c语言复习
第一节 输入输出
友情链接
部分资源图片出自对海贼科技课程的总结
https://www.haizeix.com/
引导
c语言是面向过程的编程范式
一共四种编程范式.面向过程,面向对象,函数式编程,泛型编程
函数是一种映射,
数组是展开的函数,函数是压缩的数组
函数是计算式,数组是计算式.两种方式可以相互转换
深度神经网路可以逼近任何函数
输出函数说明
printf函数
- 头文件:
stdio.h - 原型:
int printf(const char *format, ...); format:格式控制字符串- ...可变参数列表
- 返回值:成功读入的参数个数
输入函数说明
scanf函数
- 头文件:
stdio.h - 原型:
int scanf(const char *format, ...); format:格式控制字符串- ...可变参数列表
- 返回值:成功读入的参数个数
随堂练习:
- 使用
printf输出一个数字的某一位
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: wie.cpp
> Author: ldc
> Mail: litesla
> Created Time: 2018年09月13日 星期四 18时29分42秒
************************************************************************/
#include- 读入一整行字符串
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: clang_test2.c
> Author: hug
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 四 9/13 19:13:09 2018
************************************************************************/
#include
int main() {
char str[100];
scanf("%[^\n]s", str);
int n = printf("%s", str);
printf(" has %d chars\n", n);
return 0;
}
第二节:数学运算
% / * (+ -) (& | ^~)运算符速度从低到高
pow函数说明
pow函数:指数函数
- 头文件:
math.h - 原型:
double pow(double a, double b); - a:底数
- b:指数
- 返回值:返回a的b次幂结果
- 例子:
pow(2,3) = 8
sqrt函数:开平方数
- 头文件:
math.h - 原型:
double sqrt(double x); - x:被开方数
- 返回值:返回值根号x结果
- 例子:
sqrt(16) = 4
ceil向上取整函数
floor向下取整函数
abs()整数绝对值函数
fabs实数绝对值函数
log以e为底对数函数
log10以10为底对数函数
acos函数arccos()
例子:acos(-1) = 3.1415926
随堂练习 mysqrt newton
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: mysqrt.cpp
> Author: ldc
> Mail: litesla
> Created Time: 2018年09月13日 星期四 20时03分55秒
************************************************************************/
#include第三节 流程控制
计算机比人勤奋不是比人聪明
关系运算符
==, >=, >, <,<=,!, !=
条件分支判断语句
if语句
switch语句:
switch内部无法定义局部变量
循环语句
while,do while,for语句
fast_read
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: fast_read.cpp
> Author: hug
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 二 9/18 19:48:33 2018
************************************************************************/
#include 第四节 函数
函数是压缩的数组,数组是展开的函数
函数会增加程序的可读性
K&R风格函数定义
int is_prime(x)
int x;
{
for (int i = 2; i * i <= x; i++) {
if (x % i == 0) return 0;
}
return 1;
}
递归是一种编程技巧不是一种算法
程序调用自身的编程技巧叫做递归
- 明确递归函数的语义
- 设置边界条件
- 实现递归过程和处理过程
- 实现结果返回
规范化问题的思考方式
才能在遇到难题的时候寻找可行解
辗转相除法的证明
变参函数
学技术一定要有敏锐的目光

[外链图片转存失败(img-SAVc6AFa-1565924120766)(/home/tesla/github/learn/1.C语言/c复习/变参函数.png)]
变参函数代码演示
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: is_prime.c
> Author: hug
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 四 9/20 19:52:14 2018
************************************************************************/
#include my_print
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: 3.my_print.c
> Author: hug
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 四 9/20 20:26:47 2018
************************************************************************/
#include 第五节:数组与预处理命令
数组是一片连续的存储空间
元素存在递推关系的化用数组存储比较号
函数是压缩的数组
素数筛
折半查找
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: binary_search.cpp
> Author: ldc
> Mail: litesla
> Created Time: 2018年09月23日 星期日 10时41分54秒
************************************************************************/
#include开脑洞可以弥补经验上的不足
编译器预定义的宏
__DATA__
__TIME__
__LINE__
__func__
__FUNC__
........
max(a, b)宏
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: max.cpp
> Author: ldc
> Mail: litesla
> Created Time: 2018年09月23日 星期日 11时59分24秒
************************************************************************/
#include条件式编译
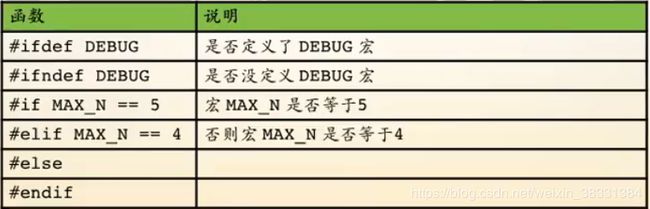
[外链图片转存失败(img-ONrhS24B-1565924120767)(/home/tesla/github/learn/1.C语言/条件编译.png)]
DEBUG演示
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: 4.define.cpp
> Author: hug
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 日 9/23 11:38:10 2018
************************************************************************/
#include 第六节 复杂结构和指针
结构体内部对齐效应
可以通过预编译命令进行调整 (这么做是为了效率)
共用体
一个共用体类型占用空间的大小是他里面存储的最大的数据类型
IP
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: ip.cpp
> Author: ldc
> Mail: litesla
> Created Time: 2018年10月04日 星期四 10时04分05秒
************************************************************************/
#include结构体代码演示
struct test{
short a;//占用两个字节只能放在距离开始位置偶数个距离的地方
char b;//占用一个字节,有个空就能差
int c;//占用四个字节,只能放在距离开始位置4个字节的地方
double e;//....
}
扩充浮点型的表示形式
信息本身没有改变关键是你怎么取看待他
一个既可以存储整形又可以存储浮点型的数组
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: 6.struct&union.cpp
> Author: hug
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: 四 10/ 4 10:17:06 2018
************************************************************************/
#include 变量的地址
指针变量存储的是变量的首地址
指针变量也是变量,也有地址
指针的类型决定了指针在解析运算符下影响了响应的操作
重点概念
- 指针变量也是变量
等价形式交换
*p = a
p + 1 = &p[1]
p->filed = (*p).filed = a.filed
函数指针
int (*add)(int, int);//变量
typedef int (*add)(int,int);//类型
指针的解析
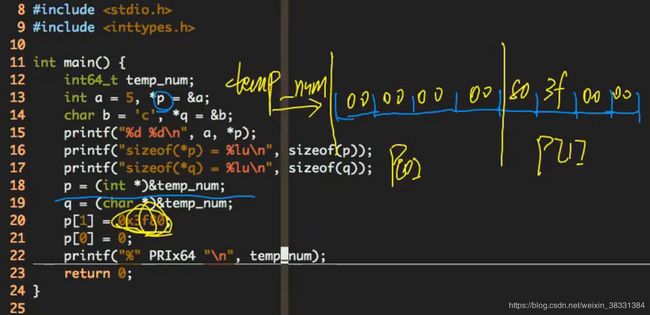
[外链图片转存失败(img-IlFsvrEc-1565924120768)(/home/tesla/github/learn/1.C语言/指针的解析.png)]
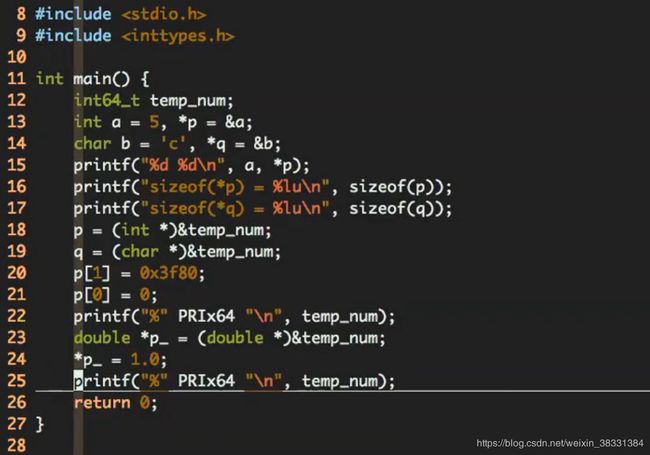
[外链图片转存失败(img-Nxk6vkwt-1565924120768)(/home/tesla/github/learn/1.C语言/指针的解析2.png)]
c函数指针语法检查
c语法在进行语法检查的时候是看函数指针的类型的参数列表,和你调用的类型对不对的上,对于你之前是那个函数他不管
main函数
是有参数的
int main(int argc, char *argv[], char *env[])
argc标记的是有几个argv
env标记结束的方式是最后一个位置指向一个空地址
取得环境变量的作用适应不同的系统或者环境
test测试框架
test.h
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: test.h
> Author: ldc
> Mail:
> Created Time: 2018年10月05日 星期五 15时17分05秒
************************************************************************/
#ifndef _TEST_H
#define _TEST_H
#include test.c
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: test.c
> Author: ldc
> Mail:
> Created Time: 2018年10月05日 星期五 15时16分21秒
************************************************************************/
#include main.c
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: text.cpp
> Author: ldc
> Mail: litesla
> Created Time: 2018年10月04日 星期四 17时52分37秒
************************************************************************/
#include 测试样例结果
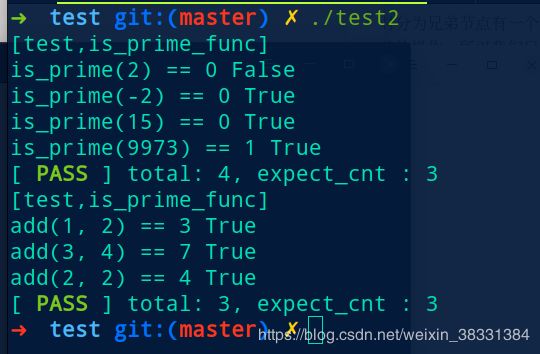
[外链图片转存失败(img-FV8UIOtT-1565924120769)(/home/tesla/github/learn/1.C语言/c复习/test测试结果.png)]

