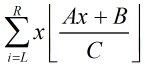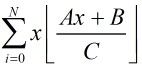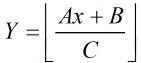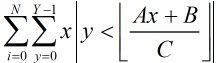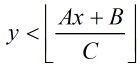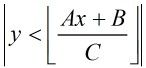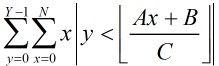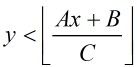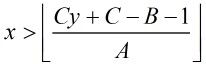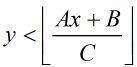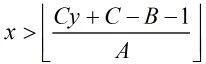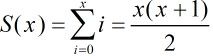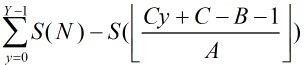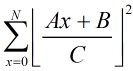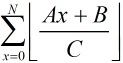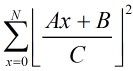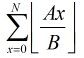BZOJ2831(小强的金字塔系列问题--区域整点数求法)
这里其实用到扩展欧几里德。(基本上参照clj的解题报告才理解的)
这里我们假设A<C和B<C,否则我们可以把它化成A<C,B<C的情况
那么式子就转化为:
这样一看我们就交换了A,C了,也就是扩展欧几里德算法,详见金斌2009论文。
这样的话与上面同样的思路继续化简:对于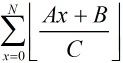 比较简单,就不写过程了。
比较简单,就不写过程了。
![]()
然后分析就完毕!
由于本题的数很大,要用高精度,用Python最好,因为一是Python高精度可以直接算,二是Python直接返回元组方便。
sum = lambda n : n*(n+1)/2
sqrtsum = lambda n : n*(n+1)*(2*n+1)/6
def f(a,b,c,r):
if r<0:
return [0]*3
if a>=c:
t=f(a%c,b,c,r)
a/=c
return [t[0]+a*sqrtsum(r),t[1]+a*sum(r),t[2]+a*a*sqrtsum(r)+2*a*t[0]]
elif b>=c:
t=f(a,b%c,c,r)
b/=c
return [t[0]+b*sum(r),t[1]+b*(r+1),t[2]+b*b*(r+1)+2*b*t[1]]
else:
if a==0:
return [0]*3
y=(a*r+b)/c
t=f(c,c-b-1,a,y-1)
ans=[y*sum(r)-(t[1]+t[2])/2,y*r-t[1],y*y*r-2*t[0]-t[1]]
return ans
a,c,b,l,r=map(int,raw_input().split())
print f(a,b,c,r)[0]-f(a,b,c,l-1)[0]
典型题目一:SPOJ4717. Grid Points in a Triangle
题意:求满足 y <= ax / b and x <= n的整点个数,x,y,a,b,n都是非负的整数。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL gcd(LL a,LL b)
{
return b? gcd(b,a%b):a;
}
LL dfs(LL n,LL a,LL b)
{
LL t=n*(n+1)/2*(a/b);
a%=b;
if(a==0) return n+1+t;
LL d=a*n/b;
t+=(n+1)*(d+1)+d/a+1;
return t-dfs(d,b,a);
}
int main()
{
LL t,n,a,b,p;
scanf("%lld",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&n,&a,&b);
p=gcd(a,b);
printf("%lld\n",dfs(n,a/p,b/p));
}
return 0;
}
典型题目二:2013年ACM全国邀请赛南京赛区一题:http://icpc.njust.edu.cn/Local/1742
分析:本题比较难,其实方法跟上题差不多,要分析的过程更加复杂些。