1. 用对象收编变量
var CheckObject = {
// 验证姓名
checkName: function () {},
// 验证邮箱
checkEmail: function () {},
// 验证密码
checkPassword: function () {}
}
使用:
CheckObject.checkName()
...
或:
var CheckObject = function () {}
CheckObject.checkName = function () {}
CheckObject.checkEmail = function () {}
CheckObject.checkPassword = function () {}
使用同上
缺点:
这个对象不能复制一份,或者说这个对象类在用new 关键字创建新的对象时,新创建的对象时不能继承这些方法。
2. 真假对象
var CheckObject = function () {
return {
checkName: function () {
// 验证姓名
},
checkEmail: function () {
// 验证邮箱
},
checkPassword: function () {
// 验证密码
}
}
}
优点:
每次调用CheckObject 方法返回的都是新的对象,每个人在使用时互补影像。
使用:
var a = CheckObject();
a.checkEmail();
缺点:
创建的新对象a 与 对象CheckObject没有任何关系
3.使用类创建对象
var CheckObject = function () {
this.checkName = function () {},
this.checkEmail = function () {},
this.checkPassword = function () {}
}
使用:
var a = new CheckObject();
a.checkEmail();
优点:
所有方法都放在了函数内部,并通过this定义,每一次使用new 关键字创建对象的时候,新创建的对象都会对类的this上的属性进行复制。
所以这些新创建的对象都会有自己的一套方法。
缺点:
因为新创建的对象也会有自己的一套方法,因此有时候造成的消耗(什么消耗?)是很奢侈的。
4.检测类
var CheckObject = function () {};
CheckObject.prototype.checkName = function () {};
CheckObject.prototype.checkEmail = function () {};
CheckObject.prototype.checkPassword = function () {};
简化写法:
var CheckObject = function () {};
CheckObject.prototype = {
checkName: function () {},
checkEmail: function () {},
checkPassword: function () {}
}
注意: 以上两种方式不能混用,否则,在后面为对象的原型对象赋值新对象时,会覆盖掉之前对prototype对象赋值的方法。
使用:
var a = new CheckObject();
a.checkName();
a.checkEmail();
a.checkPassword();
升级1:
var CheckObject = {
checkName: function () {
return this;
},
checkEmail: function () {
return this;
},
checkPassword: function () {
return this;
}
},
使用:
CheckObject.checkName().checkEmail().checkPassword();
升级2:
var CheckObject = function () {};
CheckObject.prototype = {
checkName: function () {
return this;
},
checkEmail: function () {
return this;
},
checkPassword: function () {
return this;
}
}
使用:
var a = new CheckObject();
a.checkName().checkEmail().checkPassword();
5. prototype.js
Function.prototype.addMethod = function (name. fn){
this[name] = fn;
}
// 添加方法
var methods = function () {};
// 或者
var methods = new Function();
methods.addMethod('checkName', function () {});
methods.addMethod('checkEmail', function () {});
methods.checkName();
methods.checkEmail();
链式操作:
Function.prototype.addMethod = function (name, fn) {
this[name] = fn;
return this;
}
var methods = function () {};
methods.addMethod('checkName', function() {
return this;
}).addMethod('checkEmail',function () {
return this;
});
methods.checkName().checkEmail();
类式调用:
Function.prototype.addMethod = function (name, fn) {
this.prototype[name] = fn;
}
// 添加方法
var Methods = function () {};
methods.addMethod('checkName', function () {}).addMethod('checkeEmail', function () {});
// 使用
var m = new Methods();
m.checkEmail();
JS的三类方法:
1)类方法
2)对象方法
3)原型方法
function CheckObject (name) {
this.name = name;
// 对象方法
this.checkName = function () {
console.log(' Name is ' + this.name);
}
}
// 类方法
CheckObject.checkEmail = function (email) {
console.log(" Email is " + email);
}
// 原型方法
CheckObject.prototype.checkPassword = function (password) {
console.log('Password is ' + password);
}
// 测试
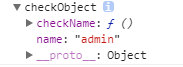
var LoginInputCheck = new CheckObject('admin');
console.log(LoginInputCheck );/* 输出:见图1 */
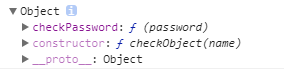
console.log(CheckObject); /* 输出:见图2 */
console.log(CheckObject.prototype); /*输出:见图3*/
LoginInputCheck.checkName(); // 输出: Name is admin
CheckObject.checkEmail('[email protected]'); // 输出: Email is [email protected]
LoginInputCheck.checkPassword('123'); // 输出: Password is 123
CheckObject.checkPassword('456');
/* 输出:报错 Uncaught TypeError: CheckObject.checkPassword is not a function */
LoginInputCheck.checkEmail('login@email');
/* 输出:报错 Uncaught TypeError: LoginInputCheck.checkEmail is not a function*/
javascript中的每个对象都有prototype属性,Javascript中对象的prototype属性的解释是:返回对象类型原型的引用。
-- 因此,改变原型,会影响通过原型创造的实例
A.prototype = new B();
A的prototype为B的一个实例,可以理解为A将B中的方法和属性全部克隆了一遍。A具有使用B的方法和属性。
函数运行时会先去本体的函数中去找,如果找到则运行,找不到则去prototype中寻找函数。或者可以理解为prototype不会克隆同名函数。如果要调用prototype指向的对象的方法可以用call()。
例如:
function A() {
this.Msg = function () {
alert(" A 's Msg");
}
}
function B() {
this.Msg = function () {
alert('B 's Msg');
}
}
B.prototype = new A();
var Ub = new B();
Ub.Msg(); // 输出: B 's Msg
// if you want to output 'A 's Msg'
var Ua = new A();
Ua.Msg.call(Ub); // 输出: A ’s Msg ; It means "将Ub当做Ua来调用,调用Ua的对象方法Msg"
为什么不直接用A.Msg.call(Ub)? --惯性