一、定义
霍夫曼(Huffman)编码是一种编码方式,主要用于数据文件的压缩。它的主要思想是放弃文本文件的普通保存方式:不再使用7位或8位二进制数表示每一个字符,而是用较少的比特表示出现频率高的字符,用较多的比特表示出现频率低的字符。
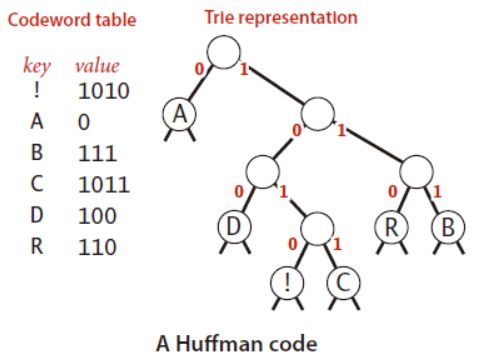
引例:假设需要对文本字符串“ABRACADABRA!”编码
- 一种方式是,用较短的比特表示所有可能的字符。
如A-0、B-1、R-00、C-01、D-10、!-11,这样“ABRACADABRA!”的编码就是0 1 00 0 01 0 10 0 1 00 0 11。这种表示方法只用了17位,而7位的ASCII编码则用了77位。但是这种方法存在一个问题:当不存在分隔符的时候,我们无法根据一连串比特码区分字符与比特码的映射关系。如01000010100100011也可以表示成CRRDDCRCB或其它字符串。 - 第二种方式是,如果任一字符的编码都不是其它字符编码的前缀,那么就不需要分隔符了。
如A-0、B-1111、R-1110、C-110、D-100、!-101。而霍夫曼编码就是寻找这种变长前缀的算法,且能使最终构造出的比特流最小。
二、实现方式
霍夫曼编码,首先需要根据输入文本,构造一棵二叉树,树的左链接表示比特"0",右链接表示比特"1",叶子结点表示字符。字符所对应的霍夫曼编码值就是从根结点到叶子结点的链接值。
总体实现步骤如下:
【压缩步骤】
压缩用于将原始文本转换成一条编码过的比特流。
- 读取输入;
- 统计输入中每个字符的频次;
- 根据频次,构造Huffman树;
- 构造编译表,用于将字符与变长前缀映射;
- 将Huffman树编码为比特字符串,并写入输出流;
- 将文本长度编码为比特字符串,并写入输出流;
- 压缩数据,即使用编译表翻译每个文本字符,写入输出流。
【解压缩步骤】
解压缩用于将一条编码过的比特流转换为原始文本。
- 读取Huffman树(编码在比特流的开头);
- 读取需要解码的字符数量;
- 根据步骤1还原的Huffman树解码压缩数据。
三、源码实现
3.1 构造Huffman树
构造一颗Huffman树的步骤如下:
1、遍历一遍文本,统计各个字符出现的频次;
2、对每个字符构造一个叶子结点,结点包含该个字符的频次;
3、每次从所有结点中选出频次最小的两个根结点,构造一个新结点,新结点作为根结点,两个根结点作为其左右子结点,新结点的频次为左右子根结点的频次和;
4、重复第3步,直到最后只剩一个根结点。
树结点定义:
private static class Node implements Comparable {
private final char ch; //字符
private final int freq; //每个结点保存以该结点为根的子树中的字符数量
private final Node left, right;
Node(char ch, int freq, Node left, Node right) {
this.ch = ch;
this.freq = freq;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
private boolean isLeaf() {
return (left == null) && (right == null);
}
public int compareTo(Node that) {
return this.freq - that.freq;
}
}
构造Huffman树:
//构造Huffman树
private static Node buildTrie(int[] freq) {
MinPQ pq = new MinPQ(); //优先级队列
for (char i = 0; i < R; i++) //R为字母表
if (freq[i] > 0)
pq.insert(new Node(i, freq[i], null, null));
//只有一个结点,特殊处理
if (pq.size() == 1) {
if (freq['\0'] == 0) pq.insert(new Node('\0', 0, null, null));
else pq.insert(new Node('\1', 0, null, null));
}
// merge two smallest trees
while (pq.size() > 1) {
Node left = pq.delMin();
Node right = pq.delMin();
Node parent = new Node('\0', left.freq + right.freq, left, right);
pq.insert(parent);
}
return pq.delMin();
}
3.2 构造编译表
编译表就是将每个字符与它的比特字符串相关联的符号表。
// 构造编译表
private static String[] buildCode(Node root) {
String[] table = new String[R];
buildCode(table, root, "");
return table;
}
private static void buildCode(String[] st, Node x, String s) {
if (!x.isLeaf()) {
buildCode(st, x.left, s + '0');
buildCode(st, x.right, s + '1');
} else {
st[x.ch] = s;
}
}
3.3 编码Huffman树,并压缩数据
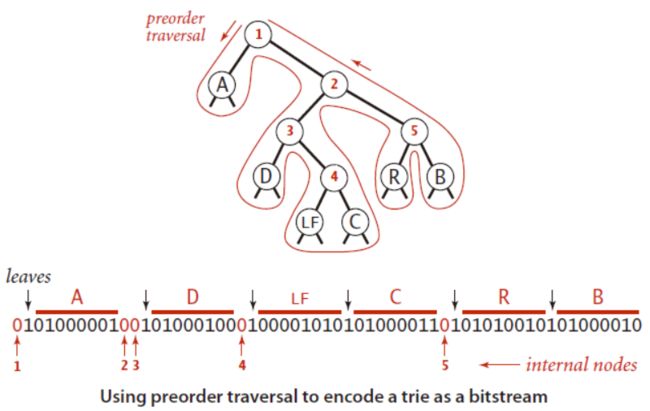
采用先序遍历对Huffman树编码。(之所以要对Huffman树编码是为了从压缩后的比特流中还原出Huffman树,这样后续才能解码)
从根结点开始,遇到内部结点写入比特"0";遇到叶子结点,写入比特"1",然后写入字符比特值。
/**
* 使用先序遍历将Huffman树编码为比特流
*/
private static void writeTrie(Node x) {
if (x.isLeaf()) {
BinaryStdOut.write(true);
BinaryStdOut.write(x.ch, 8);
return;
}
BinaryStdOut.write(false);
writeTrie(x.left);
writeTrie(x.right);
}
/**
* 压缩数据 最终的比特流结果为:Huffman树编码值+文本长度+压缩后的数据
*/
public static void compress() {
// read the input
String s = BinaryStdIn.readString();
char[] input = s.toCharArray();
// 统计频次
int[] freq = new int[R];
for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++)
freq[input[i]]++;
// 构建Huffman树
Node root = buildTrie(freq);
// 构建编译表
String[] st = new String[R];
buildCode(st, root, "");
// 编码Huffman树
writeTrie(root);
// 写入文本长度
BinaryStdOut.write(input.length);
// 压缩数据
for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
String code = st[input[i]]; // 根据编译表,得到字符对应的变长前缀
for (int j = 0; j < code.length(); j++) {
if (code.charAt(j) == '0') {
BinaryStdOut.write(false);
} else if (code.charAt(j) == '1') {
BinaryStdOut.write(true);
} else
throw new IllegalStateException("Illegal state");
}
}
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
3.4 解码Huffman树,并解压缩数据
/**
* 将比特流解码为Huffman树
*
* @return 返回Huffman树的根结点
*/
private static Node readTrie() {
boolean isLeaf = BinaryStdIn.readBoolean();
if (isLeaf) {
return new Node(BinaryStdIn.readChar(), -1, null, null);
} else {
return new Node('\0', -1, readTrie(), readTrie());
}
}
/**
* 解压缩数据
*/
public static void expand() {
// 解码比特流,还原Huffman树
Node root = readTrie();
// 解码文本长度
int length = BinaryStdIn.readInt();
// 解码文本数据
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { // i追踪字符,每次循环还原一个文本字符
Node x = root;
while (!x.isLeaf()) {
boolean bit = BinaryStdIn.readBoolean();
if (bit)
x = x.right;
else
x = x.left;
}
BinaryStdOut.write(x.ch, 8);
}
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
3.5 完整源码
public class Huffman {
private static final int R = 256; // 字母表
private Huffman() {
}
// 树结点定义
private static class Node implements Comparable {
private final char ch; // 字符
private final int freq; // 子树中所有字符的频次
private final Node left, right;
Node(char ch, int freq, Node left, Node right) {
this.ch = ch;
this.freq = freq;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
private boolean isLeaf() {
return (left == null) && (right == null);
}
public int compareTo(Node that) {
return this.freq - that.freq;
}
}
/**
* 构建Haffman树
*/
private static Node buildTrie(int[] freq) {
MinPQ pq = new MinPQ();
for (char i = 0; i < R; i++)
if (freq[i] > 0)
pq.insert(new Node(i, freq[i], null, null));
if (pq.size() == 1) {
if (freq['\0'] == 0)
pq.insert(new Node('\0', 0, null, null));
else
pq.insert(new Node('\1', 0, null, null));
}
// merge two smallest trees
while (pq.size() > 1) {
Node left = pq.delMin();
Node right = pq.delMin();
Node parent = new Node('\0', left.freq + right.freq, left, right);
pq.insert(parent);
}
return pq.delMin();
}
/**
* 构造编译表
*/
private static void buildCode(String[] st, Node x, String s) {
if (!x.isLeaf()) {
buildCode(st, x.left, s + '0');
buildCode(st, x.right, s + '1');
} else {
st[x.ch] = s;
}
}
/**
* 压缩数据 最终的比特流结果为:Huffman树编码值+文本长度+压缩后的数据
*/
public static void compress() {
// read the input
String s = BinaryStdIn.readString();
char[] input = s.toCharArray();
// 统计频次
int[] freq = new int[R];
for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++)
freq[input[i]]++;
// 构建Huffman树
Node root = buildTrie(freq);
// 构建编译表
String[] st = new String[R];
buildCode(st, root, "");
// 编码Huffman树
writeTrie(root);
// 写入文本长度
BinaryStdOut.write(input.length);
// 压缩数据
for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
String code = st[input[i]]; // 根据编译表,得到字符对应的变长前缀
for (int j = 0; j < code.length(); j++) {
if (code.charAt(j) == '0') {
BinaryStdOut.write(false);
} else if (code.charAt(j) == '1') {
BinaryStdOut.write(true);
} else
throw new IllegalStateException("Illegal state");
}
}
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
/**
* 解压缩数据
*/
public static void expand() {
// 解码比特流,还原Huffman树
Node root = readTrie();
// 解码文本长度
int length = BinaryStdIn.readInt();
// 解码文本数据
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { // i追踪字符,每次循环还原一个文本字符
Node x = root;
while (!x.isLeaf()) {
boolean bit = BinaryStdIn.readBoolean();
if (bit)
x = x.right;
else
x = x.left;
}
BinaryStdOut.write(x.ch, 8);
}
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
/**
* 将比特流解码为Huffman树
*
* @return 返回Huffman树的根结点
*/
private static Node readTrie() {
boolean isLeaf = BinaryStdIn.readBoolean();
if (isLeaf) {
return new Node(BinaryStdIn.readChar(), -1, null, null);
} else {
return new Node('\0', -1, readTrie(), readTrie());
}
}
/**
* 使用先序遍历将Huffman树编码为比特流
*/
private static void writeTrie(Node x) {
if (x.isLeaf()) {
BinaryStdOut.write(true); // 叶子结点写入"1"
BinaryStdOut.write(x.ch, 8); // 写入字符的比特值
return;
}
BinaryStdOut.write(false); // 内部结点写入"0"
writeTrie(x.left);
writeTrie(x.right);
}
/**
* 用例: Execution: java Huffman - < input.txt (compress) Execution: java
* Huffman + < input.txt (expand)
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args[0].equals("-"))
compress();
else if (args[0].equals("+"))
expand();
else
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal command line argument");
}
}
四、最优性证明
为什么根据Huffman算法,生成的字符变长前缀之和是最优的?
首先明确一个概念,即加权外部路径长度:表示Huffman树中叶子结点的频次 X 叶子结点高度的和。
*Huffman树的加权外部路径长度,就是文本编码后总比特长度。
要证明Huffman算法构造的变长前缀是最优的,就是证明Huffman树的加权外部路径长度是最短的。可以采用数学归纳法得到证明,具体可以参考《算法导论》或相关论文。