aop实现原理 - JDK动态代理(实例+源码解析)
动态代理:
jdk代理-基于接口代理
- 通过
类:java.lang.reflect.Proxy生成动态代理类 - 实现
接口:InvocationHandler - 只能基于接口进行动态代理
代码实现:
1、创建接口
public interface Subject {
void request();
void hello();
}
2、创建目标对象
/**
* @author :panda
* 目标对象
*/
public class RealSubject implements Subject {
public void request() {
System.out.println("real subject execute request..");
}
public void hello() {
System.out.println("real subject execute hello..");
}
}
3、创建代理对象
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* aop - aspect
* 要织入的切面
*/
public class JdkProxySubject implements InvocationHandler {
private RealSubject realSubject;
//强引用目标对象
public JdkProxySubject(RealSubject realSubject) {
this.realSubject = realSubject;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("before。。");
Object result = null;
try {
**//通过反射调用目标对象的方法 - 动态反射方法**
result = method.invoke(realSubject,args);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("ex:" + e.getMessage());
throw e;
} finally {
System.out.println("after..");
}
return result;
}
}
4、客户端调用
/**
* 客户端对象
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* //客户端跟代理对象打交道- 静态代理
Subject subject = new Proxy(new RealSubject());
subject.request();
subject.hello();*/
//动态代理
Subject subject = (Subject) java.lang.reflect.Proxy.newProxyInstance(Client.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Subject.class}, new JdkProxySubject(new RealSubject()));
subject.request();
subject.hello();
}
}
源码解析:
- Proxy.newProxyInstance 创建代理对象
- getProxyClass0、ProxyClassFactory、ProxyGenerator
- newInstance 通过反射new一个代理实例
1、通过Proxy.newProxyInstance 创建代理对象
![]()
2、点进去康康
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
Objects.requireNonNull(h);
final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone();
final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs);
}
/*
* Look up or generate the designated proxy class.
* 查找或者生成指定的代理类
*/
Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
3、继续点进去康康
private static Class<?> getProxyClass0(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>... interfaces) {
if (interfaces.length > 65535) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("interface limit exceeded");
}
// If the proxy class defined by the given loader implementing
// the given interfaces exists, this will simply return the cached copy;
// otherwise, it will create the proxy class via the ProxyClassFactory
//如果缓存里已经有代理对象,则返回缓存里的,否则,通过ProxyClassFactory创建一个
return proxyClassCache.get(loader, interfaces);
}
4、康康缓存
/**
* a cache of proxy classes
*/
private static final WeakCache<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>>
proxyClassCache = new WeakCache<>(new KeyFactory(), new ProxyClassFactory());
5、康康ProxyClassFactory是怎么创建代理类的
可以看到是通过ProxyGenerator类的generateProxyClass()方法为我们创建代理对象的字节码
/*
* Generate the specified proxy class.
*/
byte[] proxyClassFile = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass(
proxyName, interfaces, accessFlags);
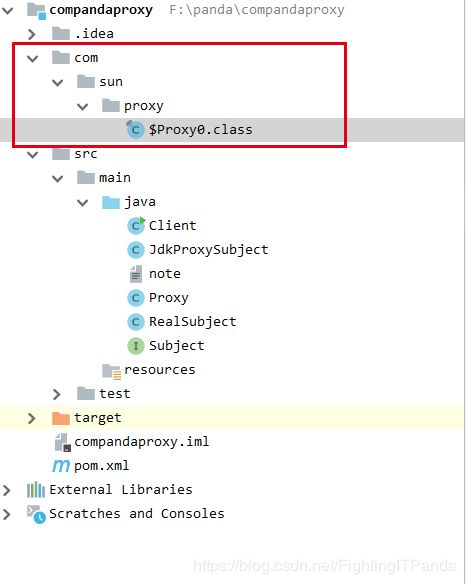
6、我们打开生成的字节码文件康康
设置系统属性,保存生成的代理文件为true,
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.getProperties().put("sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles","true");
/* //客户端跟代理对象打交道- 静态代理
Subject subject = new Proxy(new RealSubject());
subject.request();
subject.hello();*/
//动态代理
Subject subject = (Subject) java.lang.reflect.Proxy.newProxyInstance(Client.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Subject.class}, new JdkProxySubject(new RealSubject()));
subject.request();
subject.hello();
}
可以看到代理对象实现了Subject接口,
为我们动态创建了hello、request方法,
注意方法体,super.h.invoke(this, m4, (Object[])null);是通过InvocationHandler的invoke方法,通过反射去动态调用目标类的方法,这也是为什么jdk动态代理需要实现InvocationHandler接口的原因
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package com.sun.proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException;
public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements Subject {
private static Method m1;
private static Method m4;
private static Method m2;
private static Method m3;
private static Method m0;
public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler var1) throws {
super(var1);
}
public final boolean equals(Object var1) throws {
try {
return (Boolean)super.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[]{var1});
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) {
throw var3;
} catch (Throwable var4) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4);
}
}
public final void hello() throws {
try {
super.h.invoke(this, m4, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
public final String toString() throws {
try {
return (String)super.h.invoke(this, m2, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
public final void request() throws {
try {
super.h.invoke(this, m3, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
public final int hashCode() throws {
try {
return (Integer)super.h.invoke(this, m0, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
static {
try {
m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", Class.forName("java.lang.Object"));
m4 = Class.forName("Subject").getMethod("hello");
m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString");
m3 = Class.forName("Subject").getMethod("request");
m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode");
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var2) {
throw new NoSuchMethodError(var2.getMessage());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) {
throw new NoClassDefFoundError(var3.getMessage());
}
}
}