个人博客
http://www.milovetingting.cn
Android应用加固的简单实现方案
概述
Android应用加固的诸多方案中,其中一种就是基于dex的加固,本文介绍基于dex的加固方案。
原理:在AndroidManifest中指定启动Application为壳Module的Application,生成APK后,将壳Module的AAR文件和加密后的APK中的dex文件合并,然后重新打包签名。安装应用运行后,通过壳Module的Application来解密dex文件,然后再加载dex。
存在的问题:解密过程,会还原出来未加密的原dex文件,通过一些手段,还是可以获得未加密的dex。
实现
APK和壳AAR的生成
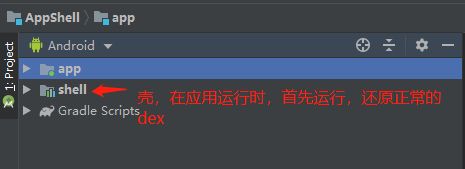
新建工程,然后新建一个Module,作为壳Module,名字随意,这里命名为shell。
在壳Module中新建继承自Application的ShellApplication,重写attachBaseContext方法,在这个方法加载原来的dex
public class ShellApplication extends Application {
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
super.attachBaseContext(base);
try {
//获取应用APK
File apkFile = new File(getApplicationInfo().sourceDir);
//解压目录
File apkUnzipDir = getDir("apk", Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
apkUnzipDir = new File(apkUnzipDir, "unzip");
//如果不存在,则解压
if (!apkUnzipDir.exists()) {
apkUnzipDir.mkdirs();
//解压
ZipUtils.unzipFile(apkFile, apkUnzipDir);
//过滤所有.dex文件
File[] files = apkUnzipDir.listFiles(new FilenameFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
return name.endsWith(".dex");
}
});
//解密
File decryptDir = new File(apkUnzipDir, "decrypt");
decryptDir.mkdirs();
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
for (File file : files) {
if (file.getName().endsWith("classes.dex")) {
list.add(file);
} else {
File decryptFile = new File(decryptDir, file.getName());
EncryptUtils.decrypt(file.getAbsolutePath(), decryptFile.getAbsolutePath());
//添加到list中
list.add(decryptFile);
//删除加密的dex文件
file.delete();
}
}
//加载.dex文件
ClassLoaderUtil.loadDex(this, list);
} else {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new File(apkUnzipDir, "classes.dex"));
File decryptDir = new File(apkUnzipDir, "decrypt");
File[] files = decryptDir.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
list.add(file);
}
//加载.dex文件
ClassLoaderUtil.loadDex(this, list);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
修改app的AndroidManifest中application节点的name为壳Module的Application
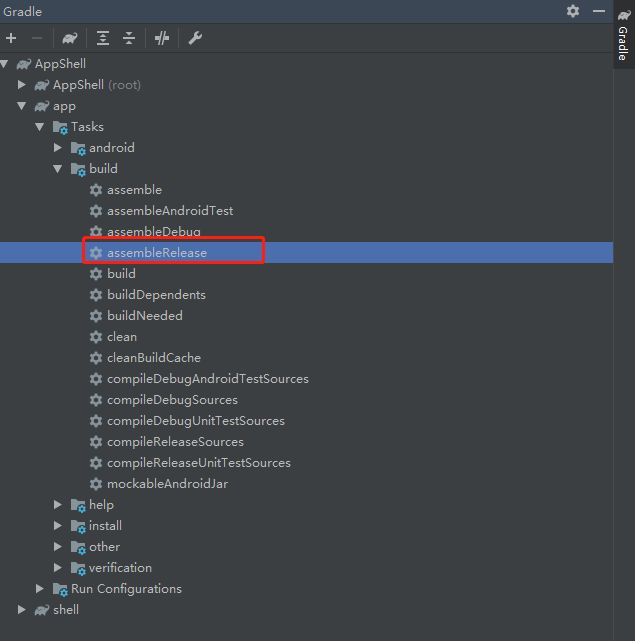
在Gradle面板,双击app/Tasks/build/目录下的assembleRelease,生成未签名的APK
在app/build/outputs/apk/release/目录下,可以找到生成的apk:app-release-unsigned.apk
在Android Studio中,点击Build-Make Module 'shell',生成AAR。
在shell/build/outputs/aar/目录下,可以找到生成的aar:shell-debug.aar
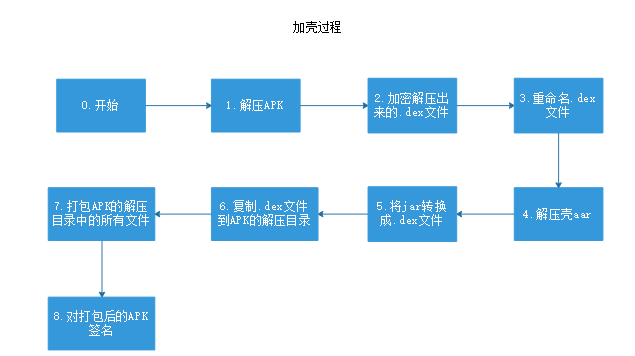
加壳的过程
加壳的实现流程如下:
这里选择Eclipse新建Java工程来操作。
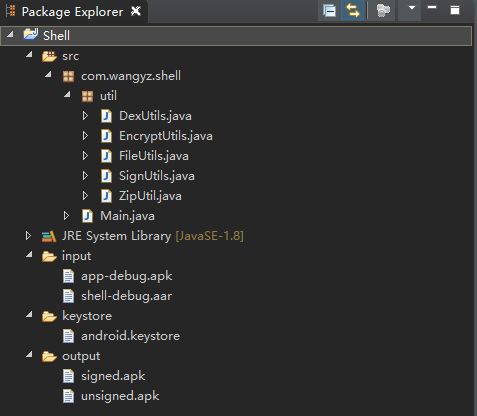
项目结构说明:
-
input:存放需要加壳的apk和aar
-
keystore:存放签名用到的keystore文件
-
output:打包后输出目录,signed为签名后的apk
需要配置的环境变量:
-
由于要用到dx来将jar转换成dex,因此需要配置dx的路径。在SDK/build-tools/下,有对应不同版本的build工具,这里选择28.0.0,进入28.0.0文件夹,可以看到dx.bat文件。在电脑的环境变量中,修改path,增加dx.bat路径:
-
由于要用到jarsigner来签名apk,因此需要配置jarsigner的环境变量。一般Java开发的话,JDK配置好了后,这个就不需要再配置了。
配置好上面的环境变量后,关掉eclipse,然后重新启动eclipse
Main类中的代码逻辑:
try {
// APK
File apkFile = new File("input/app-debug.apk");
// 壳AAR
File shellFile = new File("input/shell-debug.aar");
// 判断文件是否存在
if (!apkFile.exists() || !shellFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("apkFile or shellFile missing");
return;
}
// *************解压APK*************
System.out.println("解压APK");
// 先删除输出文件夹下的所有文件
File outputDir = new File("output/");
if (outputDir.exists()) {
FileUtils.deleteAllInDir(outputDir);
}
// 创建apk的解压目录
File apkUnzipDir = new File("output/unzip/apk/");
if (!apkUnzipDir.exists()) {
apkUnzipDir.mkdirs();
}
// 解压APK
ZipUtil.unZip(apkFile, apkUnzipDir);
// 删除META-INF/CERT.RSA,META-INF/CERT.SF,META-INF/MANIFEST.MF
File certRSA = new File(apkUnzipDir, "/META-INF/CERT.RSA");
certRSA.delete();
File certSF = new File(apkUnzipDir, "/META-INF/CERT.SF");
certSF.delete();
File manifestMF = new File(apkUnzipDir, "/META-INF/MANIFEST.MF");
manifestMF.delete();
// 获取dex文件
File[] apkFiles = apkUnzipDir.listFiles(new FilenameFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File file, String s) {
return s.endsWith(".dex");
}
});
for (int i = apkFiles.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
File file = apkFiles[i];
String name = file.getName();
System.out.println("dex:" + name);
String bakName = name.substring(0, name.indexOf(".dex")) + "_bak.dex";
System.out.println("备份dex:" + bakName);
bakName = file.getParent() + File.separator + name.substring(0, name.indexOf(".dex")) + "_bak.dex";
// 加密dex文件
EncryptUtils.encrypt(file.getAbsolutePath(), bakName);
System.out.println("加密dex:" + name);
// 删除原文件
file.delete();
}
// *************解压APK*************
// *************解压壳AAR*************
// 创建壳AAR的解压目录
System.out.println("解压壳AAR");
File shellUnzipDir = new File("output/unzip/shell/");
if (!shellUnzipDir.exists()) {
shellUnzipDir.mkdirs();
}
// 解压AAR
ZipUtil.unZip(shellFile, shellUnzipDir);
// 将jar转成dex
System.out.println("将jar转成dex");
File shellJar = new File(shellUnzipDir, "classes.jar");
File shellDex = new File(apkUnzipDir, "classes.dex");
DexUtils.dxCommand(shellJar, shellDex);
// 打包
System.out.println("打包APK");
File unsignedApk = new File("output/unsigned.apk");
ZipUtil.zip(apkUnzipDir, unsignedApk);
// 删除解压目录
FileUtils.delete("output/unzip/");
System.out.println("签名APK");
File signedApk = new File("output/signed.apk");
SignUtils.signature(unsignedApk, signedApk, "keystore/android.keystore");
System.out.println("Finished!!!");
// *************解压壳AAR*************
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
来看下具体的步骤:
解压APK
File apkUnzipDir = new File(root, "/output/unzip/apk/");
if (!apkUnzipDir.exists()) {
apkUnzipDir.mkdirs();
}
// 解压APK
ZipUtil.unZip(apkFile, apkUnzipDir);
加密解压出来的dex文件、重命名dex文件
// 获取dex文件
File[] apkFiles = apkUnzipDir.listFiles((file, s) -> s.endsWith(".dex"));
for (int i = apkFiles.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
File file = apkFiles[i];
String name = file.getName();
System.out.println("dex:" + name);
String bakName = name.substring(0, name.indexOf(".dex")) + "_bak.dex";
System.out.println("备份dex:" + bakName);
bakName = file.getParent() + File.separator + name.substring(0, name.indexOf(".dex")) + "_bak.dex";
// 加密dex文件
EncryptUtils.encrypt(file.getAbsolutePath(), bakName);
System.out.println("加密dex:" + name);
// 删除原文件
file.delete();
}
解压壳AAR
File shellUnzipDir = new File(root, "/output/unzip/shell/");
if (!shellUnzipDir.exists()) {
shellUnzipDir.mkdirs();
}
// 解压AAR
ZipUtil.unZip(shellFile, shellUnzipDir);
将jar转成dex
File shellJar = new File(shellUnzipDir, "classes.jar");
File shellDex = new File(apkUnzipDir, "classes.dex");
DexUtils.dxCommand(shellJar, shellDex);
打包
File unsignedApk = new File(root, "/output/unsigned.apk");
ZipUtil.zip(apkUnzipDir, unsignedApk);
签名
FileUtils.delete(new File(root, "output/unzip/"));
System.out.println("签名APK");
File signedApk = new File(root, "output/signed.apk");
SignUtils.signature(unsignedApk, signedApk, keystore, keyStorePassword, keyPassword, alias);
System.out.println("Finished!!!");
在output目录下,可以看到已经生成signed.apk。将apk安装在手机上,可以正常运行,达到加固的目的。
源码
源码地址:https://github.com/milovetingting/Samples/tree/master/Shell/加固-手动加壳
基于gradle的自动加固
上面的加固方式,需要在生成APK后,再生成壳Module的AAR文件,然后再通过工具来生成加固的APK。这个过程,手动操作还是比较麻烦的。可以借助gradle来生成插件,在生成APK后,自动完成加固。
插件生成
新建工程Plugins,新建module,名为shell,作为加壳的插件。
清空shell模块下的build文件内容修改如下:
apply plugin: 'groovy'
dependencies {
implementation gradleApi()
implementation localGroovy()
}
删除shell模块下的src/main/目录下的所有文件,然后新建目录groovy,在groovy中再新建包:com/wangyz/plugins,具体可以根据实际情况修改。
新建ShellConfig.java,作为自定义配置的bean
public class ShellConfig {
/**
* 壳Module名称
*/
String shellModuleName;
/**
* keystore的位置
*/
String keyStore;
/**
* keystore的密码
*/
String keyStorePassword;
/**
* key的密码
*/
String keyPassword;
/**
* 别名
*/
String alias;
}
新建ShellPlugin.groovy,主要的逻辑都在这里面
package com.wangyz.plugins
import com.wangyz.plugins.util.ShellUtil
import org.gradle.api.Plugin
import org.gradle.api.Project
class ShellPlugin implements Plugin {
def printLog(Object msg) {
println("******************************")
println(msg)
println("******************************\n")
}
def createDir(Project project) {
File shellDir = new File("${project.rootDir}/ShellAPK")
if (!shellDir.exists()) {
printLog("create dir")
shellDir.mkdirs()
}
}
def deleteDir(Project project) {
File shellDir = new File("${project.rootDir}/ShellAPK")
if (shellDir.exists()) {
printLog("delete dir")
shellDir.deleteDir()
}
}
@Override
void apply(Project project) {
printLog('ShellPlugin apply')
project.extensions.create("shellConfig", ShellConfig)
project.afterEvaluate {
project.tasks.matching {
it.name == 'assembleRelease'
}.each {
task ->
printLog(task.name)
def shellProject = project.parent.findProject("${project.shellConfig.shellModuleName}")
printLog("shellProject:$shellProject")
File shellDir = new File("${project.rootDir}/ShellAPK")
File apkFile
File aarFile = new File("${shellProject.buildDir}/outputs/aar/shell-release.aar")
project.android.applicationVariants.all {
variant ->
variant.outputs.each {
output ->
def outputFile = output.outputFile
printLog("outputFile:${outputFile.getAbsolutePath()}")
if (outputFile.name.contains("release")) {
apkFile = outputFile
}
}
}
task.doFirst {
//删除原来的文件夹
deleteDir(project)
//生成文件夹
createDir(project)
//生成aar
printLog("begin generate aar")
project.exec {
workingDir("../${project.shellConfig.shellModuleName}/")
commandLine('cmd', '/c', 'gradle', 'assembleRelease')
}
printLog("generate aar complete")
//复制文件
printLog("begin copy aar")
project.copy {
from aarFile
into shellDir
}
printLog("copy aar complete")
}
task.doLast {
printLog("begin copy apk")
//复制文件
project.copy {
from apkFile
into shellDir
}
printLog("copy ${apkFile.name} complete")
printLog("begin shell")
ShellUtil.shell(apkFile.getAbsolutePath(), aarFile.getAbsolutePath(), shellDir.getAbsolutePath(), project.shellConfig.keyStore, project.shellConfig.keyStorePassword, project.shellConfig.keyPassword, project.shellConfig.alias)
printLog("end shell")
}
}
}
}
}
ShellPlugin类实现Plugin接口,实现apply方法,当插件被apply时,就会回调这个方法。
首先创建配置,这样引用插件的gradle文件就可以定义shellConfig节点,插件就可以拿到配置节点里的内容
project.extensions.create("shellConfig", ShellConfig)
指定在assembleRelease后执行我们自己的逻辑
project.afterEvaluate {
project.tasks.matching {
it.name == 'assembleRelease'
}.each {
task ->
printLog(task.name)
}
}
具体的逻辑定义在task的闭包中,在生成apk前,执行task.doFirst里的逻辑,首先生成aar,然后执行生成apk的逻辑,然后在task.doLast中执行加壳的操作。
printLog(task.name)
def shellProject = project.parent.findProject("${project.shellConfig.shellModuleName}")
printLog("shellProject:$shellProject")
File shellDir = new File("${project.rootDir}/ShellAPK")
File apkFile
File aarFile = new File("${shellProject.buildDir}/outputs/aar/shell-release.aar")
project.android.applicationVariants.all {
variant ->
variant.outputs.each {
output ->
def outputFile = output.outputFile
printLog("outputFile:${outputFile.getAbsolutePath()}")
if (outputFile.name.contains("release")) {
apkFile = outputFile
}
}
}
task.doFirst {
//删除原来的文件夹
deleteDir(project)
//生成文件夹
createDir(project)
//生成aar
printLog("begin generate aar")
project.exec {
workingDir("../${project.shellConfig.shellModuleName}/")
commandLine('cmd', '/c', 'gradle', 'assembleRelease')
}
printLog("generate aar complete")
//复制文件
printLog("begin copy aar")
project.copy {
from aarFile
into shellDir
}
printLog("copy aar complete")
}
task.doLast {
printLog("begin copy apk")
//复制文件
project.copy {
from apkFile
into shellDir
}
printLog("copy ${apkFile.name} complete")
printLog("begin shell")
ShellUtil.shell(apkFile.getAbsolutePath(), aarFile.getAbsolutePath(), shellDir.getAbsolutePath(), project.shellConfig.keyStore, project.shellConfig.keyStorePassword, project.shellConfig.keyPassword, project.shellConfig.alias)
printLog("end shell")
}
在src/main/目录下新建目录:resources/META-INF/gradle-plugins,再创建com.wangyz.plugins.ShellPlugin.properties的文件,这里的文件名就是后面插件被引用时的名字,com.wangyz.plugins.ShellPlugin.properties内容如下:
implementation-class=com.wangyz.plugins.ShellPlugin
key为implementation-class,这个是固定的
value为com.wangyz.plugins.ShellPlugin,就是上面在groovy里创建的类
到这里,定义好了插件,还需要发布到仓库。在shell模块的build.gradle文件中增加以下配置
apply plugin: 'maven-publish'
publishing {
publications {
mavenJava(MavenPublication) {
groupId 'com.wangyz.plugins'
artifactId 'ShellPlugin'
version '1.0.0'
from components.java
}
}
}
publishing {
repositories {
maven {
url uri('E:\\Repository')
}
}
}
sync项目后,可以在Gradle面板看到新生成的task
双击publish,会将插件发布到我们指定的仓库
11:22:39: Executing task 'publish'...
Executing tasks: [publish] in project D:\Project\Plugins\shell
Parallel execution with configuration on demand is an incubating feature.
:shell:generatePomFileForMavenJavaPublication
:shell:compileJava NO-SOURCE
:shell:compileGroovy UP-TO-DATE
:shell:processResources UP-TO-DATE
:shell:classes UP-TO-DATE
:shell:jar UP-TO-DATE
Could not find metadata com.wangyz.plugins:ShellPlugin/maven-metadata.xml in remote (file:/E:/Repository)
:shell:publishMavenJavaPublicationToMavenRepository
:shell:publish
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 0s
5 actionable tasks: 2 executed, 3 up-to-date
11:22:40: Task execution finished 'publish'.
插件应用
在需要加壳的工程的根build.gradle中引入插件:
buildscript {
repositories {
maven {
url uri('E:\\Repository')
}
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.wangyz.plugins:ShellPlugin:1.0.0'
}
}
allprojects {
repositories {
maven {
url uri('E:\\Repository')
}
}
}
在app的build.gradle中应用插件:
//引入插件
apply plugin: 'com.wangyz.plugins.ShellPlugin'
//配置插件
shellConfig {
shellModuleName = 'shell'
keyStore = 'E:\\Code\\Android\\android.keystore'
keyStorePassword = 'android'
keyPassword = 'android'
alias = 'android'
}
由于插件中会用到gradle命令,因此需要先配置gradle的路径到环境变量path中。具体配置,可以找下相关资料,这里不再展开。
双击执行assembleRelease命令,就会在根目录/ShellApk/output/下生成加壳签名后的apk。
安装加壳签名后的apk,可以正常运行。
源码
源码地址:https://github.com/milovetingting/Samples/tree/master/Shell/加固-gradle插件加壳
插件的实现
上面的方案,实际操作起来还是比较麻烦。因此,可以定义一个插件,通过引入这个插件,来实现apk的加固,减少编码的工作量。
可以参考下一篇文章:Android应用加固的简单实现方案(二)