找出无向图中所有的环的算法
本文给出了一个找到无向图中所有的环的递归算法,该算法是基于DFS(深度优先搜索)的,大概的思路是:在深度优先搜索无向图的过程中,当遇到起始点的时候,会认定为出现环(在本文中只是找出了无向图中所有的长度大于等于3的环(长度为1和2的环没有意思),所以在深搜的过程中,当遇到的是起始点的时候,还需要进行判断是否是环),当确定是出现了环之后,根据是否在遇到环之前的那个点还有其他的路径,来决定是进一步的进行深度优先搜索还是进行回退,在进行深度优先搜索的过程中,将访问过的节点标记,若当前的节点无路可走(不能进行深度优先搜索了),在回退的过程中,将标记取消。算法的过程就下图做简单的介绍:
假设以1为起点进行深度优先搜索,经过访问2,3,4,5,6会得到一个环,因为节点6还有下一条路径可走,此时程序会进入7,8,9,10这些点进行深度优先搜索,但是都再没有回到节点1,于是程序会一层一层的在从7,8,9,10(不一定是这样的顺序)这些点退出来。退至节点6,5,4直到3节点(将6,5,4的标记全部取消)找到了下一条路径5,在走到6,此时又发现了另一条环1->2->3->5->6->1.以此类推。
主要代码如下:
void DFS(int startVertax)
{
setVisitedFlag(startVertax, 1);
int nextVertax;
push_stack(&loop_stack, startVertax);
nextVertax = firstAdjacentVertax(startVertax);
innerStep++;
for( ; ; )
{
if( nextVertax != -1 )
{
if( visitedFlag[nextVertax] == 1 && nextVertax == heap && innerStep == 2 ) //从1到2,又从2到1,这不算是一个环
{
nextVertax = nextAdjacentVertax(startVertax, nextVertax);
continue;
}
else if( visitedFlag[nextVertax] == 1 && nextVertax == heap && innerStep != 2 ) //找到了一个环
{
printf("loop length: %d\t", innerStep);
print_stack(loop_stack);
nextVertax = nextAdjacentVertax(startVertax, nextVertax);
continue;
}
else if( visitedFlag[nextVertax] == 0 ) //进行递归
{
DFS(nextVertax);
}
if( isRecall == 1 ) //进行回退
{
innerStep--;
temp = nextVertax;
nextVertax = nextAdjacentVertax(startVertax, nextVertax);
pop_stack(&loop_stack, &pop_value);
setVisitedFlag(temp, 0);
isRecall = 0;
continue;
}
nextVertax = nextAdjacentVertax(startVertax, nextVertax);
}
else if( nextVertax == -1 )
{
isRecall = 1;
break;
}
}
}
void DFSTraverse()
{
initialVisitedFlagArray();
initializeSequenceStack(&loop_stack);
int i;
for( heap = 1; heap <= vertax_size; heap++ )
{
for( i = 1; i <= vertax_size; i++ )
{
visitedFlag[i] = 0;
}
/*
printf("print the visitedFlag array: ");
for( i = 1; i <= vertax_size; i++ )
{
printf("%d ", visitedFlag[i]);
}
printf("\n");
*/
if( visitedFlag[heap] == 0 )
{
printf("\n-------------------the loop start and end with %d----------------\n", heap);
clear_stack(&loop_stack);
innerStep = 0;
isRecall = 0;
DFS(heap);
}
}
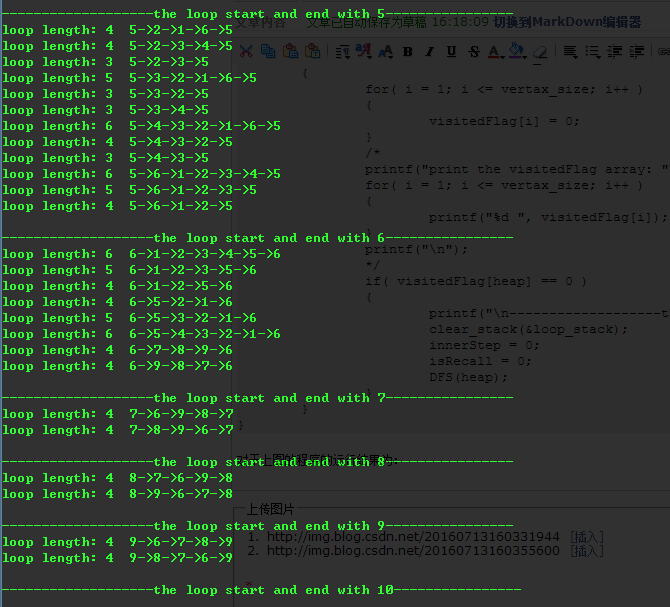
}对于上图的程序的运行结果为:(需要注意的是:对于无向图中的每一条环会出现两次,因为是有方向的:顺时针和逆时针)。
完整代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
int eage_size;
int vertax_size;
char filename_eage[200];
char filename_vertax[200];
int** eage_set;
char** vertax_set;
int** adjacentMatrix;
int* visitedFlag;
typedef struct SequenceStack
{
int* base;
int* top;
int stackSize;
}SequenceStack;
void readEageDataFromFile();
void readVertaxDataFromFile();
void createAdjacentMatrix();
void DFS(int);
void DFSTraverse();
void initialVisitedFlagArray();
void printVisitedVertax(int);
void setVisitedFlag(int,int);
int firstAdjacentVertax(int);
int nextAdjacentVertax(int,int);
void initializeSequenceStack(SequenceStack*);
void pop_stack(SequenceStack*, int*);
void push_stack(SequenceStack*, int);
void print_stack(SequenceStack);
int empty_stack(SequenceStack);
void clear_stack(SequenceStack*);
void test_stack();
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if( argc != 5 )
{
printf("\tThis algorithm require 3 parameters"
"\n\t\t1:the size of eage"
"\n\t\t2:the filename contain eage-data"
"\n\t\t3:the size of vertax"
"\n\t\t4:the filename contain vertax-data");
exit(0);
}
eage_size = atoi(argv[1]);
strcat(filename_eage, argv[2]);
vertax_size = atoi(argv[3]);
strcat(filename_vertax, argv[4]);
printf("eage_size : %d, vertax_size : %d, filename-eage : %s, filename-vertax : %s\n", eage_size, vertax_size, filename_eage, filename_vertax);
readEageDataFromFile();
readVertaxDataFromFile();
createAdjacentMatrix();
DFSTraverse();
//test_stack();
return 0;
}
void readEageDataFromFile()
{
FILE* f_read;
if( NULL == (f_read = fopen(filename_eage, "r")))
{
printf("open file(%s) error!\n", filename_eage);
exit(0);
}
//create dynamic array for storing original data form file @filename
eage_set = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * (eage_size + 1));
if( !eage_set )
{
printf("malloc error: eage_set**\n");
exit(0);
}
int i;
for( i = 1; i <= eage_size; i++ )
{
eage_set[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (2 + 1));
if( !eage_set[i] )
{
printf("eage_set[%d] malloc error", i);
exit(0);
}
}
//read original data from file
for( i = 1; i <= eage_size; i++ )
{
if( 2 != fscanf(f_read, "%d %d", &eage_set[i][1], &eage_set[i][2]))
{
printf("fscanf error: %d\n", i);
exit(0);
}
}
//test
printf("\n show the origin data from file\n");
for( i = 1; i <= eage_size; i++ )
{
printf("%d\t%d\n", eage_set[i][1], eage_set[i][2]);
}
printf("\n");
//test END
}
void readVertaxDataFromFile()
{
//create the dynamic array for saving vertax-set information
vertax_set = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*) * (vertax_size + 1));
if( !vertax_set )
{
printf("vertax_set malloc error");
exit(0);
}
int i;
for( i = 1; i <= vertax_size; i++ )
{
vertax_set[i] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (20 + 1));
if( !vertax_set[i] )
{
printf("vertax_set[%d] malloc error");
exit(0);
}
}
//open file
FILE* f_read;
if( NULL == (f_read = fopen(filename_vertax, "r")))
{
printf("open file(%s) error", filename_vertax);
exit(0);
}
//read vertax-set information
for( i = 1; i <= vertax_size; i++ )
{
if( 1 != fscanf(f_read, "%s ", vertax_set[i]) )
{
printf("fscanf vertax_set[%d] error", i);
exit(0);
}
}
//test
for( i = 1; i <= vertax_size; i++ )
{
printf("%s\n", vertax_set[i]);
}
printf("\n");
//test END
}
void createAdjacentMatrix()
{
//create the dynamic array for saving adjcaent matrix
adjacentMatrix = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * (vertax_size + 1));
if( !adjacentMatrix )
{
printf("adjacentMatrix** malloc error");
exit(0);
}
int i;
for( i = 1; i <= vertax_size; i++ )
{
adjacentMatrix[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (vertax_size + 1));
if( !adjacentMatrix[i] )
{
printf("adjacentMatrix[%d] malloc error");
exit(0);
}
}
//initial the value of adjacentMatrix
int j;
for( i = 1; i <= vertax_size; i++ )
{
for( j = 1; j <= vertax_size; j++ )
{
adjacentMatrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
//set the value for adjacentMatrix
for( i = 1; i <= eage_size; i++ )
{
adjacentMatrix[eage_set[i][1]][eage_set[i][2]] = 1;
adjacentMatrix[eage_set[i][2]][eage_set[i][1]] = 1;
}
//test
printf("\n show the information about adjacent matrix: \n");
for( i = 1; i <= vertax_size; i++ )
{
for( j = 1; j <= vertax_size; j++ )
{
printf("%d ", adjacentMatrix[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//test END
}
int loop_count;
int heap;
int innerStep = 0;
int temp;
int isRecall;
SequenceStack loop_stack;
int pop_value;
void DFS(int startVertax)
{
setVisitedFlag(startVertax, 1);
int nextVertax;
push_stack(&loop_stack, startVertax);
nextVertax = firstAdjacentVertax(startVertax);
innerStep++;
for( ; ; )
{
if( nextVertax != -1 )
{
if( visitedFlag[nextVertax] == 1 && nextVertax == heap && innerStep == 2 )
{
nextVertax = nextAdjacentVertax(startVertax, nextVertax);
continue;
}
else if( visitedFlag[nextVertax] == 1 && nextVertax == heap && innerStep != 2 )
{
print_stack(loop_stack);
nextVertax = nextAdjacentVertax(startVertax, nextVertax);
continue;
}
else if( visitedFlag[nextVertax] == 0 )
{
DFS(nextVertax);
}
if( isRecall == 1 )
{
innerStep--;
temp = nextVertax;
nextVertax = nextAdjacentVertax(startVertax, nextVertax);
pop_stack(&loop_stack, &pop_value);
setVisitedFlag(temp, 0);
isRecall = 0;
continue;
}
nextVertax = nextAdjacentVertax(startVertax, nextVertax);
}
else if( nextVertax == -1 )
{
isRecall = 1;
break;
}
}
}
void DFSTraverse()
{
initialVisitedFlagArray();
initializeSequenceStack(&loop_stack);
int i;
for( heap = 1; heap <= vertax_size; heap++ )
{
for( i = 1; i <= vertax_size; i++ )
{
visitedFlag[i] = 0;
}
/*
printf("print the visitedFlag array: ");
for( i = 1; i <= vertax_size; i++ )
{
printf("%d ", visitedFlag[i]);
}
printf("\n");
*/
if( visitedFlag[heap] == 0 )
{
printf("\n-------------------the loop start and end with %d----------------\n", heap);
clear_stack(&loop_stack);
innerStep = 0;
//printf("isRecall : %d, findLoop : %d, hasOthers : %d\n", isRecall, findLoop, hasOthers);
isRecall = 0;
DFS(heap);
}
}
}
void initialVisitedFlagArray()
{
visitedFlag = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (vertax_size + 1));
if( !visitedFlag )
{
printf("visitedFlag* malloc error");
exit(0);
}
int i;
for( i = 1; i <= vertax_size; i++ )
visitedFlag[i] = 0;
}
void printVisitedVertax(int vertaxID)
{
printf("visited: %d \n", vertaxID);
}
void setVisitedFlag(int vertaxID, int value)
{
visitedFlag[vertaxID] = value;
}
int firstAdjacentVertax(int vertaxID)
{
int i;
for( i = 1; i <= vertax_size; i++ )
{
if( adjacentMatrix[vertaxID][i] == 1 )
return i;
}
return -1;
}
int nextAdjacentVertax(int vertaxID, int nextVertaxID)
{
int i;
for( i = nextVertaxID + 1; i <= vertax_size; i++ )
{
if( adjacentMatrix[vertaxID][i] == 1 )
return i;
}
return -1;
}
void initializeSequenceStack(SequenceStack* stack)
{
stack->base = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (vertax_size + 1));
if( !stack->base )
{
printf("Sequence stack malloc error!\n");
exit(0);
}
stack->top = stack->base;
stack->stackSize = vertax_size;
}
void pop_stack(SequenceStack* stack, int* value)
{
if( empty_stack(*stack) == 1 )
{
printf("stack is empty , can not to pop!\n");
exit(0);
}
*value = *(--(stack->top));
}
void push_stack(SequenceStack* stack, int value)
{
*(stack->top) = value;
(stack->top)++;
}
int empty_stack(SequenceStack stack)
{
return stack.top == stack.base ? 1 : 0;
}
void print_stack(SequenceStack stack)
{
int temp = *(stack.base);
while( stack.top != stack.base )
{
printf("%d->", *((stack.base)++));
}
printf("%d\n", temp);
}
void clear_stack(SequenceStack* stack)
{
stack->top = stack->base;
}