最大堆,最小堆插入/删除以及最大堆的排序
先说一下最大堆如何排序:转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/luchen927/archive/2012/03/08/2381446.html
最大堆和最小堆在算法中也有运用。比如用最大堆求N个数中前K个最小的数,用最小堆求N个数中前K个最大的数。你懂了吗????不懂自己搜吧!
开始正文:
前一阵子一直在写排序的系列文章,最近因为一些事情耽搁了几天,也穿插了几篇其他类别的随笔。今天还是回到排序上面来,善始善终,呵呵。
今天要介绍的也是一种效率很高的排序——堆排序
思想
堆排序,顾名思义,就是基于堆。因此先来介绍一下堆的概念。
堆分为最大堆和最小堆,其实就是完全二叉树。最大堆要求节点的元素都要大于其孩子,最小堆要求节点元素都小于其左右孩子,两者对左右孩子的大小关系不做任何要求,其实很好理解。有了上面的定义,我们可以得知,处于最大堆的根节点的元素一定是这个堆中的最大值。其实我们的堆排序算法就是抓住了堆的这一特点,每次都取堆顶的元素,将其放在序列最后面,然后将剩余的元素重新调整为最大堆,依次类推,最终得到排序的序列。
或者说,堆排序将所有的待排序数据分为两部分,无序区和有序区。无序区也就是前面的最大堆数据,有序区是每次将堆顶元素放到最后排列而成的序列。每一次堆排序过程都是有序区元素个数增加,无序区元素个数减少的过程。当无序区元素个数为1时,堆排序就完成了。
本质上讲,堆排序是一种选择排序,每次都选择堆中最大的元素进行排序。只不过堆排序选择元素的方法更为先进,时间复杂度更低,效率更高。
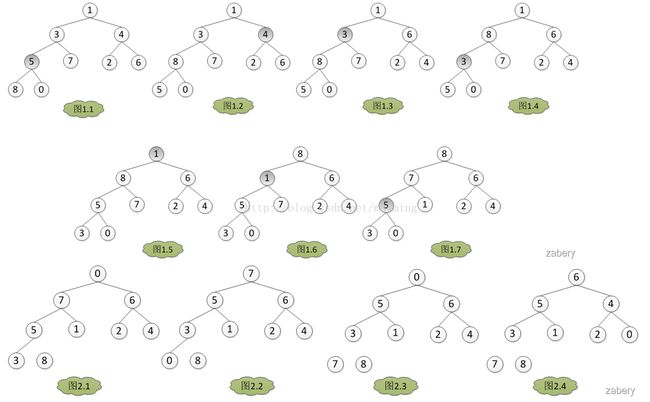
图例说明一下:(图片来自http://www.cnblogs.com/zabery/archive/2011/07/26/2117103.html)
具体步骤如下:
1 首先从第一个非叶子节点开始,比较当前节点和其孩子节点,将最大的元素放在当前节点,交换当前节点和最大节点元素。
2 将当前元素前面所有的元素都进行1的过程,这样就生成了最大堆
3 将堆顶元素和最后一个元素交换,列表长度减1。由此无序区减1,有序区加1
4 剩余元素重新调整建堆
5 继续3和4,直到所有元素都完成排序
。再来描述一下最大堆和最小堆的插入,删除等,转载自http://www.java3z.com/cwbwebhome/article/article1/1362.html?id=4745
堆有最大堆和最小堆之分,最大堆就是每个节点的值都>=其左右孩子(如果有的话)值的完全二叉树。最小堆便是每个节点的值都<=其左右孩子值的完全二叉树。
设有n个元素的序列{k1,k2,...,kn},当且仅当满足下列关系时,称之为堆。
堆的三种基本操作(以下以最大堆为例):
⑴最大堆的插入
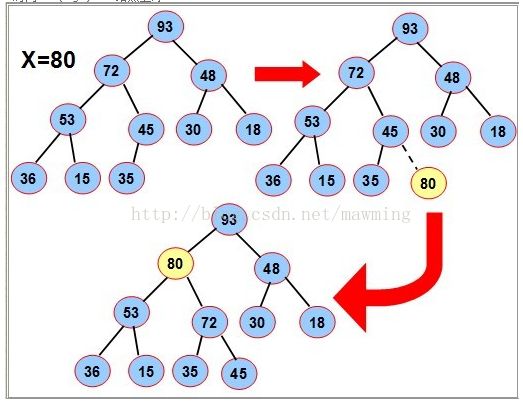
由于需要维持完全二叉树的形态,需要先将要插入的结点x放在最底层的最右边,插入后满 足完全二叉树的特点;
然后把x依次向上调整到合适位置满足堆的性质,例如下图中插入80,先将80放在最后,然后两次上浮到合适位置.
时间:O(logn)。 “结点上浮”
程序实现:
//向最大堆中插入元素, heap:存放堆元素的数组
public static void insert(List heap, int value) {
//在数组的尾部添加
if(heap.size()==0)
heap.add(0);//数组下标为0的位置不放元素
heap.add(value);
//开始上升操作
// heapUp2(heap, heap.size() - 1);
heapUp(heap, heap.size() - 1);
}
//上升,让插入的数和父节点的数值比较,当大于父节点的时候就和父节点的值相交换
public static void heapUp(List heap, int index) {
//注意由于数值是从下标为1开始,当index = 1的时候,已经是根节点了
if (index > 1) {
//求出父亲的节点
int parent = index / 2;
//获取相应位置的数值
int parentValue = (Integer) heap.get(parent);
int indexValue = (Integer) heap.get(index);
//如果父亲节点比index的数值小,就交换二者的数值
if (parentValue < indexValue) {
//交换数值
swap(heap, parent, index);
//递归调用
heapUp(heap, parent);
}
}
}
⑵删除
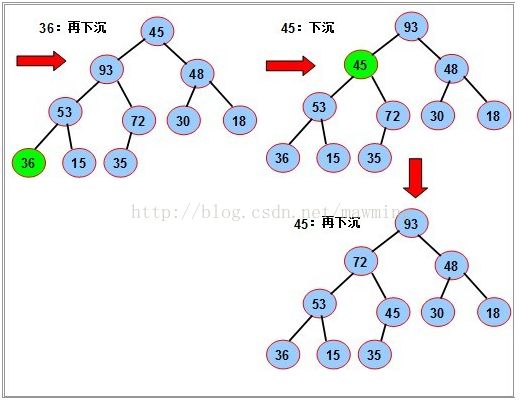
操作原理是:当删除节点的数值时,原来的位置就会出现一个孔,填充这个孔的方法就是,
把最后的叶子的值赋给该孔并下调到合适位置,最后把该叶子删除。
如图中要删除72,先用堆中最后一个元素来35替换72,再将35下沉到合适位置,最后将叶子节点删除。
“结点下沉”
程序:
/**
* 删除堆中位置是index处的节点
* 操作原理是:当删除节点的数值时,原来的位置就会出现一个孔
* 填充这个孔的方法就是,把最后的叶子的值赋给该孔,最后把该叶子删除
* @param heap
*/
public static void delete(List heap,int index) {
//把最后的一个叶子的数值赋值给index位置
heap.set(index, heap.get(heap.size() - 1));
//下沉操作
//heapDown2(heap, index);
heapDown(heap, index);
//把最后一个位置的数字删除
heap.remove(heap.size() - 1);
}
/**
* 递归实现
* 删除堆中一个数据的时候,根据堆的性质,应该把相应的位置下移,才能保持住堆性质不变
* @param heap 保持堆元素的数组
* @param index 被删除的那个节点的位置
*/
public static void heapDown(List heap, int index) {
//因为第一个位置存储的是空值,不在考虑之内
int n = heap.size() - 2;
//记录最大的那个儿子节点的位置
int child = -1;
//2*index>n说明该节点没有左右儿子节点了,那么就返回
if (2 * index > n) {
return;
} //如果左右儿子都存在
else if (2 * index < n) {
//定义左儿子节点
child = 2 * index;
//如果左儿子小于右儿子的数值,取右儿子的下标
if ((Integer) heap.get(child) < (Integer) heap.get(child + 1)) {
child++;
}
}//如果只有一个儿子(左儿子节点)
else if (2 * index == n) {
child = 2 * index;
}
if ((Integer) heap.get(child) > (Integer) heap.get(index)) {
//交换堆中的child,和index位置的值
swap(heap, child, index);
//完成交换后递归调用,继续下降
heapDown(heap, child);
}
}
⑶初始化
方法1:插入法:
从空堆开始,依次插入每一个结点,直到所有的结点全部插入到堆为止。
时间:O(n*log(n))
方法2:调整法:
序列对应一个完全二叉树;从最后一个分支结点(n div 2)开始,到根(1)为止,依次对每个分支结点进行调整(下沉),
以便形成以每个分支结点为根的堆,当最后对树根结点进行调整后,整个树就变成了一个堆。
时间:O(n)
对如图的序列,要使其成为堆,我们从最后一个分支结点(10/2),其值为72开始,依次对每个分支节点53,18,36 45进行调整(下沉).
程序:
/*根据树的性质建堆,树节点前一半一定是分支节点,即有孩子的,所以我们从这里开始调整出初始堆*/
public static void adjust(List heap){
for (int i = heap.size() / 2; i > 0; i--)
adjust(heap,i, heap.size()-1);
System.out.println("=================================================");
System.out.println("调整后的初始堆:");
print(heap);
}
/**
* 调整堆,使其满足堆得定义
* @param i
* @param n
*/
public static void adjust(List heap,int i, int n) {
int child;
for (; i <= n / 2; ) {
child = i * 2;
if(child+1<=n&&heap.get(child) (4)最大堆排序
//对一个最大堆heap排序
public static void heapSort(List heap) {
for (int i = heap.size()-1; i > 0; i--) {
/*把根节点跟最后一个元素交换位置,调整剩下的n-1个节点,即可排好序*/
swap(heap,1, i);
adjust(heap,1, i - 1);
}
}
(5)完整的代码
import java.util.*;
/**
*实现的最大堆的插入和删除操作
* @author Arthur
*/
public class Heap {
/**
* 删除堆中位置是index处的值
* 操作原理是:当删除节点的数值时,原来的位置就会出现一个孔
* 填充这个孔的方法就是,把最后的叶子的值赋给该孔,最后把该叶子删除
* @param heap 一个最大堆
*/
public static void delete(List heap,int index) {
//把最后的一个叶子的数值赋值给index位置
heap.set(index, heap.get(heap.size() - 1));
//下沉操作
//heapDown2(heap, index);
heapDown(heap, index); //节点下沉
//把最后一个位置的数字删除
heap.remove(heap.size() - 1);
}
/**
* 节点下沉递归实现
* 删除一个堆中一个数据的时候,根据堆的性质,应该把相应的位置下移,才能保持住堆性质不变
* @param heap 保持最大堆元素的数组
* @param index 被删除的那个节点的位置
*/
public static void heapDown(List heap, int index) {
//因为第一个位置存储的是空值,不在考虑之内
int n = heap.size() - 2;
//记录最大的那个儿子节点的位置
int child = -1;
//2*index>n说明该节点没有左右儿子节点了,那么就返回
if (2 * index > n) {
return;
} //如果左右儿子都存在
else if (2 * index < n) {
//定义左儿子节点
child = 2 * index;
//如果左儿子小于右儿子的数值,取右儿子的下标
if ((Integer) heap.get(child) < (Integer) heap.get(child + 1)) {
child++;
}
}//如果只有一个儿子(左儿子节点)
else if (2 * index == n) {
child = 2 * index;
}
if ((Integer) heap.get(child) > (Integer) heap.get(index)) {
//交换堆中的child,和index位置的值
swap(heap, child, index);
//完成交换后递归调用,继续下降
heapDown(heap, child);
}
}
//非递归实现
public static void heapDown2(List heap, int index) {
int child = 0;//存储左儿子的位置
int temp = (Integer) heap.get(index);
int n = heap.size() - 2;
//如果有儿子的话
for (; 2 * index <= n; index = child) {
//获取左儿子的位置
child = 2 * index;
//如果只有左儿子
if (child == n) {
child = 2 * index;
} //如果右儿子比左儿子的数值大
else if ((Integer) heap.get(child) < (Integer) heap.get(child + 1)) {
child++;
}
//如果数值最大的儿子比temp的值大
if ((Integer) heap.get(child) >temp) {
//交换堆中的child,和index位置的值
swap(heap, child, index);
} else {
break;
}
}
}
//打印链表
public static void print(List list) {
for (int i = 1; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
//把堆中的a,b位置的值互换
public static void swap(List heap, int a, int b) {
//临时存储child位置的值
int temp = (Integer) heap.get(a);
//把index的值赋给child的位置
heap.set(a, heap.get(b));
//把原来的child位置的数值赋值给index位置
heap.set(b, temp);
}
//向最大堆中插入元素
public static void insert(List heap, int value) {
//在数组的尾部添加要插入的元素
if(heap.size()==0)
heap.add(0);//数组下标为0的位置不放元素
heap.add(value);
//开始上升操作
// heapUp2(heap, heap.size() - 1);
heapUp(heap, heap.size() - 1);
}
//节点上浮,让插入的数和父节点的数值比较,当大于父节点的时候就和节点的值相交换
public static void heapUp(List heap, int index) {
//注意由于数值是从小标为一开始,当index = 1的时候,已经是根节点了
if (index > 1) {
//保存父亲的节点
int parent = index / 2;
//获取相应位置的数值
int parentValue = (Integer) heap.get(parent);
int indexValue = (Integer) heap.get(index);
//如果父亲节点比index的数值小,就交换二者的数值
if (parentValue < indexValue) {
//交换数值
swap(heap, parent, index);
//递归调用
heapUp(heap, parent);
}
}
}
//非递归实现
public static void heapUp2(List heap, int index) {
int parent = 0;
for (; index > 1; index /= 2) {
//获取index的父节点的下标
parent = index / 2;
//获得父节点的值
int parentValue = (Integer) heap.get(parent);
//获得index位置的值
int indexValue = (Integer) heap.get(index);
//如果小于就交换
if (parentValue < indexValue) {
swap(heap, parent, index);
}
}
}
/*根据树的性质建堆,树节点前一半一定是分支节点,即有孩子的,所以我们从这里开始调整出初始堆*/
public static void adjust(List heap){
for (int i = heap.size() / 2; i > 0; i--)
adjust(heap,i, heap.size()-1);
System.out.println("=================================================");
System.out.println("调整后的初始堆:");
print(heap);
}
/**
* 调整堆,使其满足堆得定义
* @param i
* @param n
*/
public static void adjust(List heap,int i, int n) {
int child;
for (; i <= n / 2; ) {
child = i * 2;
if(child+1<=n&&heap.get(child) heap) {
for (int i = heap.size()-1; i > 0; i--) {
/*把根节点跟最后一个元素交换位置,调整剩下的n-1个节点,即可排好序*/
swap(heap,1, i);
adjust(heap,1, i - 1);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
List array = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(null,
1, 2, 5, 10, 3, 7, 11, 15, 17, 20, 9, 15, 8, 16));
adjust(array);//调整使array成为最大堆
delete(array,8);//堆中删除下标是8的元素
System.out.println("删除后");
print(array);
insert(array, 99);//堆中插入
print(array);
heapSort(array);//排序
System.out.println("将堆排序后:");
print(array);
System.out.println("-------------------------");
List array1=new ArrayList();
insert(array1,0);
insert(array1, 1);insert(array1, 2);insert(array1, 5);
insert(array1, 10);insert(array1, 3);insert(array1, 7);
insert(array1, 11);insert(array1, 15); insert(array1, 17);
insert(array1, 20);insert(array1, 9);
insert(array1, 15);insert(array1, 8);insert(array1, 16);
print(array1);
System.out.println("==============================");
array=new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(null,45,36,18,53,72,30,48,93,15,35));
adjust(array);
insert(array, 80);//堆中插入
print(array);
delete(array,2);//堆中删除80的元素
print(array);
delete(array,2);//堆中删除72的元素
print(array);
}
}
程序运行:
D:\java>java Heap
=================================================
调整后的初始堆:
20 17 16 15 9 15 11 1 10 3 2 7 8 5
删除后
20 17 16 15 9 15 11 5 10 3 2 7 8
99 17 20 15 9 15 16 5 10 3 2 7 8 11
将堆排序后:
2 3 5 7 8 9 10 11 15 15 16 17 20 99
-------------------------
20 17 16 10 15 9 15 0 5 2 11 1 7 3 8
==============================
=================================================
调整后的初始堆:
93 72 48 53 45 30 18 36 15 35
93 80 48 53 72 30 18 36 15 35 45
93 72 48 53 45 30 18 36 15 35
93 53 48 36 45 30 18 35 15