解析器模式
给定一个语言,定义它的文法表示,并定义一个解释器,这个解释器使用该标识来解释语言中的句子。
这种模式被用在 SQL 解析、符号处理引擎等。
Jsoup这个源码里面用到,代码简单,功能狠强大.
可利用场景比较少,JAVA 中如果碰到可以用 expression4J 代替。
-
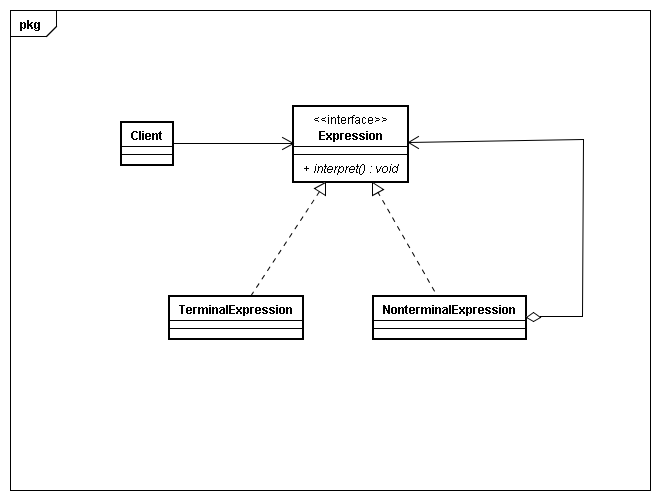
上类图:
-
代码示例:
- 创建表达式接口
package com.byedbl.interpreter;
/**
* The interface of our BooleanExp Interpreter
* BooleanExp definition is:
* BooleanExp ::= VariableExp | Constant | OrExp | AndExp
* | NotExp | '(' BooleanExp ')'
* AndExp ::= BooleanExp 'and' BooleanExp
* OrExp ::= BooleanExp 'or' BooleanExp
* NotExp ::= BooleanExp 'not' BooleanExp
* Constant ::= 'true' | 'false'
* VariableExp ::= 'A' | 'B' | ... | 'Z'
*/
public interface BooleanExp {
boolean evaluate(Context c);
BooleanExp replace(String var, BooleanExp exp);
BooleanExp copy();
}
- 创建一个终结符表达式
package com.byedbl.interpreter;
/**
* A variable expression implements BooleanExp
* A terminal expression
*/
public class VariableExp implements BooleanExp {
private String name;
public VariableExp(String _name) {
name = _name;
}
@Override
public boolean evaluate(Context c) {
return c.lookUp(name);
}
@Override
public BooleanExp copy() {
return new VariableExp(name);
}
@Override
public BooleanExp replace(String var, BooleanExp exp) {
if (var.equals(name)) {
return exp.copy();
} else {
return new VariableExp(name);
}
}
}
- 创建非终结符表达式
package com.byedbl.interpreter;
/**
* A NonterminalExpression
*/
public class AndExp implements BooleanExp {
private BooleanExp operand1;
private BooleanExp operand2;
public AndExp(BooleanExp oper1, BooleanExp oper2) {
operand1 = oper1;
operand2 = oper2;
}
@Override
public boolean evaluate(Context c) {
return operand1.evaluate(c) &&
operand2.evaluate(c);
}
@Override
public BooleanExp copy() {
return new AndExp(operand1.copy(), operand2.copy());
}
@Override
public BooleanExp replace(String var, BooleanExp exp) {
return new AndExp(
operand1.replace(var, exp),
operand2.replace(var, exp)
);
}
}
package com.byedbl.interpreter;
/**
* A NonterminalExpression
*/
public class NotExp implements BooleanExp {
private BooleanExp opernot1;
public NotExp(BooleanExp oper1) {
opernot1 = oper1;
}
@Override
public boolean evaluate(Context c) {
return !(opernot1.evaluate(c));
}
@Override
public BooleanExp copy() {
return new NotExp(opernot1.copy());
}
@Override
public BooleanExp replace(String var, BooleanExp exp) {
return new NotExp(opernot1.replace(var, exp));
}
}
package com.byedbl.interpreter;
/**
* A NonterminalExpression
*/
public class OrExp implements BooleanExp {
private BooleanExp operor1;
private BooleanExp operor2;
public OrExp(BooleanExp oper1, BooleanExp oper2) {
operor1 = oper1;
operor2 = oper2;
}
@Override
public boolean evaluate(Context c) {
return operor1.evaluate(c) ||
operor2.evaluate(c);
}
@Override
public BooleanExp copy() {
return new OrExp(operor1.copy(), operor2.copy());
}
@Override
public BooleanExp replace(String var, BooleanExp exp) {
return new OrExp(
operor1.replace(var, exp),
operor2.replace(var, exp)
);
}
}
- 环境角色
package com.byedbl.interpreter; /**
* A Context to record variable value
*/
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class Context {
private Hashtable context = new Hashtable<>();
public void assign(String name, boolean val) {
context.put(name, val);
}
public boolean lookUp(String name) {
return context.get(name);
}
public Context() {
}
}
- 客户端用法
package com.byedbl.interpreter; /**
*
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test :
// (true and x) and (y and (not x))
Context context = new Context();
VariableExp x = new VariableExp("X");
VariableExp y = new VariableExp("Y");
VariableExp bTure = new VariableExp("true");
VariableExp bFalse = new VariableExp("false");
context.assign("true", true);
context.assign("false", false);
context.assign("X", false);
context.assign("Y", true);
BooleanExp expression = new AndExp(
new AndExp(bTure, x),
new AndExp(y, new NotExp(x))
);
boolean result = expression.evaluate(context);
System.out.println("The result is:" + result);
}
}