例
private OnChildSelectedListener mOnChildSelectedListener;
public void setOnChildSelectedListener(OnChildSelectedListener onChildSelectedListener) {
this.mOnChildSelectedListener = onChildSelectedListener;
}
- 回到onLayout()中,在第一个for循环里,加上点击事件:
final int finalI = i;
child.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (v.getTag() == null) v.setTag(true);
//selectedIndex : 当前选中的child坐标,全局变量
if (selectedIndex != finalI) {//本次点击view不是上次选中的view
if (selectedIndex != -1) {
//将上一个被选中的child选中效果拿掉
getChildAt(selectedIndex).setBackground(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.tv_bg));
}
v.setBackground(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.tv_bg_selcected));//设定选中效果
selectedIndex = finalI;
TextView tv = (TextView) v;
childSelcted = (String) tv.getText();
} else {//点击的是已经选中的view,取消选中效果
selectedIndex = -1;
v.setBackground(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.tv_bg));
childSelcted = null;
}
//把当前child上的文字传过去
mOnChildSelectedListener.onChildSelected(childSelcted,v);
}
});
- 来到activity中,实现这个接口,并将被选中的文字设置到edittext中:
flowLayout.setOnChildSelectedListener(new FlowLayout.OnChildSelectedListener() {
@Override
public void onChildSelected(String content, View child) {
editText.setText(content);
}
});
搞定。
老规矩,github上的代码,点击查看
有什么bug,请及时指出,大家一起来解决 :)