面试题
(1)ArrayList和CopyOnWriteArrayList的增删改查实现原理?
(2)为什么说ArrayList查询快而增删慢?
(3)弱一致性的迭代器原理是怎么样的?
(4)CopyOnWriteArrayList为什么并发安全且性能比Vector好?
(1)ArrayList和CopyOnWriteArrayList的增删改查实现原理?
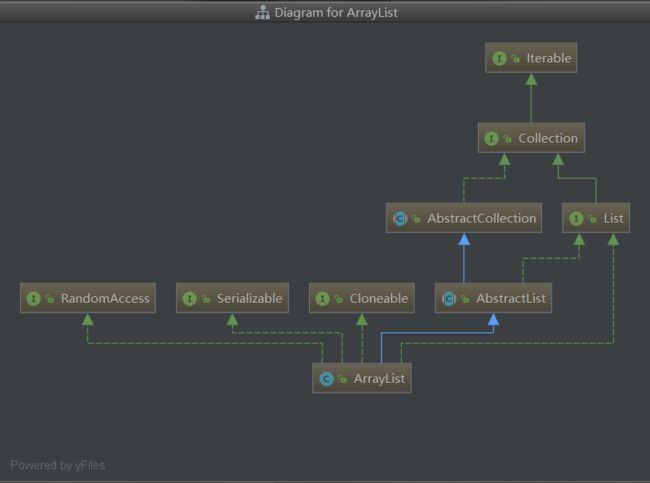
ArrayList类图
CopyOnWriteArrayList类图
1.List接口
首先我们来看List接口,如上因为ArrayList和CopyOnWriteArrayList都是实现了List接口,所有查看其相应的方法即可。
2.ArrayList的几个重点
1、底层是数组,初始化大小为10
2、插入时会判断数组容量是否足够,不够的化会进行扩容
3、所谓扩容就是新建一个数组,然后将老的数据里面的元素复制到新的数组里面
4、移除元素的时候也涉及到数组中元素的移动,删除指定index位置的元素,然后将index+1至数组最后一个元素往前移动一格
2.2增删改查
1.增
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return true (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! //——进行数组扩容,不够就扩容
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index); //——检查是否越界
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! //——进行数组容量判断,不够就扩容
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, //——将index至数据最后一个元素整体往后移动一格,然后插入新的元素
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
2.删
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index); //——判断是否越界
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0) //——若该元素不是最后一个元素的话,将index+1至数组最后一个元素整体向前移动一格
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If the list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* i such that
* (o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))
* (if such an element exists). Returns true if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return true if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/*
* Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not
* return the value removed.
*/
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
3.改
public E set(int index, E e) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
E oldValue = ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index);
ArrayList.this.elementData[offset + index] = e; //——将数组对应的index的元素进行替换
return oldValue;
}
4.查
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index); //——进行数组越界判断
checkForComodification();
return ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index); //——获取数组对应的index元素
}
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
总结
(2)为什么说ArrayList查询快而增删慢?
以上部分就是ArrayList的增删改查原理,以此就可以解决我们的第二个问题了。
ArrayList底层是数组,所以查询的时候直接根据索引可以很快地找到对应地元素,改也是如此,找到index对应元素进行替换。而增加和删除就涉及到数组元素地移动,所以会比较慢。
CopyOnWriteArrayList几个关键点
1、实现了List接口
2、内部持有一个ReentrantLock lock=new ReentrantLock()
3、底层是用volatile transient声明地数组 array
4、读写分离,写时复制出一个新地数组,完成插入、修改或者移除操作后将新数组赋值给array
增删改查
1.增
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock(); //——获得锁?
try {
Object[] elements = getArray();
int len = elements.length;
Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1); //——复制一个新的数组
newElements[len] = e; //——插入新的值
setArray(newElements); //——将新的数组指向原来的引用
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock(); //——释放锁?
}
}
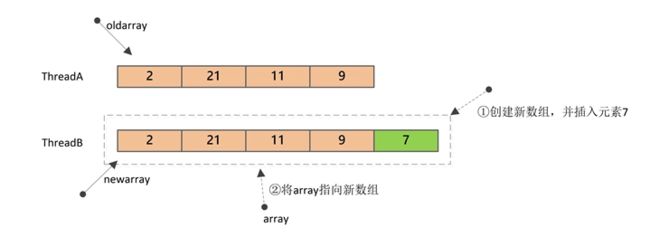
add方法首先会进行加锁,保证只有一个线程能进行修改;然后会创建一个新数组(大小为n+1),并将原数组的值复制到新数组,新元素插入到新数组的最后;最后,将字段array指向新数组。
上图中,ThreadB对Array的修改由于是在新数组上进行的,所以并不会对ThreadA的读操作产生影响。
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock(); //——获取锁?
try {
Object[] elements = getArray();
int len = elements.length;
if (index > len || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+
", Size: "+len);
Object[] newElements;
int numMoved = len - index;
if (numMoved == 0)
newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1);
else {
newElements = new Object[len + 1];
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, newElements, 0, index);
System.arraycopy(elements, index, newElements, index + 1,
numMoved);
}
newElements[index] = element;
setArray(newElements);
} finally {
lock.unlock(); //——释放锁?
}
}
如上代码可知:新数组的大小是原来数组大小增加1,所以CopyOnWriteArrayList是无界list。
2.删
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices). Returns the element that was removed from the list.
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock(); //——获得锁?
try {
Object[] elements = getArray();
int len = elements.length;
E oldValue = get(elements, index);
int numMoved = len - index - 1;
if (numMoved == 0)
setArray(Arrays.copyOf(elements, len - 1)); //——如果删除的元素是最后一个,直接复制该元素前的所有元素到新的数组
else {
Object[] newElements = new Object[len - 1]; //——创建新的数组
//——将index+1至最后一个元素像前移动一格
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, newElements, 0, index);
System.arraycopy(elements, index + 1, newElements, index,
numMoved);
setArray(newElements);
}
return oldValue;
} finally {
lock.unlock(); //——释放锁?
}
}
3.改
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the
* specified element.
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock(); //——获取独占锁?
try {
Object[] elements = getArray();
E oldValue = get(elements, index);
if (oldValue != element) {
int len = elements.length;
Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len); //——创建一个新的数组
newElements[index] = element; //——替换元素
setArray(newElements); //——将新数组指向原来的引用
} else {
// Not quite a no-op; ensures volatile write semantics
setArray(elements);
}
return oldValue;
} finally {
lock.unlock(); //——释放锁?
}
}
4.查
private E get(Object[] a, int index) {
return (E) a[index];
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
return get(getArray(), index);
}
final Object[] getArray() {
return array;
}
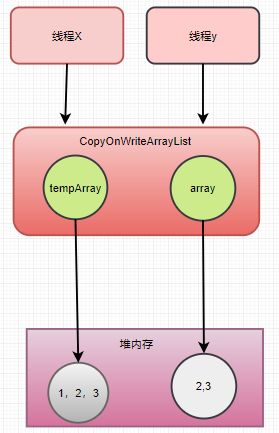
如上代码,当线程x调用get方法获取指定位置元素时,分两步走,首先获得array数组(步骤A),然后通过下标访问指定位置的元素(步骤B),整个过程没用加锁。
由于步骤A和步骤B没用加锁,这就可能导致在线程X执行完步骤A后执行步骤B前,另外一个线程Y进行了remove操作,假设删除元素1,这时候线程开始执行步骤B,
步骤B操作的数组是线程Y删除元素之前的数组,所以虽然线程Y已经删除了index元素,但是线程X的步骤B还是会返回index处的元素,这其实就是写时复制策略产生的弱一致性问题。
总结
从以上的增删改查中我们可以发现,增删改都需要获得锁,并且锁只有一把,而读操作不需要获得锁,支持并发读。
为什么增删改中都需要创建一个新的数组,操作完成之后再赋值给原来的引用?
这是为了保证get的时候,都能获取到元素,如果在增删改的过程直接修改原来的数组,可能会造成执行读操作获取不到数据。
(3)弱一致性的迭代器原理是怎么样的?
public Iteratoriterator() { return new COWIterator (getArray(), 0); }
public Spliteratorspliterator() { return Spliterators.spliterator (getArray(), Spliterator.IMMUTABLE | Spliterator.ORDERED); } static final class COWIterator implements ListIterator { /** Snapshot of the array */ private final Object[] snapshot; //——array的快照版本 /** Index of element to be returned by subsequent call to next. */ private int cursor; //——数组下标 private COWIterator(Object[] elements, int initialCursor) { //——构造函数 cursor = initialCursor; snapshot = elements; } public boolean hasNext() { //——是否遍历结束 return cursor < snapshot.length; } public boolean hasPrevious() { return cursor > 0; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E next() { //——获取元素 if (! hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return (E) snapshot[cursor++]; }
CopyOnWriteArrayList对元素进行迭代时,仅仅返回一个当前内部数组的快照,也就是说,如果此时有其它线程正在修改元素,并不会在迭代中反映出来,因为修改都是在新数组中进行的。
可以看到,上述iterator方法返回一个迭代器对象——
COWIterator,COWIterator的迭代是在旧数组上进行的,当创建迭代器的那一刻就确定了,所以迭代过程中不会抛出并发修改异常——ConcurrentModificationException。另外,迭代器对象也不支持修改方法,全部会抛出
UnsupportedOperationException异常。这也说明获取迭代器元素时,其它线程对list进行增删改不可见,因为他们操作的是两个不同的数组,这就是弱一致性。
下面通过一个例子来演示多线程下迭代器的弱一致性的效果
public class copyList {
private static volatile CopyOnWriteArrayListarrayList=new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
arrayList.add("hello");
arrayList.add("alibaba");
arrayList.add("to");
arrayList.add("hangzhou");
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
arrayList.set(1, "baba"); //——修改元素
arrayList.remove(1); //——删除元素
arrayList.remove(2);
});
Iterator iterator = arrayList.iterator(); //——保证在修改线程启动前获取迭代器
thread.start(); //——启动线程
thread.join(); //——等待子线程执行完毕
while (iterator.hasNext()){ //——迭代元素
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
输出结果
hello
alibaba
to
hangzhou
如上代码中,main函数首先初始化了arrayList,然后再启动线程前获取到了arrayList迭代器。子线程thread启动后首先修改了arrayList的第一个元素的值,然后删除了arrayList对应下标的元素。
主线程在子线程执行完毕后使用获取的迭代器遍历数组元素,从结果可知,子线程的操作一个都没有生效,这就是迭代器的弱一致性的体现。
需要注意的是,获取迭代器的操作需要在子线程操作之前进行。
(4)CopyOnWriteArrayList为什么并发安全且性能比Vector好?
我们知道Vector是增删改查方法都加了synchronized,保证同步,但是每个方法执行的时候都要去获取锁,性能就会大大降低,
而CopyOnWriteArrayList只是在增删改上加ReentrantLock独占锁,但是读操作不加锁,支持并发读,CopyOnWriteArrayList支持读多写少的情况。
总结
CopyOnWriteArrayList的思想和实现整体上还是比较简单,它适用于处理“读多写少”的并发场景。通过上述对CopyOnWriteArrayList的分析,读者也应该可以发现该类存在的一些问题:
1. 内存的使用
由于CopyOnWriteArrayList使用了“写时复制”,所以在进行写操作的时候,内存里会同时存在两个array数组,如果数组内存占用的太大,那么可能会造成频繁GC,所以CopyOnWriteArrayList并不适合大数据量的场景。2. 数据一致性
CopyOnWriteArrayList只能保证数据的最终一致性,不能保证数据的实时一致性——读操作读到的数据只是一份快照。所以如果希望写入的数据可以立刻被读到,那CopyOnWriteArrayList并不适合。
参考书籍
Java并发编程之美
参考链接
https://www.jianshu.com/p/c046b7f31228