GitHub地址:https://github.com/includebug/wc.exe
PSP2.1表格
| PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
| Planning |
计划 |
20 |
30 |
| · Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
360 |
600 |
| Development |
开发 |
300 |
800 |
| · Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
50 |
200 |
| · Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
15 |
45 |
| · Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
20 |
50 |
| · Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
15 |
30 |
| · Design |
· 具体设计 |
40 |
60 |
| · Coding |
· 具体编码 |
240 |
600 |
| · Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
40 |
60 |
| · Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
30 |
55 |
| Reporting |
报告 |
15 |
25 |
| · Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
10 |
25 |
| · Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
20 |
25 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
10 |
15 |
| 合计 |
|
1185 |
1935 |
题目描述
Word Count
实现一个简单而完整的软件工具(源程序特征统计程序)。
进行单元测试、回归测试、效能测试,在实现上述程序的过程中使用相关的工具。
进行个人软件过程(PSP)的实践,逐步记录自己在每个软件工程环节花费的时间。
WC 项目要求
wc.exe 是一个常见的工具,它能统计文本文件的字符数、单词数和行数。这个项目要求写一个命令行程序,模仿已有wc.exe 的功能,并加以扩充,给出某程序设计语言源文件的字符数、单词数和行数。
实现一个统计程序,它能正确统计程序文件中的字符数、单词数、行数,以及还具备其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。
具体功能要求:
程序处理用户需求的模式为:
wc.exe [parameter] [file_name]
基本功能列表:(完成)
wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数
wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的词的数目
wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的行数
扩展功能:(完成)
-s 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件。
-a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)。
空行:本行全部是空格或格式控制字符,如果包括代码,则只有不超过一个可显示的字符,例如“{”。
代码行:本行包括多于一个字符的代码。
注释行:本行不是代码行,并且本行包括注释。一个有趣的例子是有些程序员会在单字符后面加注释:
} //注释
在这种情况下,这一行属于注释行。
[file_name]: 文件或目录名,可以处理一般通配符。
高级功能:(未完成)
-x 参数。这个参数单独使用。如果命令行有这个参数,则程序会显示图形界面,用户可以通过界面选取单个文件,程序就会显示文件的字符数、行数等全部统计信息。
需求举例:
wc.exe -s -a *.c
返回当前目录及子目录中所有*.c 文件的代码行数、空行数、注释行数。
遇到的问题:
困难描述:
1.没怎么接触过文件的操作
2.对_finddata_t的学习
做过哪些尝试:
上csdn跟博客园等上面查找相关的资料,然后自己创建一个项目,把他们的代码下载下载下来玩,尝试着去弄明白那些函数的特性跟使用的注意事项。在设计时本来是直接一个文件写完的,把那几个功能封装成一个函数,后来想着把这些东西封装成一个类,可以保存程序后的结果,但是写着写着就变形了,想到了怎么去改,但是时间成本太高,也想过把测试的结果写入txt的,没弄.。接触了下MFC和QT,但是来不及去弄了。如何解决通配符的问题。
是否解决:
通配符是在看到别人的在文件下搜索所有符合的文件(不能查找子文件夹)的代码基础上加上自己写的一个递归函数完成的。在边查边写时解决了路径问题,期间忘了’/‘在输出时要用“//”,在寻找同学的帮助下解决。
有何收获:
学会了文件的操作和模糊查找文件的操作,有些功能看似很难实现,实际上写完再回头看也不难,就是写代码的不规范或者对函数的不熟悉导致了很多问题,还是要多打代码,做多点实践。
解题思路:
对文件的操作都选择为对文件的每一行进行操作,统计。
代码
下面就是我在Filecount.h定义的类
class Filecount
{
public:
Filecount();
void recount(); //把private存的数据清空
~Filecount();
void wordcount(string &filename); //单词数计算
void charcount(string &filename); //字符数计算
void linecount(string &filename); //所有的行数计算,包含代码行注释行等的操作
void codelinecount();
void emptylinecount();
void notelinecount();
int search(string &srcPath, string &filename,string s[],int &i); //在指定文件夹内搜索符合条件的文件,用string s[] 返回
void filesearch(string &srcPath, string &filename,string s[],int &i); //
void filecount(string filename, string order);
private:
int words; //单词数
int lines; //总行数
int charnums; //字符数
int emptylines; //空行
int notelines; //注释行
int codelines; //代码行
};
行数统计
void Filecount::linecount(string &filename)
{
string str;
int count = 0;
ifstream file(filename);
if (!file.is_open())
{
cout << "文件名可能有错,无法打开" << endl;
return;
}
while (!file.eof())
{
getline(file, str);//从文件中读取一行
lines++;
remove(str.begin(), str.end(), ' '); //这个算法函数在algorithm头文件中,删除一行中的空格
remove(str.begin(), str.end(), '\t'); //删除一行中的制表符,因为制表符和空格都是空的
string notechar = "//";
string::size_type idx;
if (str.size() <= 1) //清除空格后,这一行的长度小于等于1就是空行
emptylinecount();
else if ((idx = str.find(notechar)) != string::npos) //如果在这一行找到//就是注释行
notelinecount();
int count = 0;
for (int j = 0; (j < str.size()) && (count <= 2); j++) //一行中多余2个英文字母为代码行
{
if ((str[j] >= 65 && str[j] <= 90) || (str[j] >= 97 && str[j] <= 122))
count++;
}
if (count >= 2)
codelinecount();
}
file.close();
}
单词统计
void Filecount::wordcount(string &filename)
{
string str;
bool isWord = false;
ifstream file(filename);
if (!file.is_open())
{
cout << "文件名可能有错,无法打开" << endl;
return;
}
int count = 0;
while (!file.eof()) //判断条件为file时,会重复读最后一行,最后一行为回车时正常行数
{
getline(file, str);//从文件中读取一行
isWord = false; //重置,错误原因,没有回到false导致计算单词数少了,
//每行末尾置isWord为true,导致下一行第一个单词不能计算
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
if (str[i] == ' ' || str[i] == '\n' || str[i] == '(' || str[i] == ')' || str[i] == '\0') //单词末尾的标志
{
isWord = false;
}
else
{
if (isWord == false) //isWord为true证明单词继续,遇到单词末尾的标志就结束
{
isWord = true;
words++;
}
}
}
}
file.close();
}
字符数统计
void Filecount::charcount(string &filename) { string str; ifstream file(filename); if (!file.is_open()) { cout << "文件名可能有错,无法打开" << endl; return; } int count = 0; while (!file.eof()) //判断条件为file时,会重复读最后一行,最后一行为回车时正常行数 { getline(file, str);//从文件中读取一行 for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) { if (str[i] == ' ' || str[i] == '\n' || str[i] == '\0') ; //如果是这些字符什么都不做 else charnums++; } } file.close(); }
查找符合条件的文件
int Filecount::search(string &srcPath, string &filename, string s[], int &i) //在指定文件夹搜索符合的文件,不能查子文件夹的 { long handle; //用于查找句柄 struct _finddata_t fileinfo; //文件信息的结构体 string Name = srcPath + "\\" + filename; //路径加上模糊搜索文件名 handle = _findfirst(Name.c_str(), &fileinfo); //第一次查找 if (-1L == handle) return 1; else { s[i] = srcPath + "\\" + fileinfo.name; i++; } while (!_findnext(handle, &fileinfo)) { s[i] = srcPath + "\\" + fileinfo.name; i++; } _findclose(handle);//别忘了关闭句柄 return 0; } void Filecount::filesearch(string &srcPath, string &filename, string s[], int &i) //搜索文件夹内所有符合条件的文件 { if (srcPath == "") return; _finddata_t FileInfo; string startFindPath = srcPath + "\\*"; //文件路径下的所有文件 long handle = _findfirst(startFindPath.c_str(), &FileInfo); // search(srcPath, filename, s, i); //在这个文件夹下搜索符合的文件 if (handle == -1L) return; //逐层递进搜索子目录 do { if (FileInfo.attrib == _A_SUBDIR) //判断是否为子文件夹 { if ((strcmp(FileInfo.name, ".") != 0) && (strcmp(FileInfo.name, "..") != 0)) //屏蔽这两个文件,不知道为什么 { string newPath = srcPath + "\\" + FileInfo.name; filesearch(newPath,filename,s , i); } } } while (_findnext(handle, &FileInfo) == 0); _findclose(handle); }
对命令的解析
void Filecount::filecount(string filename, string order)
{
if (order.compare("-c") == 0)
{
charcount(filename);
cout << "文件的字符数为" << charnums << endl;
}
else if (order.compare("-w") == 0)
{
wordcount(filename);
cout << "文件的单词数为" << words << endl;
}
else if (order.compare("-l") == 0)
{
linecount(filename);
cout << "文件的行数为" << lines << endl;
}
else if (order.compare("-a") == 0)
{
linecount(filename);
cout << "文件的空行" << emptylines << endl;
cout << "文件的注释行" << notelines << endl;
cout << "文件的代码行" << codelines << endl;
}
else if (order.compare("-s") == 0)
{
//该操作在main函数里完成
}
else
cout << "命令有错误,无法识别" << endl;
recount();
}
主函数main的调用
#include "Filecountclass.h" #include#include using namespace std; int main() { string Path = "D:\\vs代码\\fileline\\fileline"; string testorder = "-a"; string testfilename = "*.txt"; string s[20] = { "" }; string orders[5] = { "-c","-w","-l" ,"-a","-s"}; //总命令和 string trueorder[5] = {}; string orderline = ""; Filecount testfile ; cout << "请输入要在哪里搜索文件(如D:\\vs代码\\fileline\\fileline)" << endl; getline(cin,Path); cout << "请输入要执行的指令行(可连续输入,重复输入同一个无效)" << endl; cout <<"-c返回字符数 -w返回单词数 -l返回行数 -a返回复杂的行数数据 -s查找符合条件的文件返回"<<endl; getline(cin, orderline); cout << "请输入要搜索的文件名(如 *.txt /test.txt)" << endl; getline(cin, testfilename); int p = 0; //记录命令的真正个数 for (int t = 0; t < 5; t++) { if (orderline.find(orders[t]) != string::npos) { trueorder[p] = orders[t]; p++; } } int i = 0; testfile.filesearch(Path, testfilename, s, i); //在Path里搜索符合的文件名 if (i == 0) cout << "无符合的文件,输入错误!" << endl; if (p == 0) cout << "无效指令,无法执行!" << endl; for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { cout << "文件" << s[j] << "的数据:" << endl; for (int k = 0; trueorder[k] != ""&& k< p ;k++) { testfile.filecount(s[j], trueorder[k]); } } //Filecount对象只有一个却对应多个文件 system("pause"); return 0; }
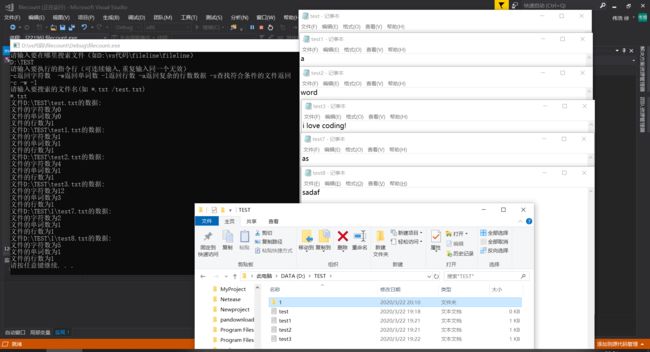
测试运行
基础功能(文件名只能输一个)
扩展功能
项目小结
对github的使用很不熟悉,学会了sting的很多方法以及_finddata_t,在写代码之前要多加构思,不能想到什么就写什么,效率极低。这里面的函数每次都是写好了又改,搞得测试做了很多,但是没什么参考价值。按我的想法应该是一个文件对应一个Filecount的实例化对象,可以保存程序运行的结果,但是在一些地方的想法实现时让代码很难修改回这个模式,所以说还是对函数的不熟悉,导致面对问题时不能快速想到用什么函数,如何去做。思路的不清晰导致行为的不确定,这次的项目写了很久,算是对自己能力的一次测试吧。希望自己在今后的学习可以更进一层楼。