C语言解决棋盘覆盖问题
棋盘覆盖问题是典型的利用分治法解决问题
把大问题分解成为相同性质的子问题
分治的技巧在于如何划分棋盘,使划分后的子棋盘的大小相同,并且每个子棋盘均包含一个特殊方格,从而将原问题分解为规模较小的棋盘覆盖问题。k>0时,可将2^k×2^k的棋盘划分为4个2^(k-1)×2^(k-1)的子棋盘,如图4.11(a)所示。这样划分后,由于原棋盘只有一个特殊方格,所以,这4个子棋盘中只有一个子棋盘包含该特殊方格,其余3个子棋盘中没有特殊方格。为了将这3个没有特殊方格的子棋盘转化为特殊棋盘,以便采用递归方法求解,可以用一个L型骨牌覆盖这3个较小棋盘的会合处
void chessBoard(int row, int column, int x, int y, int siz) {
// 递归出口
if(siz == 1) {
return;
}
// 对半划分成2^(siz - 1) * 2^(siz - 1)的棋盘
int s = siz / 2;
// L型牌编号自增
int t = ++number;
// 中间点,以此判别(x,y)在哪个子棋盘中
int centerRow = row + s;
int centerColumn = column + s;
// 黑色方格在左上子棋盘
if(x < centerRow && y < centerColumn) {
chessBoard(row, column, x, y, s);
} else {
// 不在则填充左上子棋盘的右下角
chess[centerRow - 1][centerColumn - 1] = t;
// 然后覆盖其他格子,注意这时(x,y)要看做已填充位置
chessBoard(row, column, centerRow - 1, centerColumn - 1, s);
}
// 黑色方格在右上子棋盘
if(x < centerRow && y >= centerColumn) {
chessBoard(row, centerColumn, x, y, s);
} else {
// 不在则填充右上子棋盘的左下角
chess[centerRow - 1][centerColumn] = t;
// 然后覆盖其他格子,注意这时(x,y)要看做已填充位置
chessBoard(row, centerColumn, centerRow - 1, centerColumn, s);
}
// 黑色方格在左下子棋盘
if(x >= centerRow && y < centerColumn) {
chessBoard(centerRow, column, x, y, s);
} else {
// 不在则填充左下子棋盘的右上角
chess[centerRow][centerColumn - 1] = t;
// 然后覆盖其他格子,注意这时(x,y)要看做已填充位置
chessBoard(centerRow, column, centerRow, centerColumn - 1, s);
}
// 黑色方格在右下子棋盘
if(x >= centerRow && y >= centerColumn) {
chessBoard(centerRow, centerColumn, x, y, s);
} else {
// 不在则填充右下子棋盘的左上角
chess[centerRow][centerColumn] = t;
// 然后覆盖其他格子,注意这时(x,y)要看做已填充位置
chessBoard(centerRow, centerColumn, centerRow, centerColumn, s);
}
}
解决此递归方程可得T( k )= O ( 4^k )
由于覆盖一个2^k*2^k棋盘所需的L型骨牌个数为( 4^k-1 )/ 3.
这个算法ChessBoard是一个在渐进意义下最优的算法。
代码实现
棋盘覆盖
#include
const int maxNum = 1 << 10;
// 棋盘
int chess[maxNum][maxNum];
// L型牌编号
int number;
void chessBoard(int row, int column, int x, int y, int siz) {
// 递归出口
if(siz == 1) {
return;
}
// 对半划分成2^(siz - 1) * 2^(siz - 1)的棋盘
int s = siz / 2;
// L型牌编号自增
int t = ++number;
// 中间点,以此判别(x,y)在哪个子棋盘中
int centerRow = row + s;
int centerColumn = column + s;
// 黑色方格在左上子棋盘
if(x < centerRow && y < centerColumn) {
chessBoard(row, column, x, y, s);
} else {
// 不在则填充左上子棋盘的右下角
chess[centerRow - 1][centerColumn - 1] = t;
// 然后覆盖其他格子,注意这时(x,y)要看做已填充位置
chessBoard(row, column, centerRow - 1, centerColumn - 1, s);
}
// 黑色方格在右上子棋盘
if(x < centerRow && y >= centerColumn) {
chessBoard(row, centerColumn, x, y, s);
} else {
// 不在则填充右上子棋盘的左下角
chess[centerRow - 1][centerColumn] = t;
// 然后覆盖其他格子,注意这时(x,y)要看做已填充位置
chessBoard(row, centerColumn, centerRow - 1, centerColumn, s);
}
// 黑色方格在左下子棋盘
if(x >= centerRow && y < centerColumn) {
chessBoard(centerRow, column, x, y, s);
} else {
// 不在则填充左下子棋盘的右上角
chess[centerRow][centerColumn - 1] = t;
// 然后覆盖其他格子,注意这时(x,y)要看做已填充位置
chessBoard(centerRow, column, centerRow, centerColumn - 1, s);
}
// 黑色方格在右下子棋盘
if(x >= centerRow && y >= centerColumn) {
chessBoard(centerRow, centerColumn, x, y, s);
} else {
// 不在则填充右下子棋盘的左上角
chess[centerRow][centerColumn] = t;
// 然后覆盖其他格子,注意这时(x,y)要看做已填充位置
chessBoard(centerRow, centerColumn, centerRow, centerColumn, s);
}
}
int main() {
// 大小,黑色方格位置
int siz, x, y;
while(true) {
printf("(x,y)从(0,0)开始,输入数据为0 0 0即结束程序。" );
printf( "请输入棋盘大小");
scanf_s("%d",&siz);
printf( "请输入黑色方格位置(x,y):");
scanf_s("%d",&x);
scanf_s("%d",&y);
// 退出条件
if(siz == 0) {
break;
}
// 涂黑(x,y),初始化L型牌编号
chess[x][y] = number = 1;
// 分治法填满棋盘
chessBoard(0, 0, x, y, siz);
// 输出该棋盘
for(int i = 0; i < siz; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < siz; j++) {
printf("%d\t" ,chess[i][j] );
}
printf("\n\n\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
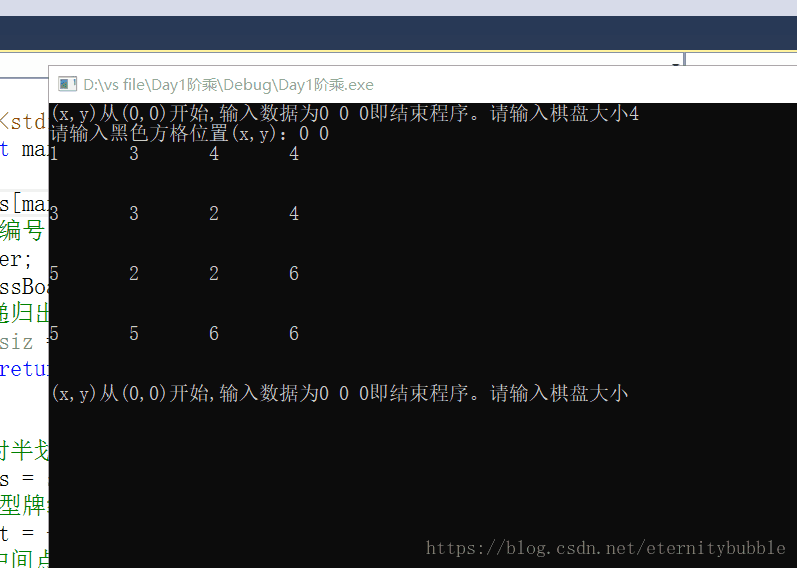
根据运行结果可以看出L型骨牌的分布情况